
TOOLS OF GEOMETRY: ANGLES
 |
Unit Overview
In this unit, students will be able to define, identify, and name an angle and its parts. Students will use a protractor and the angle addition postulate to find the measure of angles.
Key Vocabulary

Angles
An angle measures the amount of turn. As the angle increases, the name changes: |
Measures less than 90 degrees but more than 0 degrees |
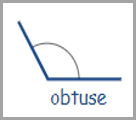 |
Measures greater than 90 degrees but less than 180 degrees |
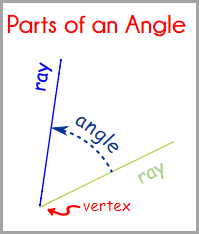 |
The corner point of an angle is called the vertex And the two straight sides are called rays The angle is the distance between the two rays, the two sides of the angle. |
Practice
Which angle measure is greater?
|
Which angle measure is greater?
|
Which angle measure is greater?
|
 |
Click on the icon to the left to understand the importance of Names of Angles in Geometry. |
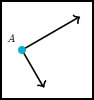
An angle is made up of two rays which meet at a common point called a VERTEX.
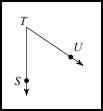 |
|
A portion of a line which starts at a point and goes off in a particular direction to infinity is the SIDES of each angle.
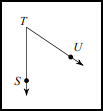 |
|
 |
Click on the link to watch the video "Naming Angles".
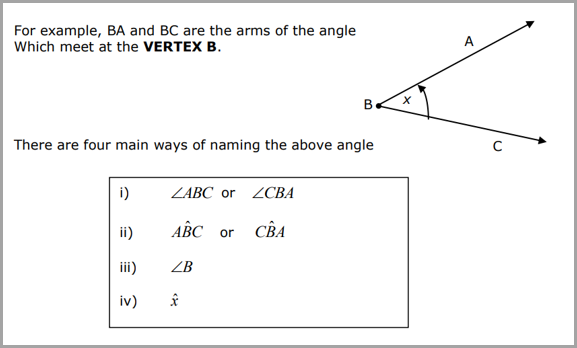
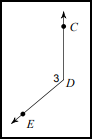
Let's Practice
 |
 |
 |
|
Angle Basics Review
What is an angle?
An angle is two rays that share a vertex.
Intersecting lines or line segments also form angles.
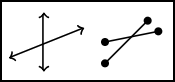
Let's Practice
Which of the following figures is an angle?
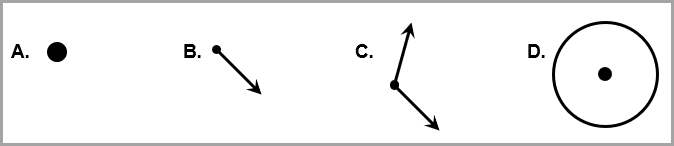 |
Measuring Angles
Angles are measured in degrees.
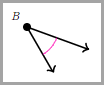
The wider an angle is open, the greater its measure. If you compare these two angles, the first one is open wider.
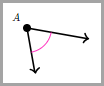
is greater than the measure of this angle.
Let's Practice
Which angle measure is greater?
|
Measuring Angles with a Protractor
When constructing angles, you can use a protractor to help you construct an angle of a given amount of degrees. There are 360 degrees in a full rotation.
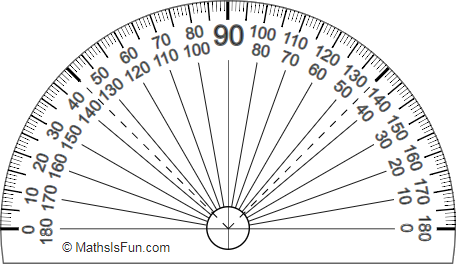 |
The protractor protractor measure 0° to 180° |
Steps to measure an angle:
1.) Put the center of your protractor on the point of the angle.
2.) Lie a zero line of the protractor over one side of the angle.
3.) Follow the correct scale round the edge of the protractor from 0 to the other side of the angle.
4.) Read the size of the angle.
Click on the link to watch the video "Constructing angles".
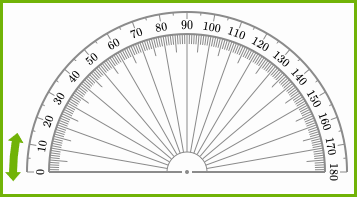
Let's Practice
Click on the protractor to draw angles.
 |
Angle Bisector and Angle Addition Postulate
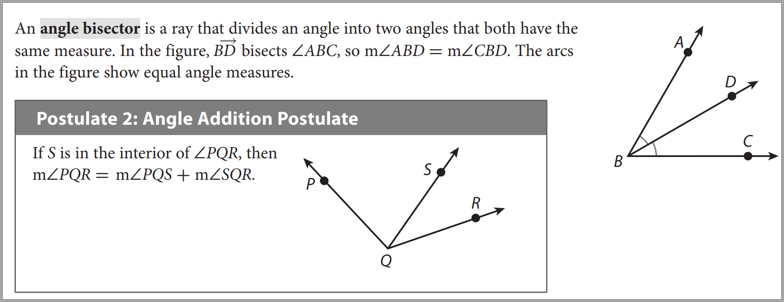 |
Click on the link to watch the video "Angle Addition Postulate - Additional Examples".
Let's Practice
Find the missing angle measurement using the angle addition postulate.
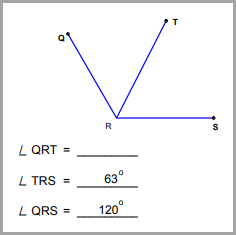 |
Find the missing angle measurement using the angle addition postulate.
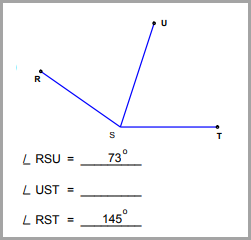 |
 |
 Click on the BrainPOP icon to watch a video on Angles. Click on the BrainPOP icon to watch a video on Angles. |
 Click on the icon to the left to complete the BrainPOP Quiz. Click on the icon to the left to complete the BrainPOP Quiz. |