REGIONS OF THE WESTERN HEMISPHERE
Unit Overview
In this unit, we will be learning that regions can be determined using various criteria (e.g., landform, climate, population, cultural, and economic). We will identify and describe the regions within the Western Hemisphere using such criteria.
Regions
The United States is often divided up into geographical regions. These regions help describe a large area. They also help group together states that are similar in features such as geography, culture, history, and climate. A region is an area of land that has common features. A region can be defined by artificial features like language, government, or religion, or it can be defined by natural features like forests, wildlife, or climate. A common way of referring to regions in the United States is to group them into 5 regions according to their geographic position on the continent: the Northeast, Southwest, West, Southeast, and Midwest. Geographers who study regions may also find other physical or cultural similarities or differences between these areas.
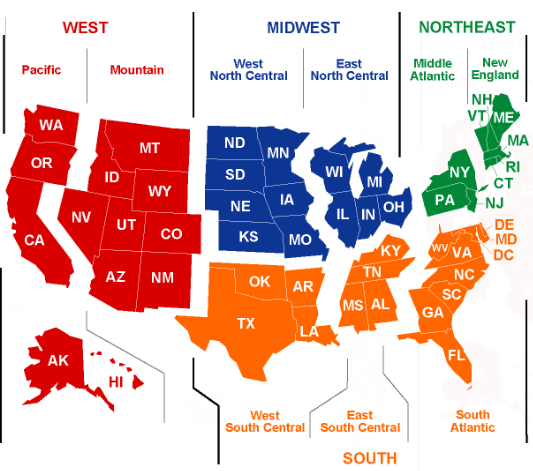
The United States is a large and diverse country described by regions (places with similar traits). In this song, we will learn the climate, landforms and natural resources that define the five geographic regions of the United States. We will experience the snowy winters of the Northeast and the hot summers of the Southeast. We will take a tour of the Rocky Mountains and Grand Canyon in the Southwest, see the technology and movie industries out West and visit the Farm, Corn and Dairy Belts of the Midwest.
Let's Practice! Print and complete the following activities to learn more about the Regions of North America!
U.S. Regions Map (color each region a different color)
Landforms
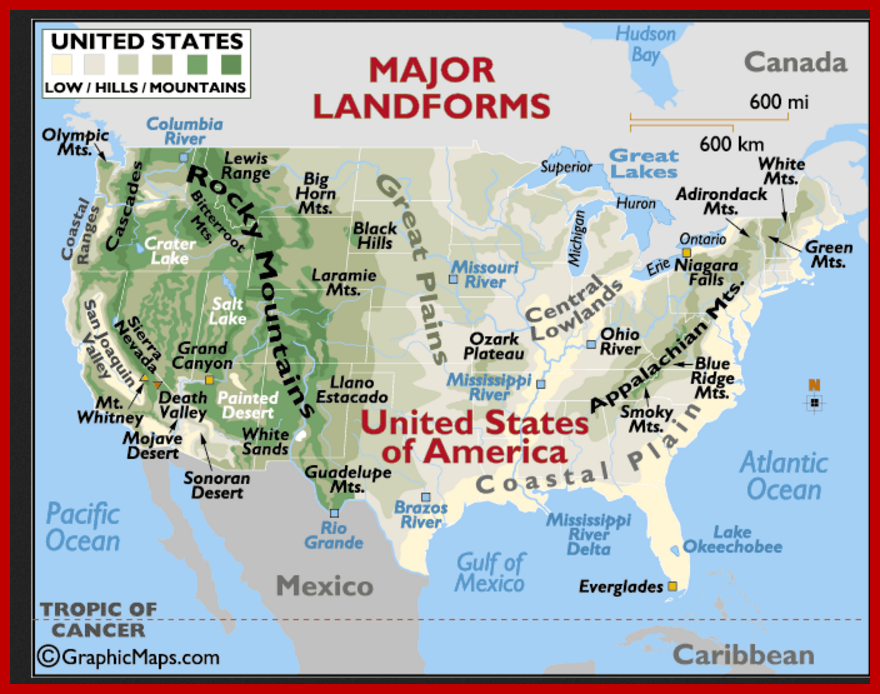
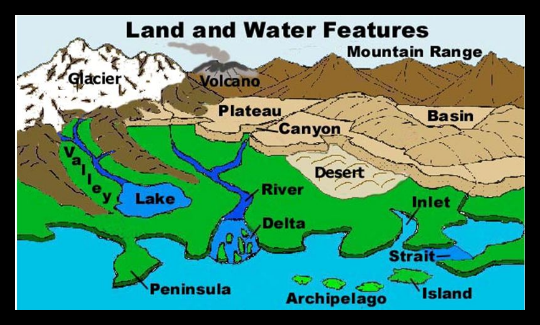
Landform refers to the shape, form, or nature of physical features of the earth's surface (e.g., plains, hills, plateaus, mountains). A landform region is an area of land that has similar landforms all over it. The United States is made up of the following landforms and water features:
Coastal Plains

The Coastal Plains is one of the largest landform regions in the United States. It is made up of low, flat land and extends from the Atlantic Ocean to the Gulf of Mexico. In the Coastal Plains, you will find wetlands.
