THE SYSTEM'S UNIT
Unit Overview
“What’s in the box?” In this unit, the student will answer that question by delving into the inside of the computer. The common computer parts and their functions will also be identified. The student will also uncover the mystery surrounding many of the acronyms used in the computer industry.
 |
Computer Internal Layout
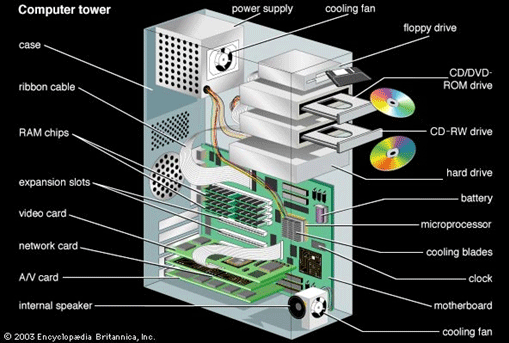
The system’s unit is the computer tower or computer case that contains the electronic components of the computer system. The motherboard is the main system unit component. It is a flat circuit board contained within the computer’s housing.
Computer Case
 |
The computer case is important because it provides protection for the internal electronic components of the computer. The computer case must also provide sufficient ventilation and room for expansion. Most computer cases are designed to accommodate specific motherboard types.
|
Case Front Panel

The case front panel of this computer case contains four 5.25 inch drive expansion bays, which could be used for a CD/DVD-ROM drive or CD-RW drive. The case also contains one 3.5 inch expansion drive bay, which could be used for a zip drive or floppy disk drive. Typically, the front panel of a computer case contains an on/off switch, a reset button, a power indicator light, and a hard disk drive activity light. In addition, many computer case front panels contain USB ports for easily connecting digital cameras and other electronic devices to the computer.
Case Rear Panel
 |
The case rear panel contains many openings, which are shown in the picture to the left. The expansion slot covers can be removed to connect a variety of expansion cards. The small holes down the right side of the case rear panel are used to increase ventilation. |
Case Fan

Because computer components generate a lot of heat, the computer case fan is essential for maintaining the functionality of the computer. The case fan is the primary source for cooling internal components. Some computer cases are built to accommodate additional case fans.
Power Supply and Cables

The power supply provides the electricity supply to the motherboard and computer drives. Power supplies usually have wattages of 200 watt to 250 watt, but more powerful models are available. The power supply cables contain red, yellow, and black wires. The black wires are ground wires, while the red wire supplies five volts of power and the yellow wire supplies twelve volts of power. The power cable connector connects the power supply with the computer’s drives.
 The floppy disk drive allows you to transfer files using 3.5 inch disks. Some retail programs still come with floppy disks and many people have data saved on floppies from their previous computers. Floppies are outdated, but still come in handy occasionally.
The floppy disk drive allows you to transfer files using 3.5 inch disks. Some retail programs still come with floppy disks and many people have data saved on floppies from their previous computers. Floppies are outdated, but still come in handy occasionally.
Optical Disk Drive

