| |
| For the first two problems, fill in the blanks. |
|
|
| |
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
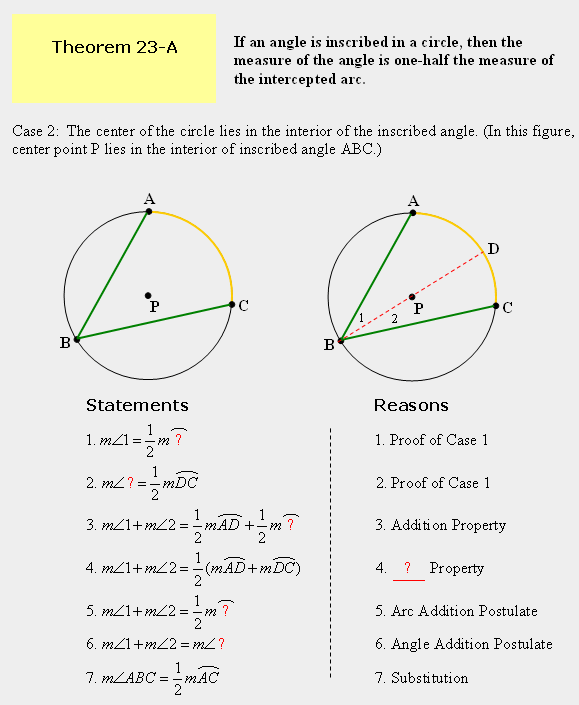
| 5) In the unit link to “Inscribed Angles”, there is a proof for Case 1 of Theorem 23-A. Study the proof and apply its concepts to prove case 2. Parts of the proof are shown below. Fill in the missing parts of the proof for steps 1 through 6. |
 |
4000 character(s) left
Your answer is too long. |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| Refer to the figure below to answer the next four questions about circle W based on the given information. |
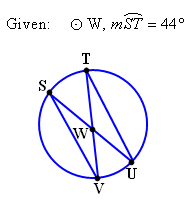 |
|
| |
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| 12) Since angles VSU and SUT are congruent, what is true about chord SV and chord TU? |
|
|
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| Refer to the figure and the information given below to answer the next two questions. |
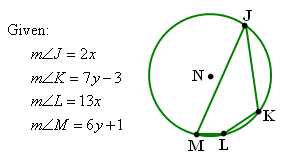 |
|
| |
| |
|
| |
|
| |
| For the remaining figures in this unit, assume that any lines that appear to be tangent to a circle are indeed tangent lines. |
|
|
| |
| |
|
| 20) Describe a “point of tangency”. |
|
4000 character(s) left
Your answer is too long. |
|
|
Attachments |
|
| |
|
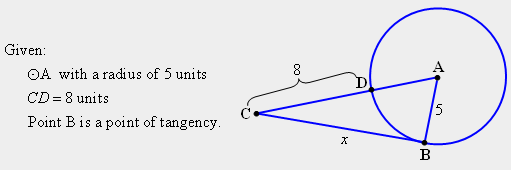
| 22) In triangle ABC shown below, (a) explain why angle ABC is a right angle, (b) state the length of AC, and (c) determine the value of “x”? |
 |
4000 character(s) left
Your answer is too long. |
|
|
Attachments |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| 25) Common external tangents (do, do not) intersect a line segment that has its endpoints on the centers of the two circles. |
|
|
|
| |
|
| 26) Common internal tangents (do, do not) intersect a line segment that has its endpoints on the centers of the two circles. |
|
|
|
| |
|
| 27) For the figure and the information shown below, explain how the Angle Angle Side Theorem (AAS) can be developed to show that segment AD is congruent to segment DB? |
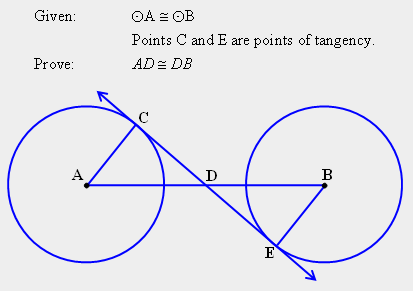 |
4000 character(s) left
Your answer is too long. |
|
|
Attachments |
|
| |
|
| Activity: Print out the triangle below. Complete the following steps to construct a specific circle. (1) Using a compass, bisect angles A and B, extending the bisectors out so that they intersect. Name the point of intersection, point D. (2) From point D, construct a line perpendicular to segment AB. Name the point of intersection of the bisector and segment AB, point E. (3) Set the metal point of the compass on point D and the pencil point of the compass on point E. This setting is the radius of circle D. (4) Draw circle D. |
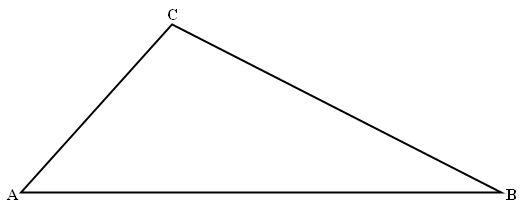 |