Appalachian Mountains
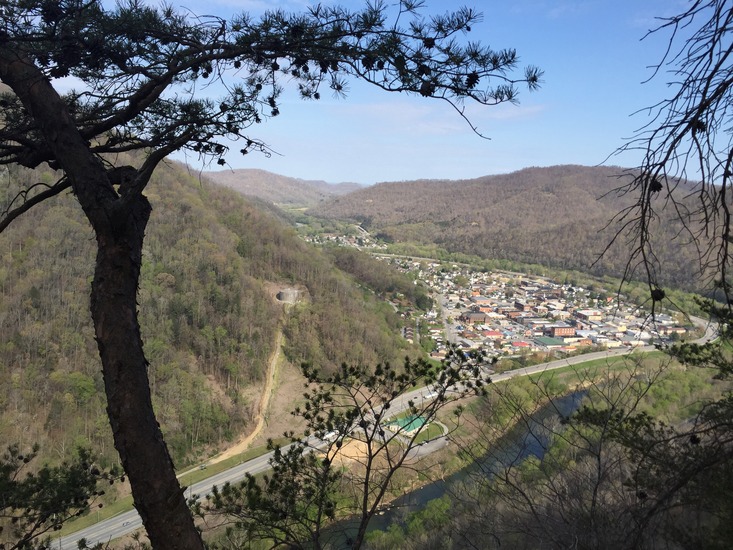

West of the Coastal Plain lie the Appalachian mountains. The oldest mountains in North America, they are smooth and round, having been worn down over centuries from erosion. The mountains and the areas around them are covered in trees. The highest peaks in the range are around 6,700 feet high!
Interior (Great) Plains
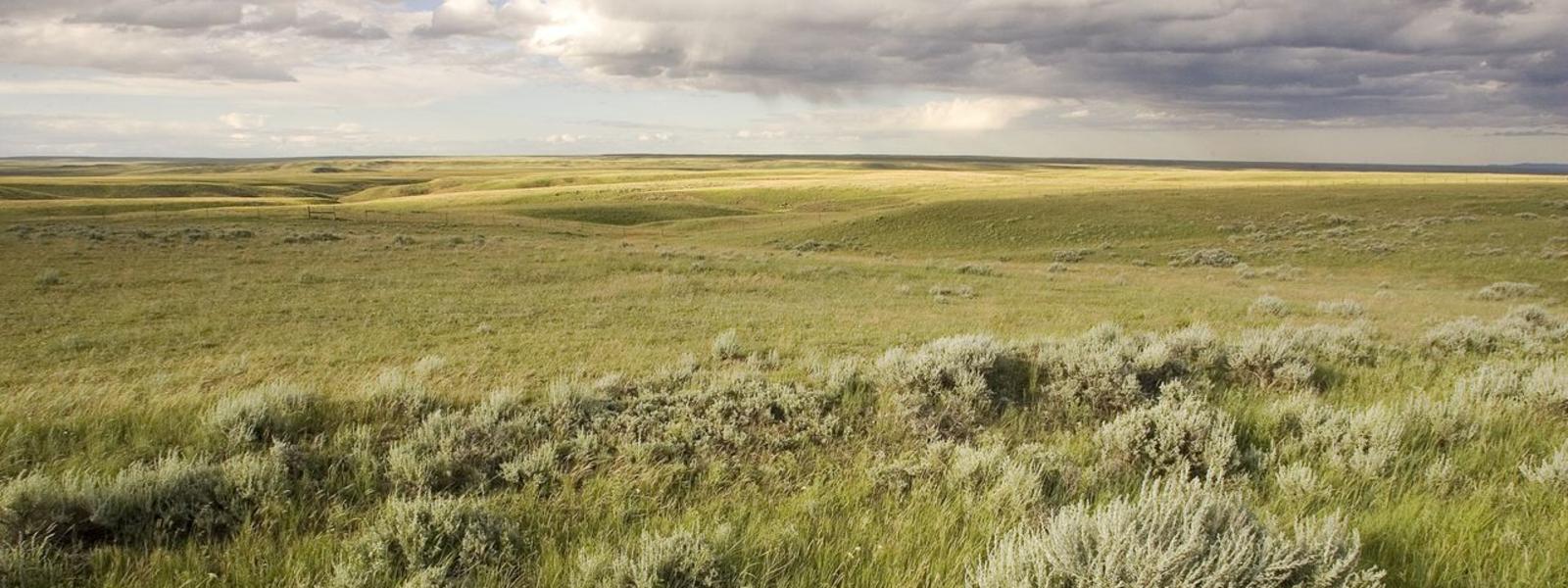

The Interior Plains are the biggest region in the United States, stretching across the middle of the country and covering many states. The Interior Plains are mostly flat, with forests to the east and grasslands to the west.
