PERIODIC TABLE OF THE ELEMENTS
Unit Introduction
In the last two units,
you have been exposed to some information about the periodic table. The purpose
of this unit is to give you an overview of the history, allow you to more
thoroughly understand the information on the periodic squares, and to
investigate trends on the periodic table.
History of the Periodic Table
The periodic table
organizes all known elements in the universe. Dmitri Mendeleev is thought to be
the father of the modern periodic table, but several other scientists have
helped in the development of its current format. The elements are arranged
chronologically according to atomic number in the modern periodic table. Not
all currently known elements were on Mendeleevís periodic table. He was able to
classify and arrange the elements known at the time as well as predict the
spots that future elements would fit into. This is what set Mendeleevís
periodic table apart from others that were being developed.
The
First Periodic Table:
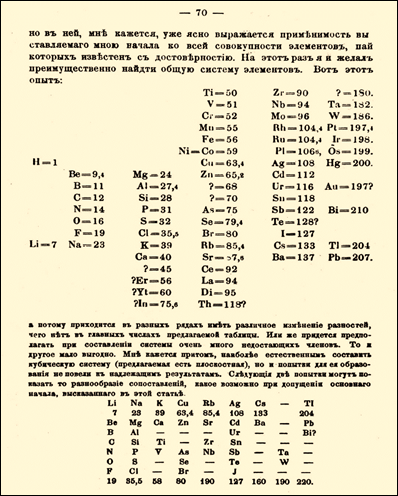
What you see below is
Mendeleevís organization of elements according to their increasing atomic
weights. You can see the blank spaces at the bottom where he knew other
elements would be discovered and fit into those places.
Please read the following
article, which has more information about Mendeleevís personal and professional
life. As you read, construct a timeline of his life. Submit your work as
question #15 in the assessment portion of the unit.
Printable: Timeline Document
Squares of the Periodic Table
There are over 100 known
elements at this time. Each element has its own square on the periodic table.
Each square displays the same information, though one periodic table can have
the information arranged differently from another periodic table. Here is a
close-up view of what is on the periodic square for carbonó
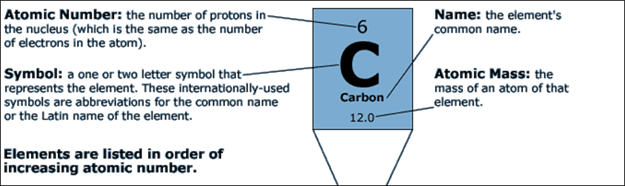
If you need to know an
elementís symbol, atomic number, or atomic mass, you can look to the periodic
table to find this information and more.
Practice: Fill in the
blanks for the element vanadium using the periodic square. Record your answers
for questions 1-3 in the assessment portion of the unit.

1. Element symbol:
____________________
2. Atomic mass: ______________________
3. Atomic number:
_____________________
Periodic Table Organization
The periodic table is
organized according to increasing atomic numbers of the elements. Hydrogen, the
first element, has the atomic number of 1. Helium, the next element, has the
atomic number of 2. When elements are listed in order of increasing atomic
number, the same sequence of properties appears over and over again; this is
the periodic law. The periodic table can be read similar to reading textóleft
to right and top to bottom.
One may wonder why the
periodic table has such an unusual shape.†
By arranging elements in the configuration that is shown, they are close
to elements with similar properties.
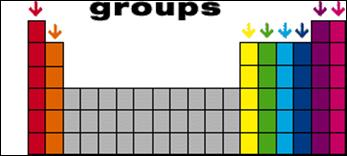
A group is a vertical
column in the periodic table. Elements in the same group have very similar
properties to one another. Elements in the same group also have the same number
of valence electrons, which helps to predict how they will form compounds with
other elements.
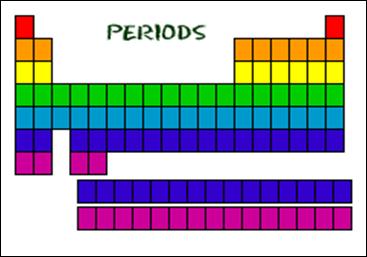
A period is a horizontal
row of the periodic table. Elements in the same period have the same number of
orbitals, or shells, for electrons.
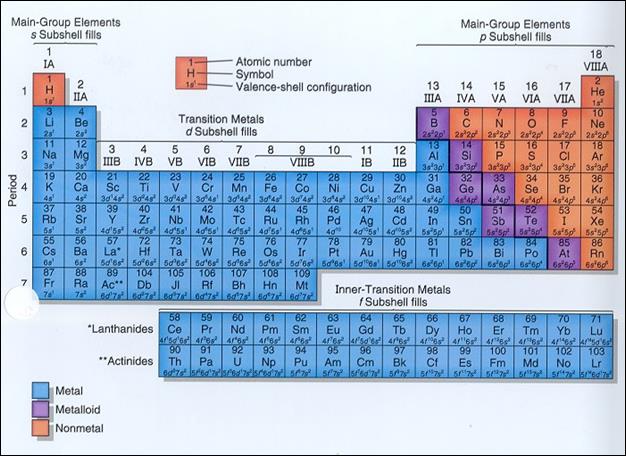
Metals, metalloids, and
nonmetals can be easily found in large groupings across the periodic table. Looking
at the periodic table below, you will notice that the metals are all found on
the left side.† Most of the elements are
metals.† Hydrogen (H) is a gas but it is
placed on the left side above the Alkali Metals.† Hydrogen is a family of one.† The nonmetals are found on the right side of
the periodic table.† If you look closely
at the periodic table you will notice a dark, stair-step line.† This line divides the metals from the
nonmetals.† The elements found along this
line are known as the metalloids.† They
have properties of both metals and nonmetals.†
Aluminum (Al) is found along this line, but it is a true metal not a
metalloid.
