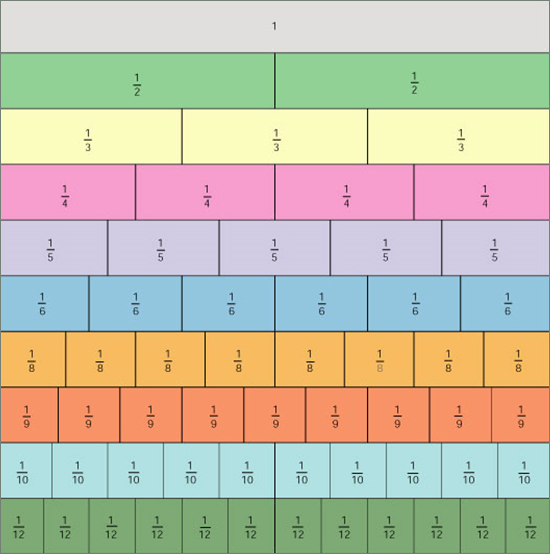
Look over these fraction strips. Each strip represents 1 whole.
1 = 2 halves, 3 thirds, 4 fourths, 5 fifths, 6 sixths, and so on.
Thus, 1 = 2/2 = 3/3 = 4/4 = 5/5 = 6/6 and so on…
EQUIVALENT FRACTIONS AND GCF
Fractions are used to represent parts of a whole. First, we'll examine how the whole number "1" may be expressed as a fraction.
Equivalent fractions represent the same fractional part. We'll use fraction bars to observe some equivalent fractions and how they look differently, but mean the same fractional part.
Reducing a fraction is finding an equivalent fraction in simplest form. A simplified fraction makes working with it easier.
Factors of a number are numbers multiplied together to get the number. One set of factors for six is 2 × 3. Another set of factors for six is 1 × 6. We will use factors to find greatest common factor (GCF).
Write fraction answers using the form in these examples.
Example 1: two-thirds is written as 2/3.
Example 2: five and three fourths is written as 5 3/4.
| Fraction Bars and Equivalence to One Look over these fraction strips. Each strip represents 1 whole. 1 = 2 halves, 3 thirds, 4 fourths, 5 fifths, 6 sixths, and so on. Thus, 1 = 2/2 = 3/3 = 4/4 = 5/5 = 6/6 and so on…
|
Equivalent Fractions and Reducing Fractions
Understanding Equivalent Fractions
Fractions that represent the same amount are called equivalent fractions.
 This method is permitted because 2/2 = 1 and when you multiply by 1 as a fraction you get the same number back with a different appearance.
The fraction strips above prove that 3/4 = 6/8 because they represent the same amount. Reducing Fractions
Reducing a fraction is finding an equivalent fraction that is in simplest form. Simplest form means that the only number that will divide into both the numerator and denominator is 1.  |
| The Britannica login and password may be required for some of the activities. Login: vla Password: student |
| GCF (Listing Factors) The Greatest Common Factor (GCF) of two numbers is the largest factor that is the same when all the factors in a number have been listed. Follow the steps in this example to find the GCF. Find the GCF of 18 and 24. To find the GCF, look for the largest factor that is the same in both lists.
{1, 2, 3, 6, 9, 18} {1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, 24}
The GCF is 6. |
 |
| Unit 6 Fractions Worksheet |
| Unit 6 Greatest Common Factor Worksheet |