| |
| |
|
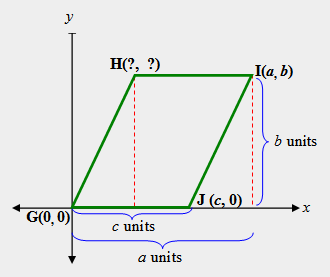
| 2) What is the ordered pair for point H in parallelogram GHIJ? |
 |
|
|
| |
|
| |
|
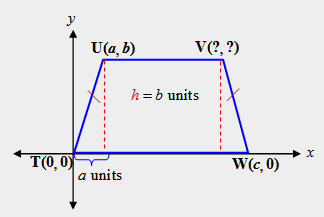
| 4) What is the ordered pair for point V in isosceles trapezoid TUXY? |
 |
|
|
| |
|
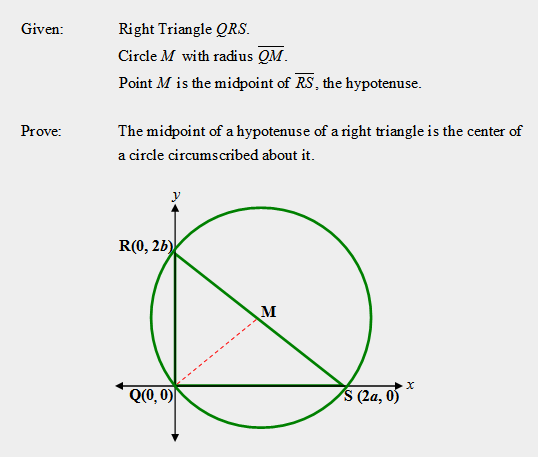
| 5) Read and study the information and the figure shown below to answer the following questions: (a) What is the ordered pair for midpoint M? (b) In terms of “a” and “b”, what is the length of segment MQ? (c) In terms of “a” and “b”, what is the length of segment MR? (d) In terms of “a” and “b”, what is the length of segment MS? |
 |
4000 character(s) left
Your answer is too long. |
|
| |
|
| 6) Based on the information collected in the previous problem, justify the following statement: “The midpoint of the hypotenuse of a right triangle is the center of a circle circumscribed about it”. |
|
4000 character(s) left
Your answer is too long. |
|
| |
|
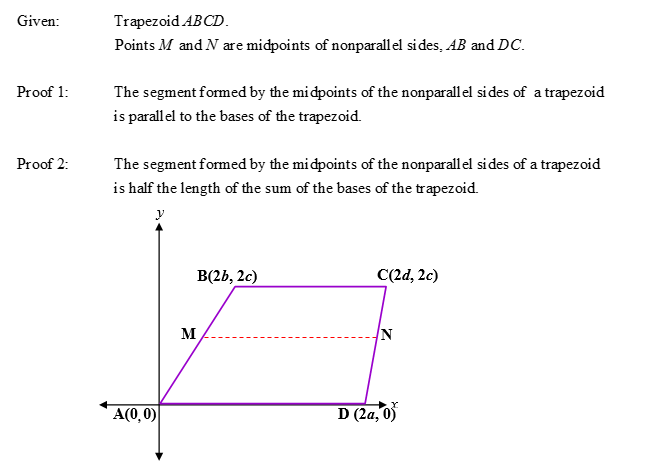
Read and study the information and the figure shown below to answer the next four questions.