The optical disk drive allows you to install software, play music CDs and watch DVD movies. This drive can also be used to make music disks and copy movies.
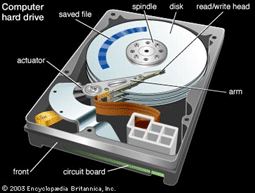
The computer hard drive contains disks that are made of aluminum or glass. The disks in a typical hard disk drive cannot be removed or replaced. Hard drives are measured in gigabytes. One gigabyte is the equivalent of one thousand million bytes or about 1 1/3 CD-ROM disks. The hard disk drive stores the files and programs that are used by your computer everyday. The hard disk drive is referred to as Drive C:
Motherboard
The motherboard is a circuit board inside the computer. The motherboard uses electrical paths to connect each component of the computer. The motherboard has slots or sockets for the central processing unit, memory, video, audio, etc.
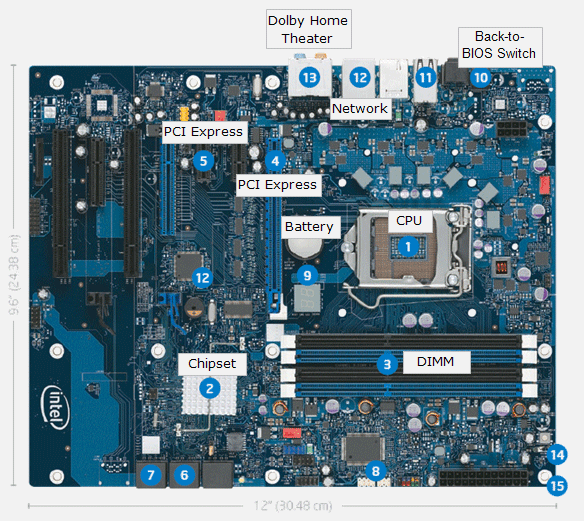
The chipset is the most important element of the motherboard. It guides and controls the flow of data between the computer’s components. The Intel P55 Express Chipset introduces a new generation of chipsets with a single chip replacing the traditional two-chip approach. The new architecture is designed to deliver the quality and performance needed for faster multitasking, digital media creation and gaming.
Motherboard Battery
The motherboard battery’s main purpose is to maintain the computer clock’s time and the computer’s Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) settings when the computer is turned off.
System Bus
The system bus is copper tracing on the motherboard that transports data between the CPU and memory. The system bus width or number of electrical paths determines the amount of bits of data that can be transported at one time. The system bus width is dependent on the CPU design and is an indication of the computer’s strength. Bus speed determines how fast the data travels through the system. Bus speed is measured in megahertz (MHz).
BIOS: Basic Input/Output System
The BIOS program is written permanently on the BIOS chip. The BIOS program controls the computer when it is first turned on. It sets up the computer’s hardware and performs systems checks. Then it turns over control to the computer’s operating system. The BIOS stores information in CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor). The BIOS program can be accessed through the computer’s setup.
Back-to-BIOS Switch
Intel has a new feature, a back-to-BIOS switch, which allows easy system recovery with all the BIOS settings kept intact after pushing the performance envelope too far.
Microprocessor
 The microprocessor contains the central processing unit or CPU and the cache memory. The CPU is the “brain” of the computer. Intel makes most of the CPU’s on the market today. For example, there is an Intel Pentium Processor Family, as well as an Intel Core Processor Family. The Pentium chip boosts a computer’s ability to generate graphics, video, and sound because of the multimedia instructions it contains. The Intel Core processors are the newest, smartest, and fastest processors.
The microprocessor contains the central processing unit or CPU and the cache memory. The CPU is the “brain” of the computer. Intel makes most of the CPU’s on the market today. For example, there is an Intel Pentium Processor Family, as well as an Intel Core Processor Family. The Pentium chip boosts a computer’s ability to generate graphics, video, and sound because of the multimedia instructions it contains. The Intel Core processors are the newest, smartest, and fastest processors.
The CPU is comprised of three parts: the control unit, the arithmetic/logic unit, and the memory. The control unit manages the computer by obtaining, interpreting, implementing, and saving the data inside the computer. The arithmetic/logic unit conducts all of the mathematical calculations and logical comparisons and stores the most frequently used instructions and data in the CPU’s cache memory. The speed at which a processor runs is measured in mega hertz (MHz). The larger the number of MHz the faster the processor will work. The memory stores the program instructions and data that the processor is currently using.
Memory Components
The DIMM sockets, or Dual Inline Memory Module sockets are the location on the motherboard where the Random Access Memory (RAM) is installed. DIMM stands for Dual Inline Memory Module and refers to the fact that both sides of the memory card have separate connections to the DIMM socket.
Everything that is done on the computer is temporarily stored in the RAM until it is saved to a disk. There are two types of RAM: static RAM (SRAM) and dynamic RAM (DRAM). As long as power is maintained, SRAM will hold its content without involvement from the CPU. DRAM must be continuously refreshed from the CPU in order to maintain its contents.