Rocky Mountains

The Rocky Mountains fall to the West of the Great Plains and make up an entire region. This mountain range extends all the way up and down the country, from Mexico to Canada. While the Appalachians are smooth after centuries of erosion, the Rockies are a younger mountain range and are much sharper and more jagged. Some points in the Rockies are high enough to be covered by snow year round.
The West
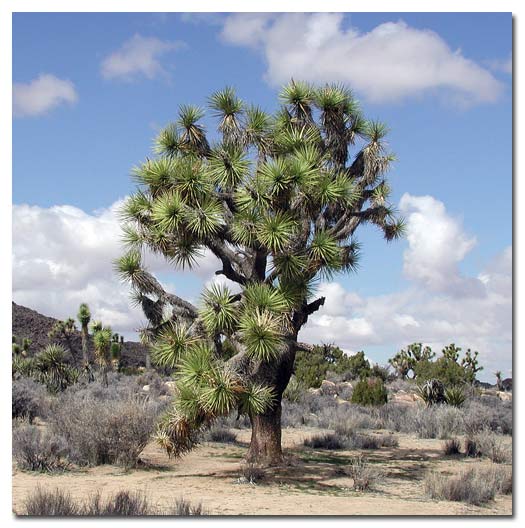

The Joshua Tree, Mojave Desert
West of the Rocky Mountains, the land is uneven and unpredictable. Deserts, beaches, forests and mountain ranges live side by side. All deserts are dry but not all are hot. "Hot deserts" like the Sonoran and Mojave Deserts, have a high daytime temperature during the long summer and a cold nighttime temperature. Death Valley in California is the lowest point on the continent, more than 280 feet below sea level. Along the coast, the beaches range from sandy and sunny to cold and rocky. The Great Basin Desert, a low, flat area surrounded by higher ground, makes up much of Nevada and some of the states around it. It is a "cold desert" because it is generally cooler due to its more northern latitude, as well as higher elevations. Its precipitation is generally 7-12 inches anually.
Let's practice! Print and complete the following activities to learn more about landforms of North America!
Landforms and Landscapes Geography Study
Landforms Crossword (Crossword Key)
Map Reading Activity: Topography
Culture and Population
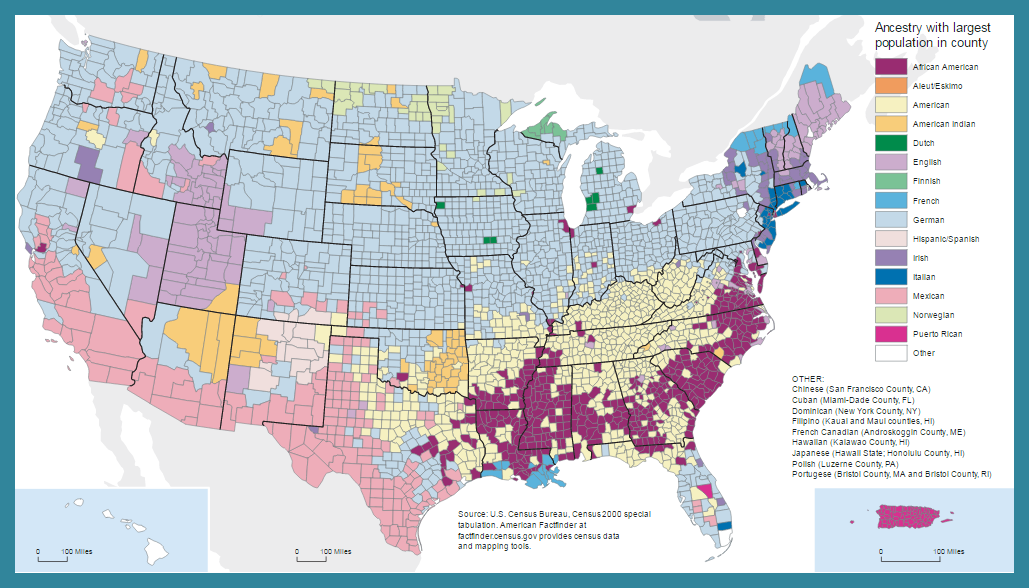
Does the city or town in which you live have a neighborhood in which a language other than English is spoken? Are there restaurants that specialize in foods from other countries? How did these diverse cultural features come to your city or town? The movement of people, goods, or ideas from one place to another is part of a process known as diffusion. Cultural regions are based on human features such as history and language. Culture is the learned behavior of people, including belief systems and languages. The mixing of world cultures through different ethnicities, religions, and nationalities has increased with advanced communication, transportation, and technology.
