OPERATIONS WITH NUMBERS AND EXPONENTS

Unit Overview
This unit begins with a review of real numbers, their properties, and the order of operations. In addition, the various properties of integer exponents are reviewed and extended to include rational exponents. Using the property of exponents and rational exponents, expressions in radical form will be rewritten in exponential form and vice versa.
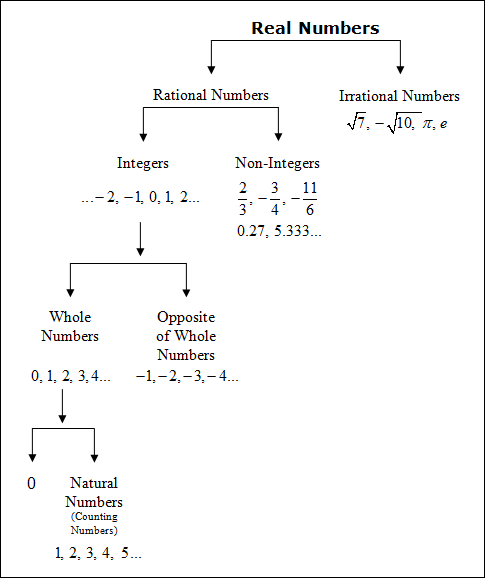
Operations with Numbers
Types of Numbers
|
![]() Rational Numbers -- Recipes (02:54)
Rational Numbers -- Recipes (02:54)
irrational numbers: numbers whose decimal part does not terminate or repeat real numbers: all rational and all irrational numbers |
![]() Irrational Numbers -- Travel (02:22)
Irrational Numbers -- Travel (02:22)
|
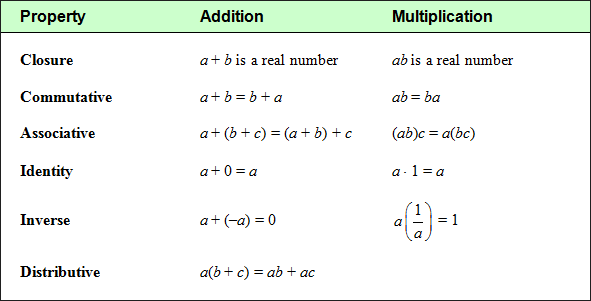
Properties of Real Numbers
 |
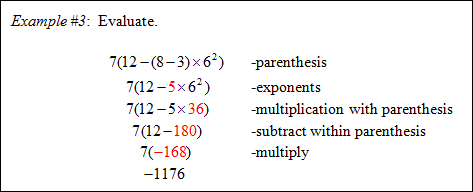
Order of Operations
To simplify algebraic expressions you must use an order of operations.
Parentheses, Exponents, Multiply, Divide, Add, Subtract
“Please Excuse My Dear Aunt Sally”
*If multiplication and division are the only two operations, work the problem from left to right
*If addition and subtraction are the only two operations, work the problem from left to right.
![]() Introduction (02:08)
Introduction (02:08)
 |
![]() Simple Orders--Roller Coaster Capacity (02:33)
Simple Orders--Roller Coaster Capacity (02:33)
 |
 |
![]() Exponents--Around the Loop (03:02)
Exponents--Around the Loop (03:02)
Stop! Go to Questions #1-4 about this section, then return to continue on to the next section.