Today, most computers have between 512 MB and 1 GB of RAM. However, a typical desktop will have about 2 GB of RAM. Most computers on the market will support between 4 and 8 GB of RAM, maximum. SDRAM or synchronous dynamic random access memory is a newer memory used in most computers today, which is able to perform at higher data transfer bus speeds. RDRAM or rambus dynamic random access memory is the latest RAM available. Even though it is faster than SDRAM, it is still too expensive for the average computer user.
ROM or read only memory holds the programs and data that were permanently recorded into memory at the factory. ROM cannot be changed by the user and its contents remain even, when power is turn off. The boot routine of the computer is stored in
Video Card The video card is the component that operates the monitor. It interprets instructions from Windows or another program and displays images, graphics and videos on the screen. The video card contains a processor chip and memory. |
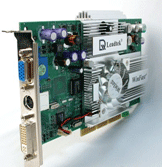 |
GPU
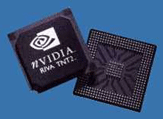 |
GPU stands for Graphics Processing Unit. The video card is in charge of controlling the video display. Much like the CPU's relationship with the motherboard, the brain of the video card is the GPU. It is responsible for making the decisions for processing the video card's graphical input and output data. I It is usually located under the fan to prevent it from overheating. |
AGP Expansion Slot
![]() The AGP expansion slot connects video cards to a motherboard. AGP stands for Accelerated Graphics Port. Video cards simply plug into an AGP expansion slot and connect a monitor or other video display device to a computer.
The AGP expansion slot connects video cards to a motherboard. AGP stands for Accelerated Graphics Port. Video cards simply plug into an AGP expansion slot and connect a monitor or other video display device to a computer.
ISA Slot
An ISA or Industry Standard Architecture slot allows modems and other expansion cards to be connected to the motherboard.
PCI Slot
The PCI or Peripheral Component Interconnect slot is replacing the ISA slot. PCI slots can handle more data than ISA slots. PCI slots are also used to connect modems and other expansion cards to the motherboard.
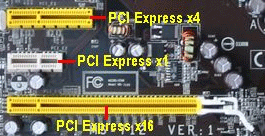
PCI Express is a more recent technology that is slowly replacing AGP. PCI Express x16 slots can transfer data at 4GB's per second.
Audio Cables
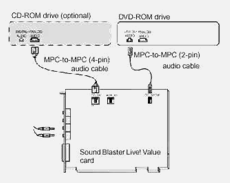 Audio cables connect multimedia drives, such as the CD-ROM and DVD drives to the computer’s sound card. The audio cables enable sound data to be transferred so it can be decoded and played. The computer’s sound card and speakers determine the computer’s sound quality. A four pin cable is used for analog audio, while a two pin cable is used for digital audio. Intel enables a high-quality integrated audio with Dolby Home Theater.
Audio cables connect multimedia drives, such as the CD-ROM and DVD drives to the computer’s sound card. The audio cables enable sound data to be transferred so it can be decoded and played. The computer’s sound card and speakers determine the computer’s sound quality. A four pin cable is used for analog audio, while a two pin cable is used for digital audio. Intel enables a high-quality integrated audio with Dolby Home Theater.
In the picture below, the front panel connector and the IDE connectors are displayed. IDE is short for Integrated Device Electronics. The IDE connectors allow you to connect devices to the motherboard. The motherboard also contains a floppy connector to connect a floppy drive. IDE cables are made up of either 40 individual wires or 80 individual wires that are used to transfer data between the motherboard and the drives.
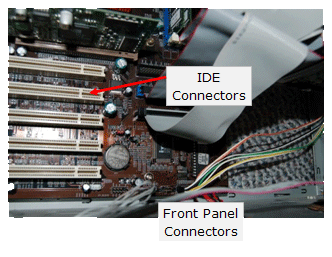 |
The front panel connector is the place where the front panel wiring is connected to the motherboard. The front panel wires control the reset button, power button, and the hard disk drive activity light.
The front panel also contains the wiring for the case speakers. |
Peripherals
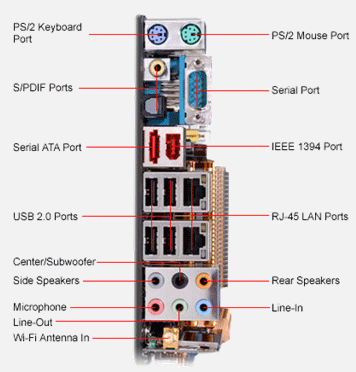
Peripherals are all external devices that will not be installed inside the case. They will allow you to interact with the computer by inputting commands, viewing the screen, as well as printing out documents and pictures.
I/O is short for input and output. PS/2 ports are typically used to connect input devices like the computer’s keyboard and mouse. USB ports or Universal Serial Bus ports are used to connect a variety of devices such as a mouse, digital cameras, and even printers. The most common output device, the computer’s monitor, is connected using a serial port. Printers, game controllers, microphones, and speakers are all connected to the computer using I/O ports.