WELCOME!
We will explore lots of exciting topics in math and examine applications of the concepts learned in real world settings. Let’s begin with the basics, and then see how we apply them to actual math problems that are encountered in every day math.
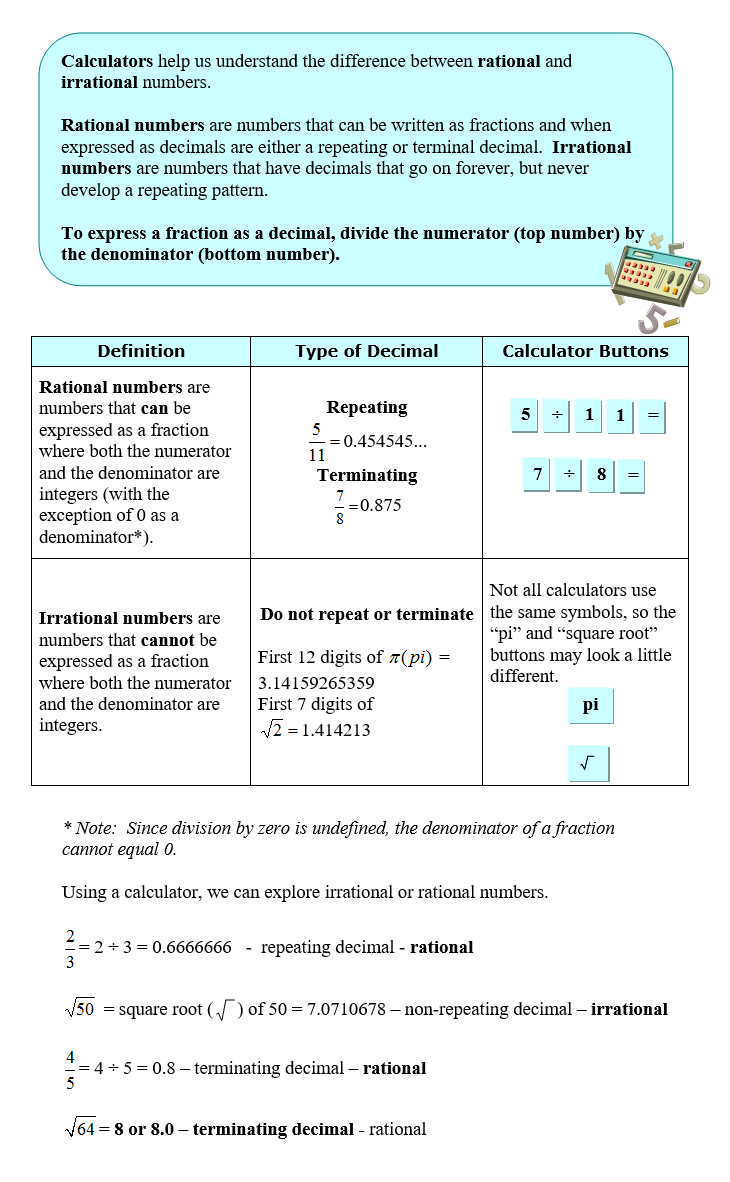
RATIONAL AND IRRATIONAL NUMBERS
We will begin by looking at rational and irrational numbers. Rational numbers are numbers that can be expressed as a fraction where both the numerator and the denominator are integers with the exception of 0 as a denominator (division by 0 is undefined). Some rational numbers have decimals that terminate while others have decimals that form a repeating pattern and go on forever. Irrational numbers are numbers that cannot be expressed as a fraction where both the numerator and the denominator are integers. The decimals for irrationals are decimals that go on forever and never form a repeating pattern.
ADDING FRACTIONS AND MIXED FRACTIONS
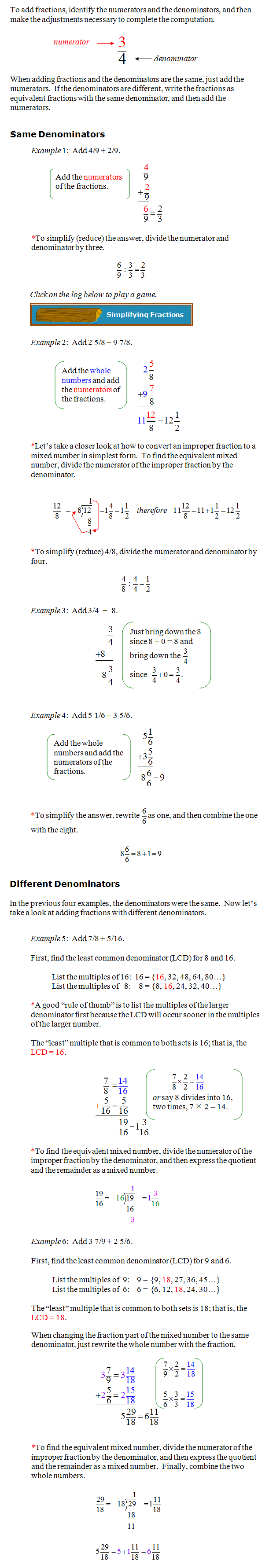
Fractions are rational numbers. We will review addition of fractions and mixed fractions. Remember, to add fractions with like denominators, add just the numerators. We’ll practice adding fractions and mixed fractions with like denominators. Next we’ll practice adding a fraction with a whole number and also adding mixed fractions whose sum totals a whole number.
To add fractions with unlike denominators, we must find the least common denominator (LCD), and then add the numerators. When adding mixed fractions with unlike denominators, we must find the LCD, add the numerators, add the whole numbers, and then look for ways to simplify the answer as needed.
Write fraction answers using the form in these examples.
Example 1: two-thirds is written as 2/3.
Example 2: five and three fourths is written as 5 3/4.
Rational and Irrational Numbers
 |
Addition of Fractions
 |
 |
| Adding Simple Fractions |
| Adding Mixed Numbers |