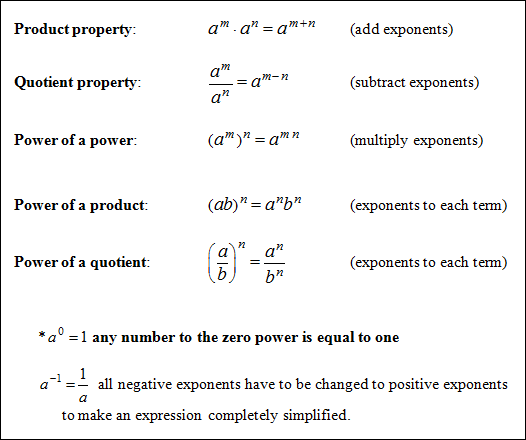
Properties of Exponents

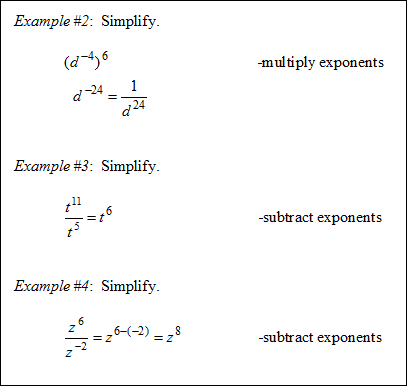 |
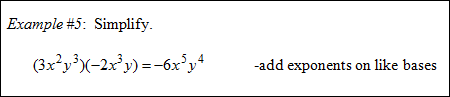 |
![]() Multiplying Expressions with Like Bases (01:53)
Multiplying Expressions with Like Bases (01:53)
 |
![]() Dividing Expressions with Like Bases (01:56)
Dividing Expressions with Like Bases (01:56)
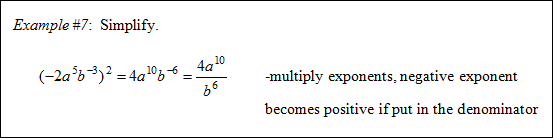 |
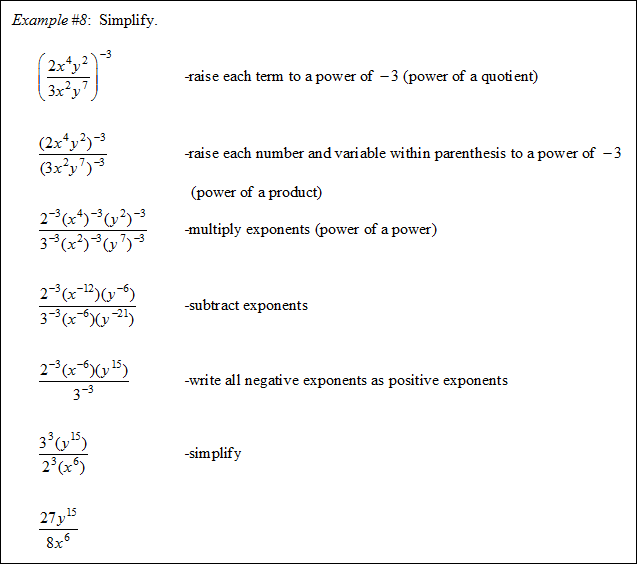
![]() Raising a Power to a Power (02:01)
Raising a Power to a Power (02:01)
 |
![]() Raising a Power to a Power in Rational Expressions (02:54)
Raising a Power to a Power in Rational Expressions (02:54)
 |
Stop! Go to Questions #5-12 about this section, then return to continue on to the next section.
Rational Exponents
Rational exponents are exponents that are fractions.
Rational exponents are an alternate way to express roots and can be very useful when dealing with more complicated expressions.
First, let's review the terms associated with radicals.
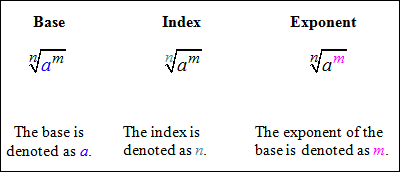 |
Now, let's take a look at what a rational exponent is.
 |
 |
Practice: Write ![]() in radical form, and then answer the following questions.
in radical form, and then answer the following questions.
![]() What is the index of the radical?
What is the index of the radical?
The index is 7.
"Click here" to check the answer.
![]() What is the power of x under the radical?
What is the power of x under the radical?
The power of x is 3.
"Click here" to check the answer.
Solution: ![]()
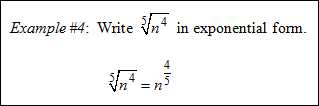 |
Practice: Write ![]() in exponential form, and then answer the following questions.
in exponential form, and then answer the following questions.
![]() What is base of the expression?
What is base of the expression?
The base is 5y.
"Click here" to check the answer.
![]() What is rational exponent of the expression?
What is rational exponent of the expression?
The exponent is 1 ⁄ 2.
"Click here" to check the answer.
Solution: ![]() (The index of the radical is understood to be 2.)
(The index of the radical is understood to be 2.)
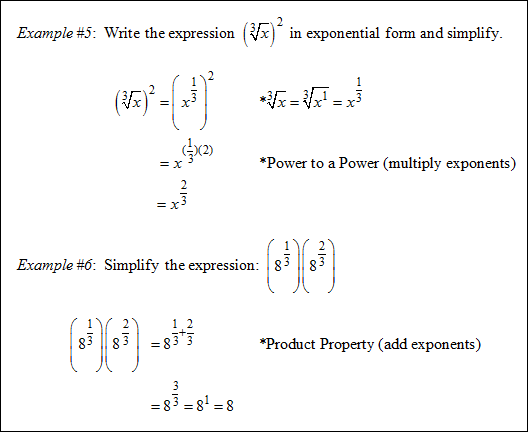 |
Practice: Simplify ![]() and then answer the following questions.
and then answer the following questions.
![]() What do you do with the exponents?
What do you do with the exponents?
Add the exponents.
"Click here" to check the answer.
![]() What is the simplified expression?
What is the simplified expression?
