AREA
Area is the coverage within a closed figure. We find the number of square units it takes to cover the area of the figure. Some shapes have formulas to simplify the computations. Area is measured by square units.
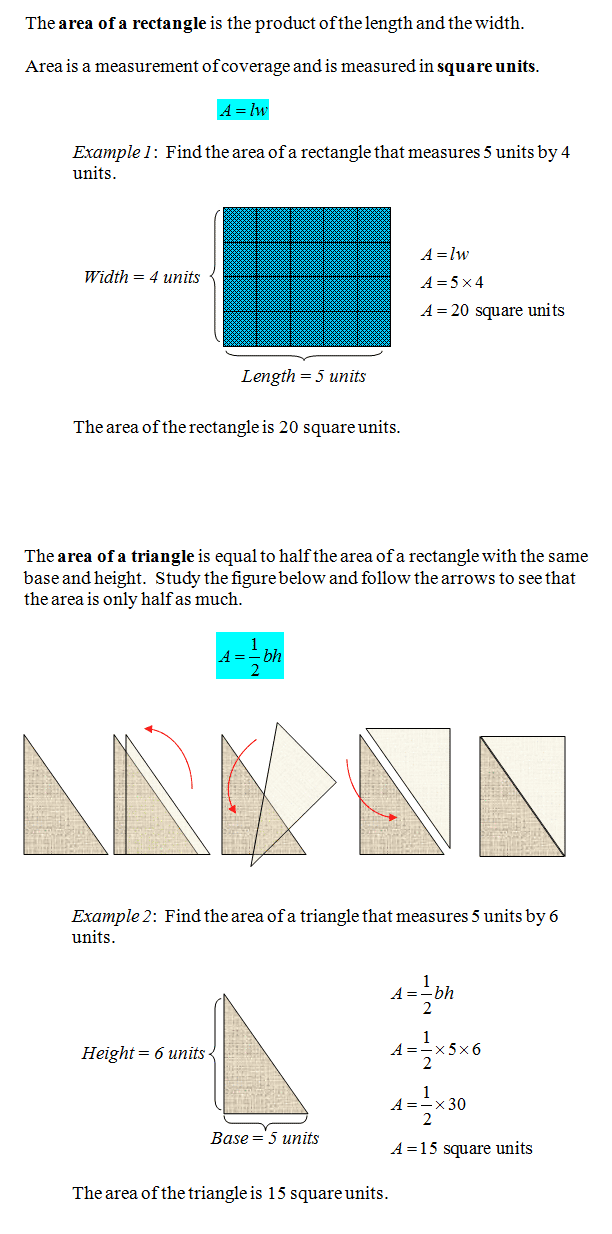
First, we’ll look at finding the area of rectangles and triangles. To find the area of a rectangle multiply base times height. To determine the area of a triangle, multiply base times height, and then divide by two.
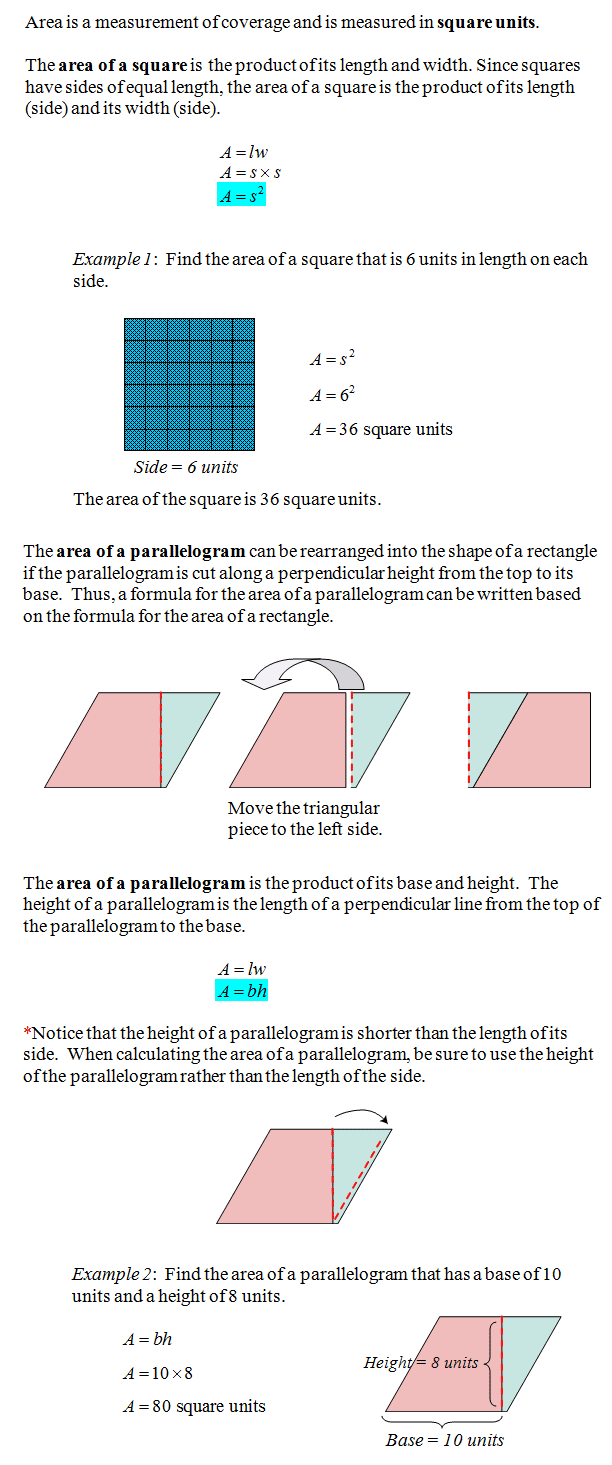
Next, we’ll look at finding the area of squares and parallelograms. To find the area of a square, square one side. To determine the area of a parallelogram, multiply base times height where height is the perpendicular distance between the parallel sides.
