EXPONENTIAL FUNCTIONS
|
Unit Overview
In this unit, you will study exponential functions which are used in the real world to model population, growth, finance, and scientific experiments.
Exponential Growth
 |
![]() Try this: $4500 is invested at 1.25% interest for 3 ¼ years. How much money do you have at the end of the 3 ¼ years?
Notice this problem uses values that are not whole numbers, but you solve it just the same.
Try this: $4500 is invested at 1.25% interest for 3 ¼ years. How much money do you have at the end of the 3 ¼ years?
Notice this problem uses values that are not whole numbers, but you solve it just the same.
Remember to use A = P(1 + r)n.
P = 4500, r = 0.0125, n = 3.25
A = 4500 (1+.0125)3.25
Use a calculator to solve. A = 4500 (1.0412) = $4685.40
"Click here" to check the answer.
Stop! Go to Questions #1-7 about this section, then return to continue on to the next section.
Growth Factor
 |
Stop! Go to Questions #8-13 about this section, then return to continue on to the next section.
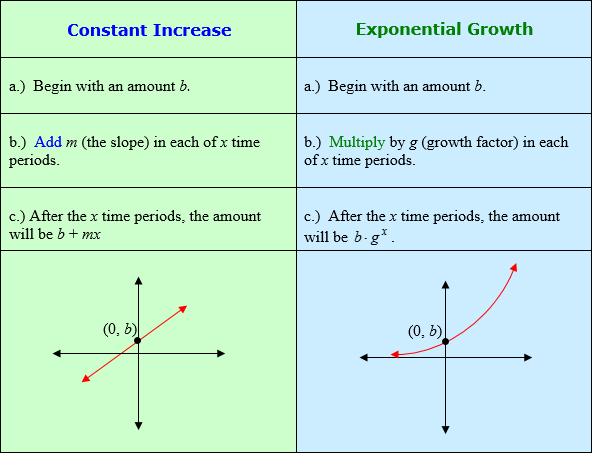
Constant Increase and Exponential Growth
 |
 |
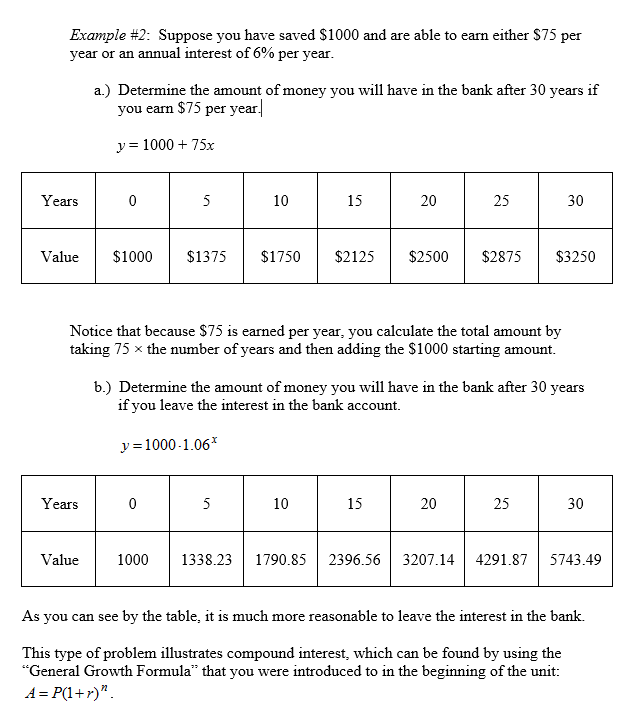 |
![]() Why is there $1000 at year 0?
Why is there $1000 at year 0?
Year 0 is the beginning and $1000 is the starting amount. No interest has been earned at this point.
"Click here" to check the answer.
![]() Why is $1000 being multiplied rather than added as in part a?
Why is $1000 being multiplied rather than added as in part a?
In this case, you are calculating 6% each year, adding the interest, and then calculating 6% of the new amount for the next year. This continues for the total number of years. This results in the formula y = b • gx which allows you to do the problem in one step rather than calculating each year separately.
"Click here" to check the answer.
24a11b4
Stop! Go to Questions #14-31 to complete this unit.
Exponential Decay
Exponential decay is a situation in which the original amount is repeatedly multiplied by a growth factor between zero and one. Exponential-decay situations have graphs that go downward as you move to the right of a coordinate plane. Exponential decay can occur with populations if the growth factor is less than 1. To determine the growth factor for exponential decay, subtract the rate of change from 1.
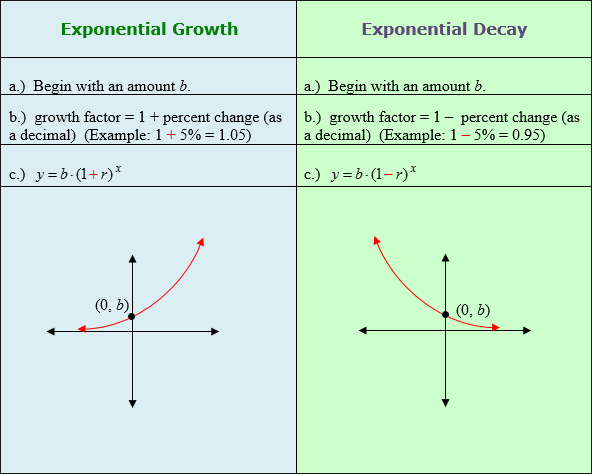 |
 |
Note that the following video uses the same formula but assigns different letters for variables. Don't let this confuse you. Rather than A, f(t) is used. Instead of P being used for the initial amount, a is used. Don't let the a confuse you. The formula is the same, just set up with her choice of variables. Please notice that the set up of the problem is the same.
Click here to watch the video "how do you solve a word problem with exponential decay?"
Final Thoughts
** If something is increasing (growth), such as a bank account, the final answer should be higher than the starting amount. Likewise, the growth rate should be greater than 1.
** If something is decreasing (decay), such as population, the final answer should be lower than the starting amount. Likewise, the growth rate should be between 0 and 1.
** Population should be whole numbers.
** Money should be rounded to the nearest cent (2 decimal places.)
Stop! Go to Questions #32-37 to complete this unit.