Solution: x1 = x
"Click here" to check the answer.
 |
Practice: Simplify ![]() and then answer the following questions.
and then answer the following questions.
![]() What do you do with the exponents?
What do you do with the exponents?
Subtract the exponents.
"Click here" to check the answer.
![]() What is the simplified expression?
What is the simplified expression?
Solution: n(4 ⁄ 8) = n(1 ⁄ 2)
"Click here" to check the answer.
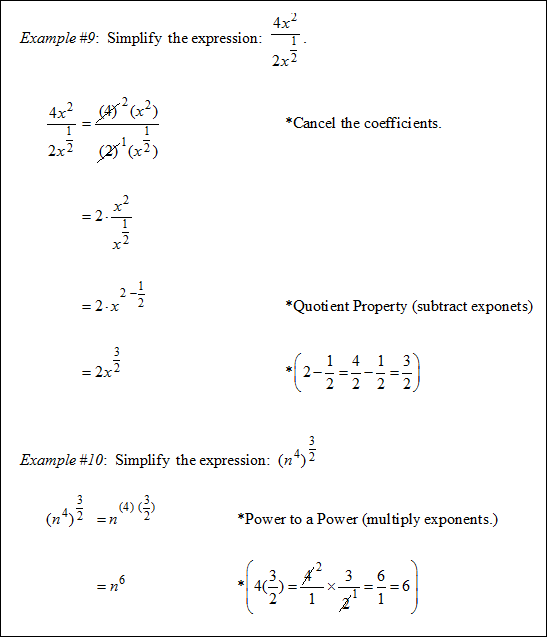 |
Practice: Simplify ![]() and then answer the following questions.
and then answer the following questions.
![]() What do you do with the exponents?
What do you do with the exponents?
Multiply the exponents.
"Click here" to check the answer.
![]() What is the simplified expression?
What is the simplified expression?
Solution: b(12 ⁄ 4) = b3
"Click here" to check the answer.
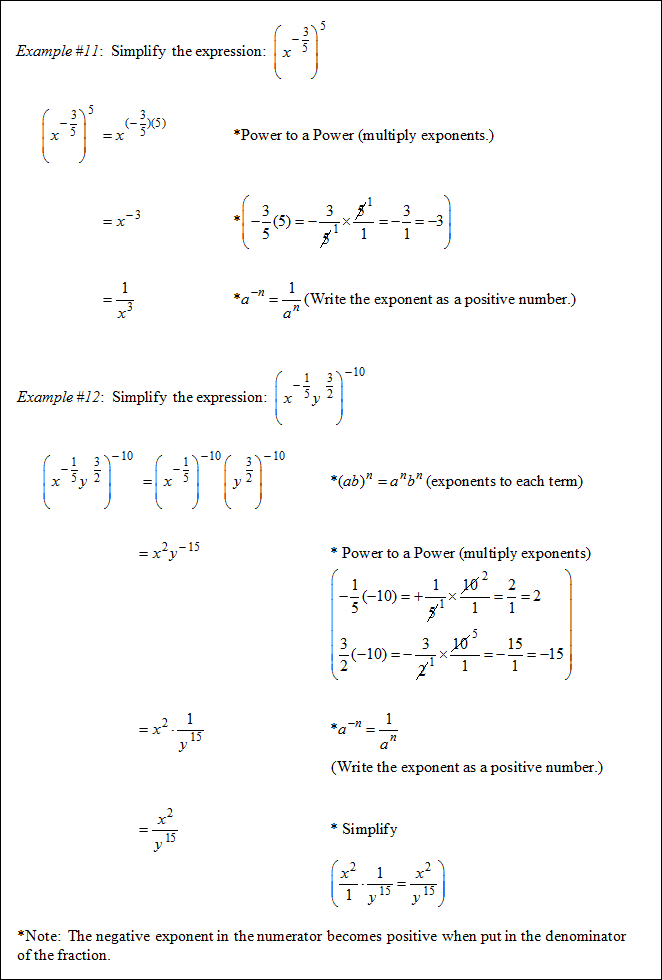 |
Practice: Simplify ![]() and then answer the following questions.
and then answer the following questions.
![]() What is the coefficient of the expression in the numerator?
What is the coefficient of the expression in the numerator?
8 to the (1 ⁄ 3) means cube root of 8 which equals 2.
"Click here" to check the answer.
![]() What is the entire expression in the numerator of the solution?
What is the entire expression in the numerator of the solution?
2k(3 ⁄ 3) = 2k1 = 2k
"Click here" to check the answer.
m(6 ⁄ 3) = m2
"Click here" to check the answer.
*Remember: The negative exponent in the numerator becomes positive when put in the denominator of the fraction.
