LOOKING BACK AT
HISTORY AND GEOGRAPHY

Mount Rushmore in South Dakota
Unit Overview
You have learned so many things
about history and geography is just a few short weeks. You have studied everything from timelines to
landforms. Let’s see what you remember!
Units 1-4
In these units, you learned that
time can be measured in days, weeks, months and years. Are you still using your flashcards to review
the days of the week and the months of the year? See if you can still put the months and days
of the week in their correct order quickly.
You also placed dates and years in their correct order on a
timeline. Sometimes you looked at pictures
to see how different clothes and homes were in earlier times.
![]() Go to Questions 1-5.
Go to Questions 1-5.
Units 5-7
Today many of us use cell phones,
texting or email to communicate; we travel quickly by cars, high-speed trains
and airplanes. This was not always the
case, however. In units 5, 6 and 7, you
looked at many inventions that have been replaced or changed through science
and technology. You also read about
Thomas Edison, a famous inventor. Many
of the things we use every day, such as light bulbs, movies and wax paper, are
the results of his work. You also
learned that Edison was successful because he never gave up and made the best
of every situation.

Edison and the electric light bulb
Thomas Edison did much of his work at his factory and laboratory in West Orange, New Jersey. Here Edison and his employees put new ideas into practice.
![]() Go to Questions 6-12
Go to Questions 6-12
Unit 8
Do you remember reading about
Abraham Lincoln? His nickname was
“Honest Abe” because he believed honesty and integrity were very important
qualities. Mr. Lincoln was President of
the United States during the Civil War, a very difficult time in American
history. He had to make many hard
decisions and is an excellent example of a good leader.

Abraham Lincoln Looking Over the Emancipation Proclamation
![]() Go to Questions 13-15
Go to Questions 13-15
Units 9 and 10
In these units, you began your
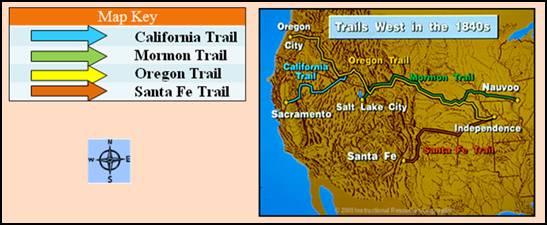
study of geography by looking at many different kinds of maps. You quickly learned how important they are
when people want to travel from one place to another. Maps use all kinds of symbols to help us find
places. These are explained in the map
key. A compass rose is another map
tool. It keeps us moving in the right
direction.
![]() Go to Questions 16-18.
Go to Questions 16-18.
Units 11-15
Many different types of landforms
and bodies of water cover the continents of the earth. They influence the ways we eat, dress, work
and play. In North America, for example,
grasslands called the Great Plains help people earn a living by farming, ranching
and packaging food for grocery stores.
Would you wear the same clothes in the cold regions of Antarctica as you
would in the hot, dry Sahara Desert? Of
course, you wouldn't! The landforms in
each place change what we wear.

Sometimes landforms make it
difficult to travel from one place to another.
This happens in the Andes Mountains in South America and on the Tibetan
Plateau in Asia. As a result, people
need to make meals, clothing and houses from things that they find or grow
nearby. In other places, landforms and
bodies of water bring people together.
They are able to share the art, culture and stories that they have
created. Do you remember reading about
the peninsulas and rivers in Europe?
Because they were able to travel on the waterways, Europeans shared
their ways of life and borrowed ideas from one another.
![]() Go to Questions 19-27.
Go to Questions 19-27.
Units 16 and 17
The world's land can be used in
many different ways. In rural areas, it
provides farms, forests and open spaces.
In urban areas, the land is the basis for buildings, businesses and
streets. People often change landforms
or remove them altogether to make their lives better. Both good and bad things happen as a
result. Roads and bridges make our
travel safer and faster, but changes in the land can destroy the habitats of
black bears, mountain lions and other animals.

Mountain Lion
in its Habitat
![]() Go to Questions 28-30.
Go to Questions 28-30.