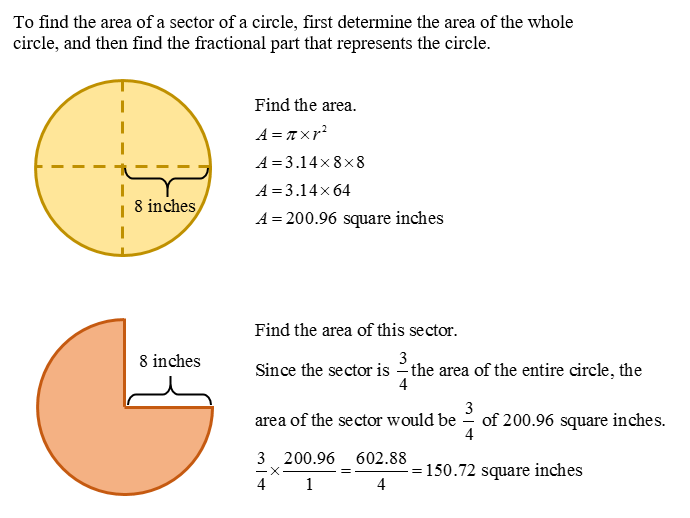
We will then look at finding the area of a circle. When we work with circles we must consider the value of “pi”. For most problems we will round the value of “pi” to 3.14. To determine the area of a circle multiply the radius-squared times pi.
A circle sector is a portion of the circle. We will determine the area of a circle sector by finding the area of the entire circle first, and then multiplying by the fraction that represents the sector.