|
 |
|
| |
| 7) Answer the following questions for Proof 1: (a) What are the coordinates of point M? (b) What are the coordinates of point N? (c) What is the slope of segment BC? (d) What is the slope of segment MN? (e) What is the slope of segment AD? |
|
4000 character(s) left
Your answer is too long. |
|
| |
|
| 8) Use the information collected in the previous problem to justify the following statement: “The segment formed by the midpoints of the nonparallel sides is parallel to the bases of the trapezoid”. |
|
4000 character(s) left
Your answer is too long. |
|
| |
|
| 9) Answer the following questions for Proof 2: (a) What is the length of segment MN? (b) What is the length of segment BC? (c) What is the length of segment AD? (d) What is the sum of the lengths of segments AD and BC? |
|
4000 character(s) left
Your answer is too long. |
|
| |
|
| 10) Use the information collected in the previous problem to justify the following statement: “The length of the segment formed by the midpoints of the nonparallel sides of a trapezoid is half the length of the sum of the bases of the trapezoid”. |
|
4000 character(s) left
Your answer is too long. |
|
| |
|
| |
| |
|
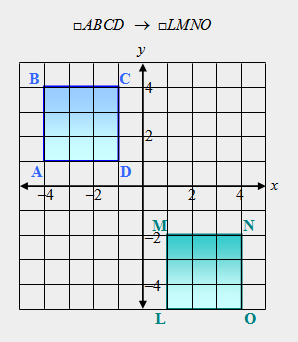
| 12) True or False. Points A and L are corresponding vertices, points B and M are corresponding vertices, points C and N are corresponding vertices, and points D and O are corresponding vertices. |
 |
|
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| Isometry and Similarity Transformations |
|
|
| |
| |
|
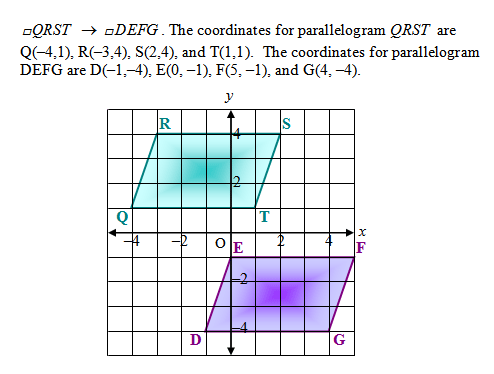
| Refer to the mapping shown below to answer the next two questions. |
 |
|
| |
| 17) What are the lengths of (a) QR and DE, (b) TS and GF, (c) RS and EF, and (d) QT and DG? |
|
4000 character(s) left
Your answer is too long. |
|
| |
|
| 18) True or False: The mapping of parallelogram QRST to parallelogram DEFG is an isometry. |
|
|
|
| |
|
| |
|
| For the figure shown below, find the length of each of the following segments using the distance formula: CD, DE, CE, JK, KL, JL, and then answer the next two questions. Write each of the lengths as a simplified radical. |
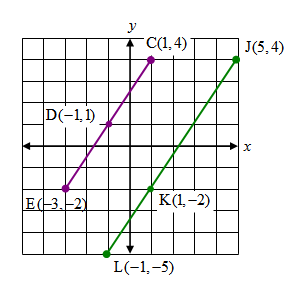 |
|
| |
| 20) Which ratio(s) simplifies to 1/2? |
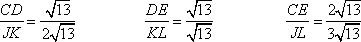 |
|
|
| |
|
| 21) True or False: The mapping shown below is a similarity transformation. |
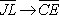 |