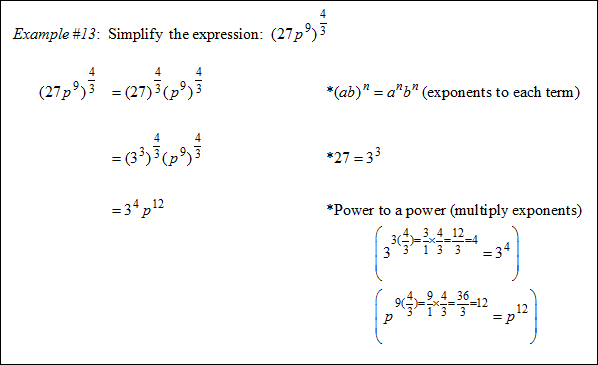 |
Practice: Simplify ![]() and then answer the following questions.
and then answer the following questions.
![]() What is the coefficient of the solution?
What is the coefficient of the solution?
23 = 8
"Click here" to check the answer.
![]() What is the exponent of y in the solution?
What is the exponent of y in the solution?
The exponent of y is (2 ⁄ 3)(3 ⁄ 1) = 6 ⁄ 3 = 2
"Click here" to check the answer.
![]() What is the solution to the expression?
What is the solution to the expression?
8y2
"Click here" to check the answer.
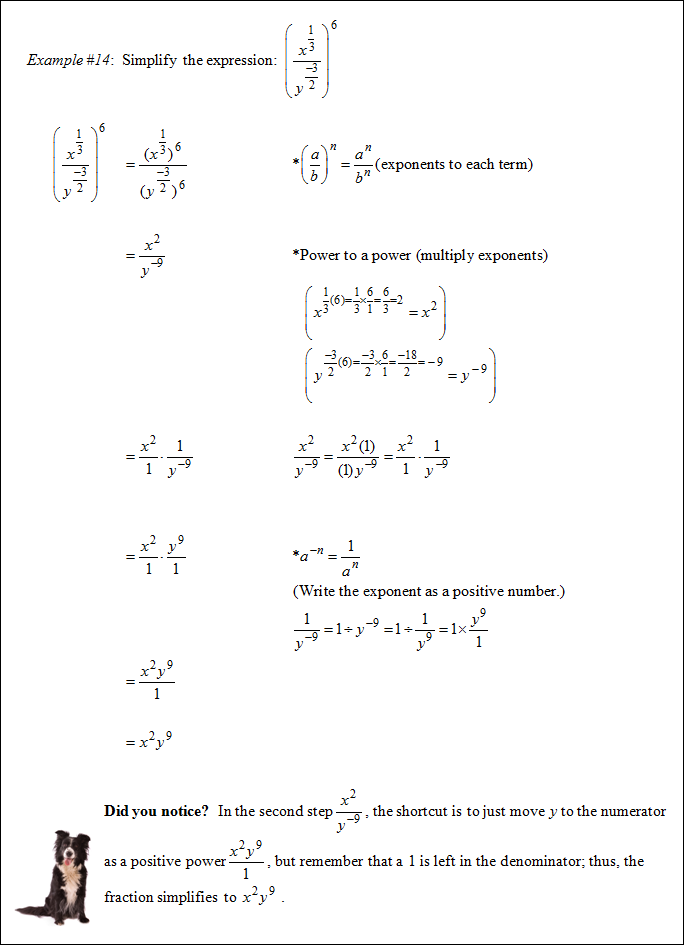 |
Practice: Simplify ![]() and then answer the following questions. Use the shortcut to simplify your work.
and then answer the following questions. Use the shortcut to simplify your work.
![]() What is the numerator of the solution?
What is the numerator of the solution?
4y3 (The y is moved to the numerator with a positive power.)
"Click here" to check the answer.
![]() What is the denominator of the solution?
What is the denominator of the solution?
3x2 (The x is moved to the denominator with a positive power.)
"Click here" to check the answer.
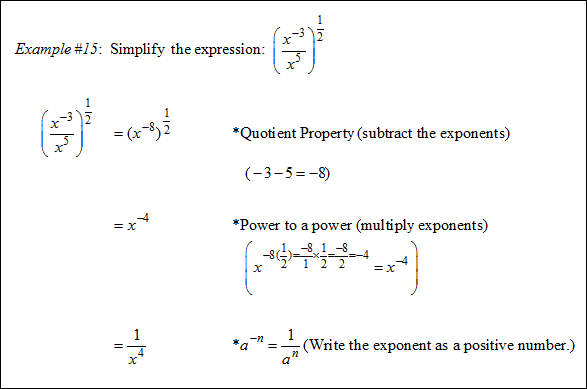 |
Stop! Go to Questions #13-29 to complete this unit.