The ancestry or nationality of a group of people afffect the culture of a region. The map below shows the ancestry with the largest population per county in the United States.
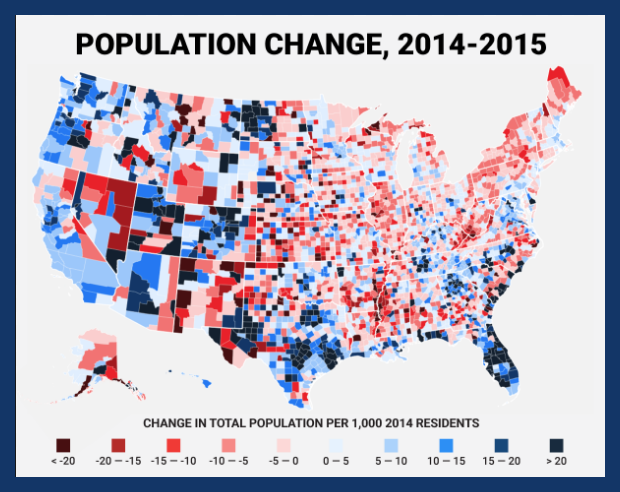
Population includes data about the people who live in a selected area (for example, population density, culture, birth rates). The map below shows the population changes from 2014-2015 in the United States per 1,000 people.
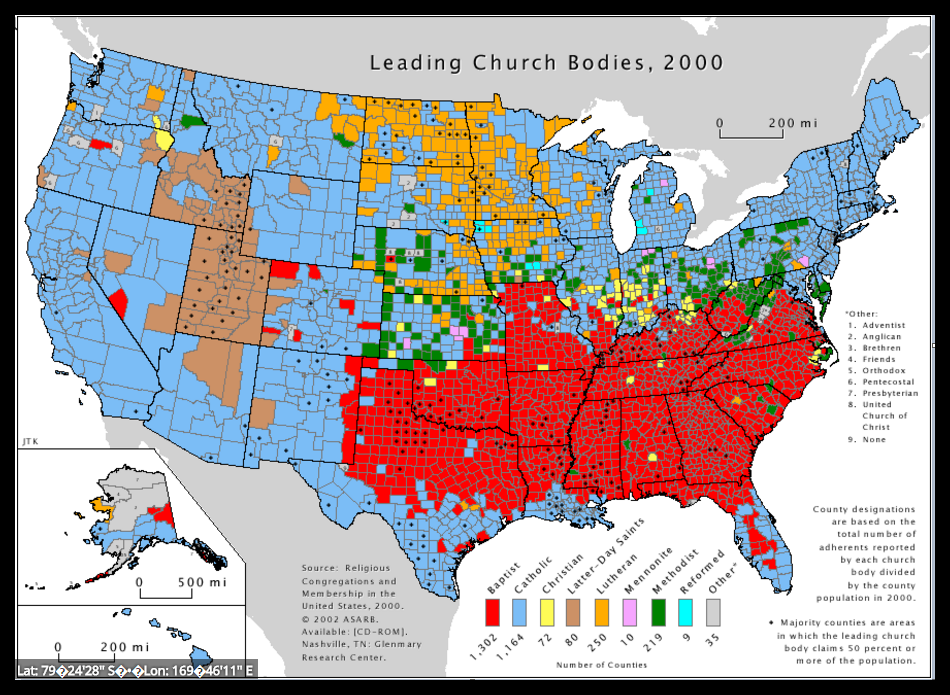
Religion is part of a region's culture. Christianity started in Israel and has spread all over the world. As you can see from the map below, religions vary in different regions of the United States.