|
|
| |
|
| |
|
| Transformations: Translations |
|
|
| |
| 23) True or False: The transformation shown below is a translation. |
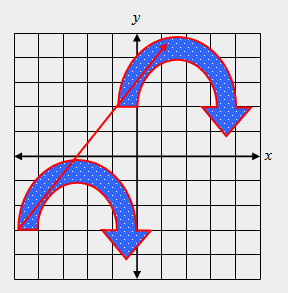 |
|
|
| |
|
| |
|
| 25) Which notation describes the translation of the sailboat B(70, 20) to the lighthouse B'(10, 80) as a change in (x, y)? |
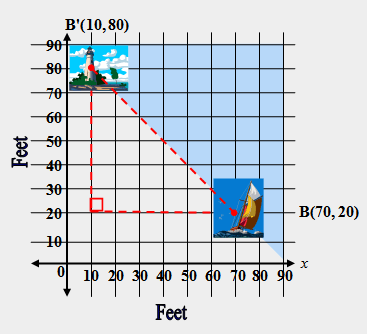 |
|
|
| |
|
| 26) The vertices of a quadrilateral are J(–4, 0), K(–2, 5), L(1, 1), M(–2, –2). Print out the figure of the pre-image shown below and graph the translation naming the image, J’K’L’M’. What are the coordinates of each of the new vertices of the image? |
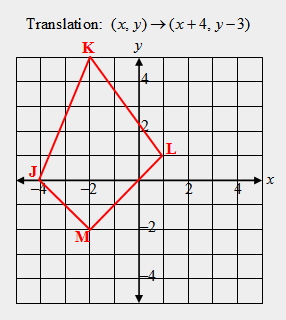 |
4000 character(s) left
Your answer is too long. |
|
| |
|
| Transformations: Reflections |
|
|
| |
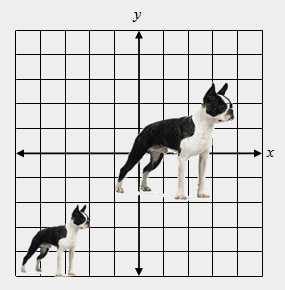
| 27) True or False: The transformation shown below is a reflection. |
 |
|
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| 30) The coordinates of the endpoints of line segment CD are C(–4, 1) and D(3, 4). Reflect the line segment over the x-axis. (a) State the coordinates of the image of the endpoints of segment C'D'. (b) Write a rule that would pertain to all points reflected over the x-axis. |
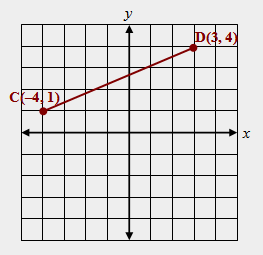 |
4000 character(s) left
Your answer is too long. |
|
| |
|
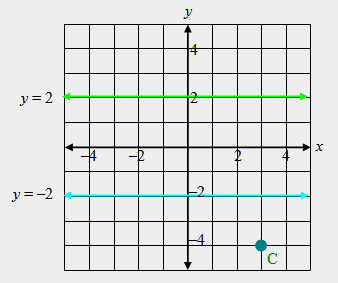
| 31) Reflect point C over the line, y = –2, and name it point C’. Reflect point C’ over the line, y = 2, and name it point C’’. What is the location of C’’? |
 |
|
|
| |
|
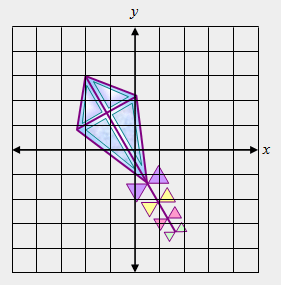
| 32) Which parts of the kite are symmetrical? Select the BEST answer. |
 |
|
|
| |
|
| |
|
| Transformations: Rotations |
|
|
| |
| 34) True or False: The transformation shown below is a rotation. |
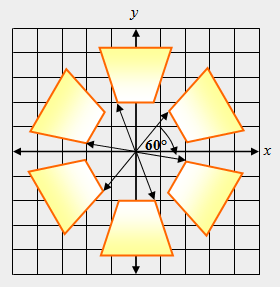 |
|
|
| |
|
| 35) In the figure below, pre-image trapezoid Z is rotated about point X to image trapezoid Z’. Rotations can be derived from two reflections. Explain how this same transformation can be made by completing two reflections. A faint dotted trapezoid is provided to help with the explanation. |
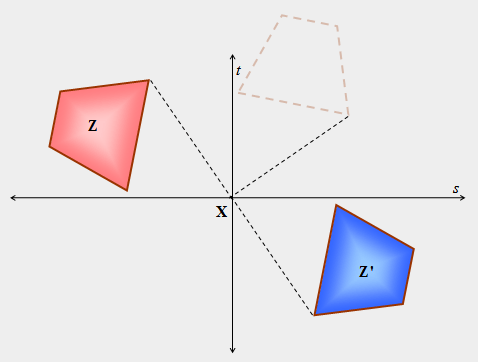 |
4000 character(s) left
Your answer is too long. |
|
|
Attachments |
|
| 36) In the figure shown below, a 70-degree angle is formed by lines “s” and “t”, the lines of reflection. What is the angle of rotation that transformed pre-image R to image R’ around point Q. |