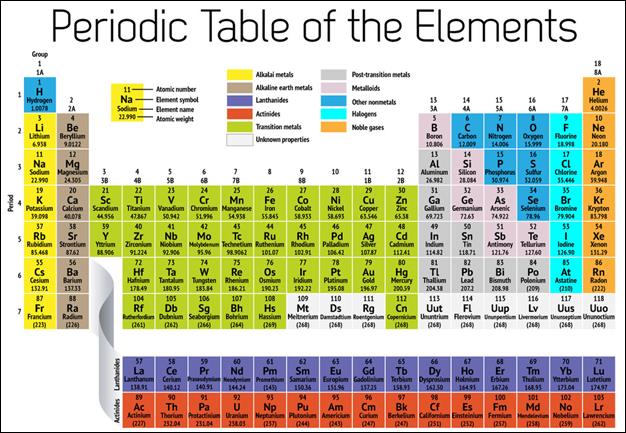
Element Groups
The element groups on the
periodic table are referred to by their group numbers or names. The group
numbers are listed 1-18 across the top of the periodic table, or if the
transition metals are skipped over, the rest of the groups are listed as 1A-8A
across the top of the periodic table. You can see both numbering schemes on the
periodic table below.
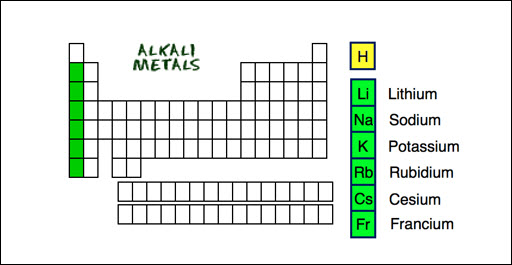
Group 1 is known as the
alkali metals. All elements in group 1 except for hydrogen are included. They
are soft and gray in color. They are extremely reactive, and you rarely see
them as elements in nature because of their strong tendency to form compounds with
other elements. All elements in group 1 have 1 valence electron.
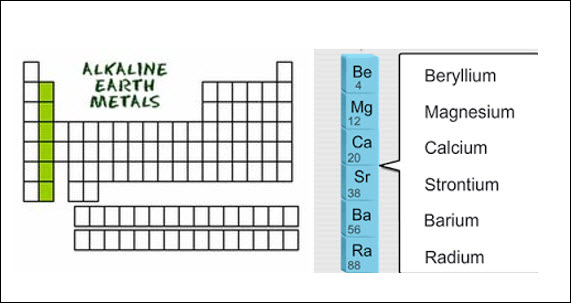
Group 2 is known as the
alkaline earth metals. They are also reactive but not as reactive as the Group
1 elements. All elements in group 2 have 2 valence electrons.
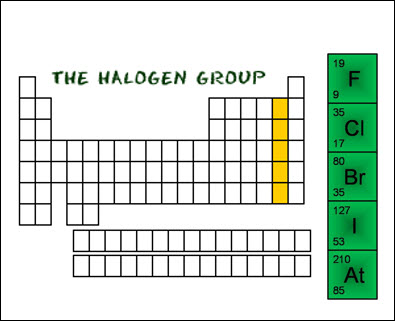
Group 17
is known as the halogens. Halogens are very reactive nonmetals and have a
strong tendency to form compounds with Group 1 elements. All elements in group
17 have 7 valence electrons.
The
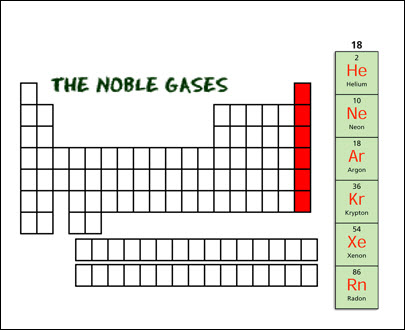
noble gases are found in Group 18. They have a full outer shell of electrons,
which means they are stable and exist as elements in nature.
Watch
the following video for more information about the organization of the periodic
table:
Element Uses
Each
element on the periodic table is unique. Consequently, the elements are useful
in many different ways. Check out the link below to learn more about common
uses of each element. Select 20 elements and describe their uses. Find a
picture to include for each chosen element.
http://elements.wlonk.com/ElementUses.htm