|
| |
| |
|
| |
|
| 31) Examine the figure and the information given below. Answer the following questions about the figure: (a) Why can it be stated that segments VU and VW are congruent? (b) What property of equality justifies the statement that segment TV is congruent to itself? (c) What theorem in this unit justifies the statement that segments TU and TW are congruent? (d) What postulate can be used to deduce that triangles TUV and TWV are congruent? |
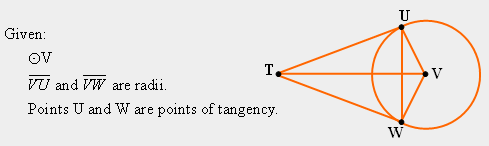 |
4000 character(s) left
Your answer is too long. |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
| 33) Describe a secant. |
|
4000 character(s) left
Your answer is too long. |
|
|
Attachments |
|
| 34) Select the answer that completes Theorem 23-H: If a secant and a tangent intersect at the point of tangency, then the measure of each angle formed is _________ the measure of its intercepted arc. |
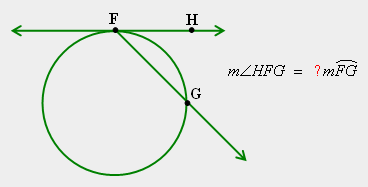 |
|
|
| |
|
| 35) Select the answer that completes the Theorem 23-I: If two secants intersect in the interior of a circle, then the measure of an angle formed is one-half the sum of the measures of the arcs intercepted by the __________ and its _________ __________. |
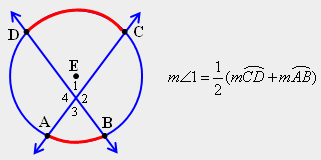 |
|
|
| |
|
| |
|
| 37)
For the figure and the information provided below, answer the following questions: (a) What is the value of “x”? (b) What is the measure of arc AB? (c) What is the measure of arc CD? (d) What is the measure of angle DFC? |
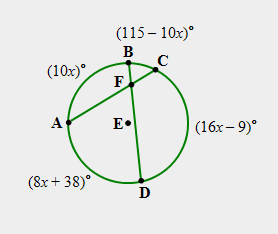 |
4000 character(s) left
Your answer is too long. |
|
| |
|
| 38) Select the answer that completes the Theorem 23-J: The measure of an angle formed by two secants, a secant and a tangent, or two tangents intersecting in the exterior of a circle is equal to one-half the __________ __________ of the measures of the intercepted arcs. |
|
|
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| 41) For circle L and the information given below, answer the following questions: (a) What is the value of “x”? (b) What is the value of “y”? (c) What is the value of “z”? |
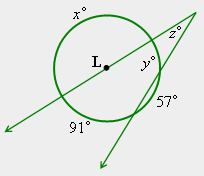 |
4000 character(s) left
Your answer is too long. |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| 46) Activity: Modify the steps for constructing a hexagon to make the inscribed six-pointed star below. Explain how you created the star. |
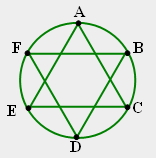 |
4000 character(s) left
Your answer is too long. |
|
|
Attachments |
|
| 47) If you were directed by your school to complete Offline Activities for this course, please enter the information on the Log Entry form. |
|
| No offline activities found |
0 Hour(s) & 0 Minute(s)
|
|
|
Attachments |
|