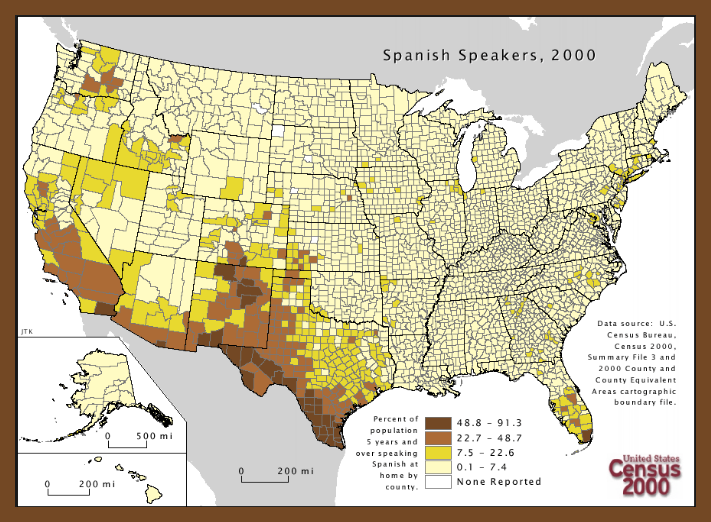
The English language is a good example of diffusion, as it contains many words from other languages. In many Southern cities in the United States, especially border towns, people speak in both English and Spanish. Signs are also written in both languages for them to easily understand. The map below shows the percentage of the United States population that have five years or more speaking Spanish at home, according to the 2000 census. Whereas, the French Quarter in New Orleans show diffusion of French culture, including history, language, and food.
Climate
Climate includes long-term trends in weather elements and atmospheric conditions (e.g., average temperature, average rainfall).
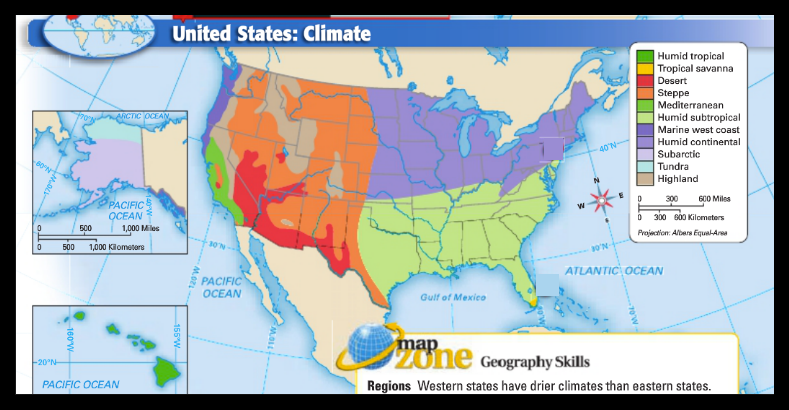
Climate in the Southwest
Ranging from Arizona to portions of Louisiana, the Southwest is the hottest region of the United States. More eastern portions of the range produce a high volume of rainfall, and tourists must be prepared for severe thunderstorms and even tornadoes.
Climate in the Southeast
From Virginia to points south, the Southeast region of the United States is hot and dry during the summer but mild during the winter. While snow may occur during the winter months, precipitation overall is moderate year round.
Climate in the Northeast
The Northeast climate region in the New England states provides four distinct seasons. The summer months are sunny and warm, while the winter months are cold and punctuated by heavy snow and ice.
Climate in the Midwest
The climate in Minnesota, North Dakota and other states in the Midwest is similar to weather in the Northeast. While the region is drier overall, there are four distinct seasons ranging from mild summer months to bitterly cold winter months.
Climate in the West
The climate in the Mid/South Pacific region is variable. While states like California boast near-perfect weather all year round, the winter months in states like Colorado and Montana can be very cold and laden with snow. The Northwest Pacific climate region of the United States is the wettest part of the country. Temperatures in Oregon and Washington remain mild throughout the year, and fog and light drizzle are commonplace on most days.
Economics
The states that share resources also share an ecomomy. The economy is the way a region uses its resources to provide what people need. Economics refers to the set of principles by which a society decides and organizes the ownership, allocation and use of resources. Economic characteristics include natural resources, agricultural products and levels of income.
Conclusion
Few countries in the world can match the United States for its sheer diversity of landforms, bodies of water, and species of plants and animals, as well as its multicultural human population. Discover how the landforms, waterways, farms, natural resources, and people of each region differ. Observe the trends that are causing the regions to become more alike.