ACCELERATION

Unit Introduction
In the last unit, you
learned about average speed and velocity. In this unit, you will learn about
another descriptor of motion that can impact speed and velocity: acceleration.
Acceleration
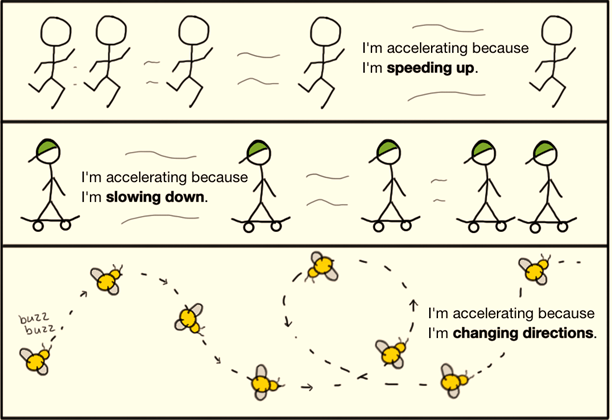
Acceleration is the name given to any process that changes the
velocity of an object. When an object’s speed increases over time, this is
known as positive acceleration. If an object’s speed
decreases over time, it is called negative acceleration, or deceleration.
Since velocity is both a speed and a direction, if an object changes direction,
this also produces a change in the object’s acceleration. If an object has no
acceleration, it can either be standing still or moving at a constant velocity.
In this unit you will
work on problems that deal with uniform acceleration.
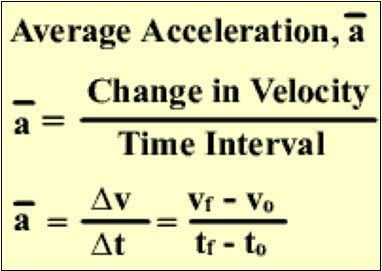
Average acceleration can
be calculated by dividing the change in velocity by the time that has elapsed.
The standard unit for acceleration is meters per second squared, or m/s2.
The formula for average acceleration is as follows:
Now, try to solve a
problem using the formula for average acceleration.
A roller coaster car
rapidly picks up speed as it rolls down a slope. As it starts down the slope,
its speed is 4 m/s. But 3 seconds later, at the bottom of the slope, its speed
is 22 m/s. What is its average acceleration?
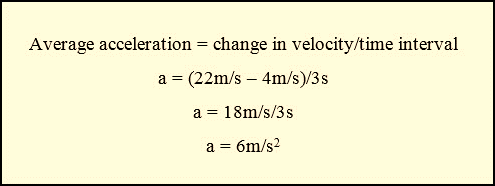
The roller coaster’s average acceleration is 6m/s2.

Read the following
article to learn more about acceleration.
Since you now understand
velocity and acceleration, watch the following video. Use the video notes to
solve the problem along with the video clip. Submit your work as question #7 in
the assessment portion of the unit.
Printable: AIRBUS VIDEO NOTES
Acceleration Due to Gravity
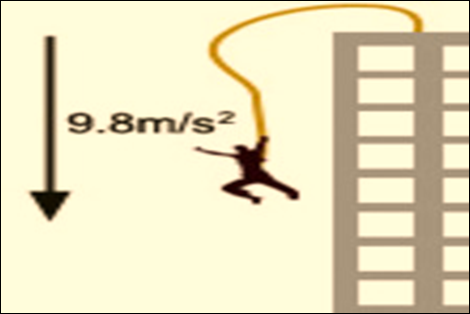
An object in freefall
will accelerate at a rate of 9.8m/s2 toward the Earth, which is due
to the force of Earth’s gravity on the object. This is known as acceleration
due to gravity.
Here’s a
thought-provoking question. What factors can influence the acceleration due to
gravity? If an object is in space or on or near another planet, the force of
gravity will be different, due to the change in gravitational forces. Watch the
following video clip on acceleration due to gravity at the international space
station. This video is just to get you thinking. You are not responsible for
the mathematics presented in this clip.
Try a practice problem
for acceleration due to gravity.
An apple falls from the
top of an apple tree. Its final velocity is 19.6m/s. How long did it take for
the apple to hit the ground?
This problem assumes that
you know the acceleration due to gravity, which is 9.8m/s2. Use that
in the acceleration formula. You need to rearrange the formula to solve for
time.
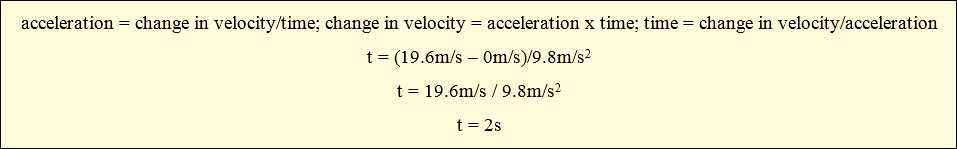
It took the apple 2
seconds to hit the ground.
Please complete the
acceleration practice problems now. Submit your work as question #8 in the
assessment portion of the unit.
Printable: ACCELERATION PRACTICE PROBLEMS DOCUMENT
Virtual Car: Acceleration
The virtual car at the
following website demonstrates acceleration in a way that you can see and
manipulate. Click “launch” and use the arrows to make the car speed up, slow
down, and change direction, which are all ways of accelerating.
Discovery Education Video
Review the concepts of velocity, acceleration, and deceleration as you watch the following video clip. Complete the guided notes and submit your work as question #9 in the assessment portion of the unit.
Printable: Video Guided Notes
![]() Velocity, Acceleration, and Deceleration (03:41)
Velocity, Acceleration, and Deceleration (03:41)
QUIZLET VOCABULARY
 Now answer
questions 1 through 9.
Now answer
questions 1 through 9.