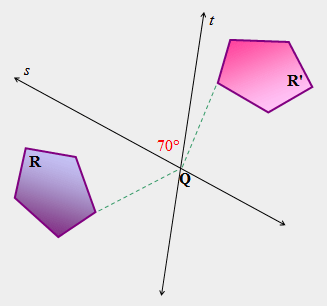 |
|
|
| |
|
| 37) Draw quadrilateral ABCD with vertices of A(–4, 0), B(–4, 4), C(–2, 3), and D(–2, –1). Rotate the quadrilateral 90 degrees clockwise around the origin and draw quadrilateral A’B’C’D’. What are the coordinates of each of the vertices in image A’B’C’D’? State the name of each vertex and the corresponding coordinates. |
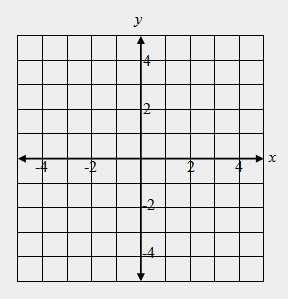 |
4000 character(s) left
Your answer is too long. |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| 39) Describe how to create Figure 2 from Figure 1. |
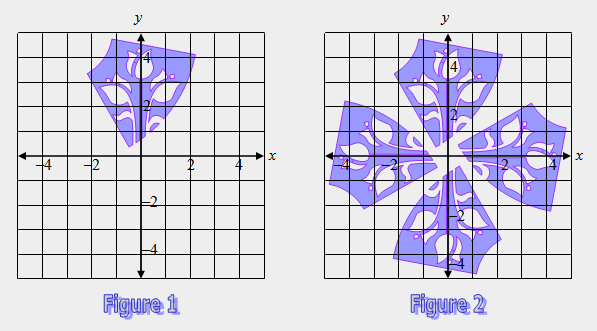 |
4000 character(s) left
Your answer is too long. |
|
|
Attachments |
|
| Transformations: Dilations |
|
|
| |
| |
|
| 41) In the figure below, segment AB is a dilation of segment CD with respect to point Q as the center of dilation. The length of segment QC is 5 and the length of segment CA is 10. What scale factor was used to create the dilation? |
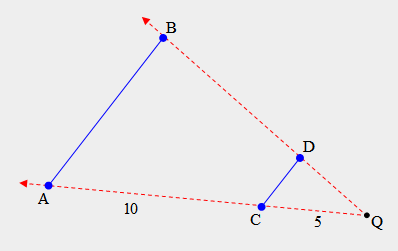 |
|
|
| |
|
| 42) In the figure below, hexagon A'B'C'D'E'F’ is the image of ABCDEF after a dilation. What is the scale factor? |
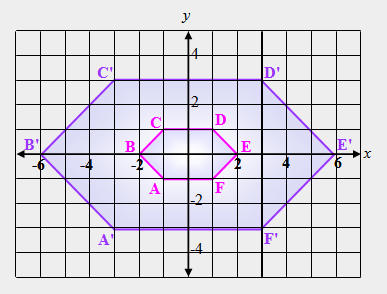 |
|
|
| |
|
| |
|
| 44) Compare the lengths of the image (larger picture) and its dilation (smaller picture). What is the scale factor? |
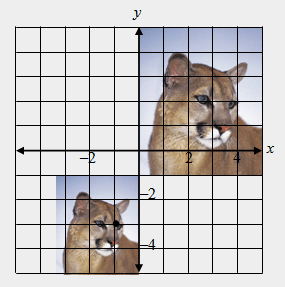 |
|
|
| |
|
| 45) The vertices of four-point star ABCD are A(–2, 0), B(–4, 2.5), C(–2, 5), and D(0, 2.5). Find and write the coordinates of the vertices of image, A’B’C’D', after a dilation of a scale factor, k = 2, with respect to the origin as the center of dilation. |
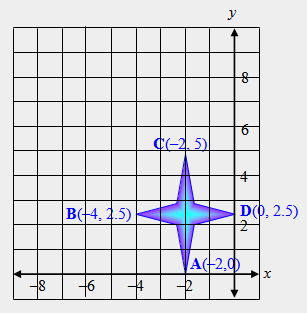 |
4000 character(s) left
Your answer is too long. |
|
| |
|
| 46) Dilate parallelogram PQRS by a scale factor of 0.6 with point P as the center of dilation. The length of segment RS is 4.8 cm and the length of segment QR is 10.8 cm. P and P' are the same point. (a) What is the length of PQ’? (b) What is the length of S’R’? (c) What is the length of Q’R’? (d) What is the length of PS’? |
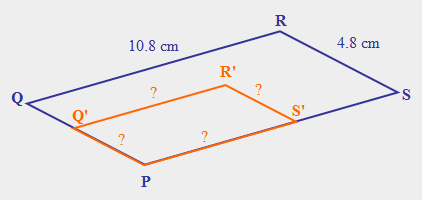 |
4000 character(s) left
Your answer is too long. |
|
| |
|
| 47) If you were directed by your school to complete Offline Activities for this course, please enter the information on the Log Entry form. |
|
| No offline activities found |
| 0 Hour(s) & 0 Minute(s) |
|
|
Attachments |
|