Composite shapes are a combination of basic shapes. We will find the areas of each of the shapes that make up the figure, and then add.
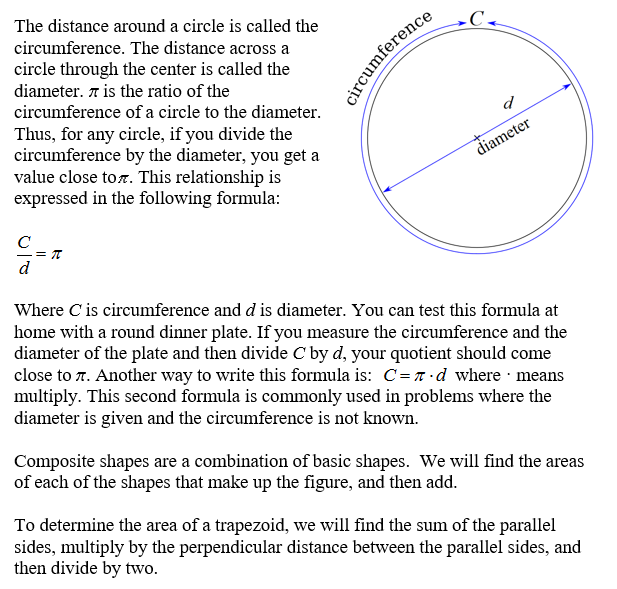
To determine the area of a trapezoid, we will find the sum of the parallel sides, multiply by the perpendicular distance between the parallel sides, and then divide by two. |
 |
 |
Area of a Circle
 |
 |
Area of Composite Shapes
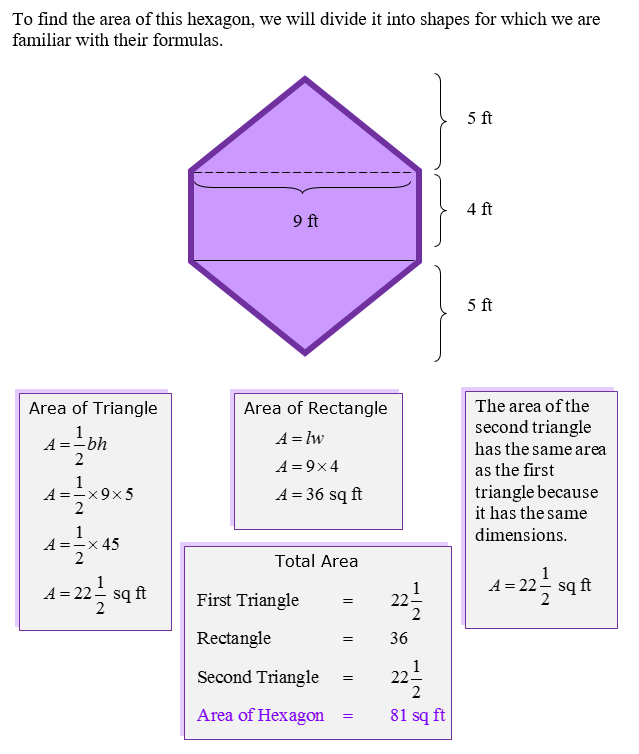 |
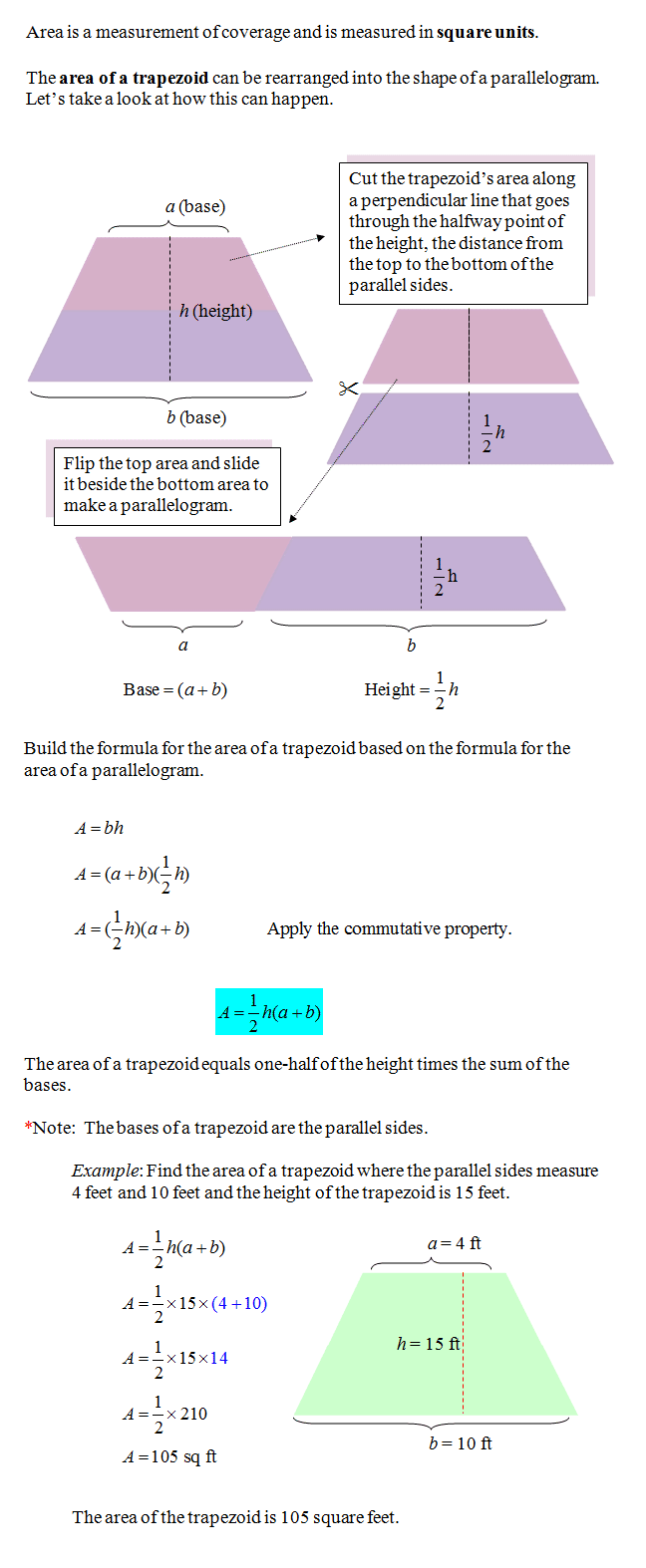 |
 |
| Area of a Circle |
| Area of a Triangle |
| Compound Shapes |