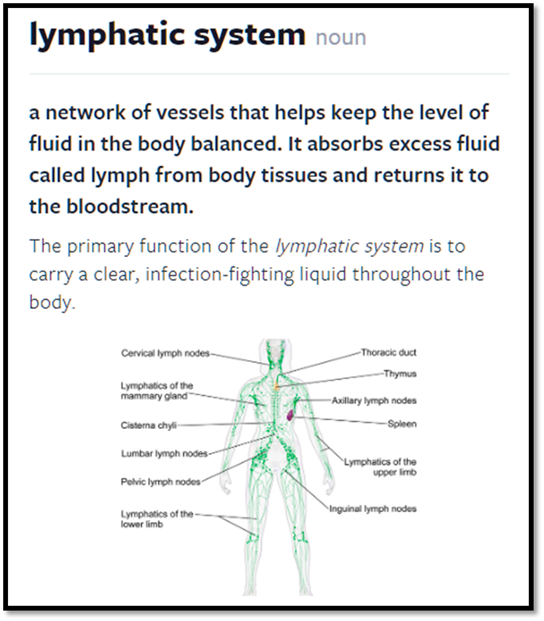
The Lymphatic System

Learning Objectives
Identify and describe the major structures and functions of the lymphatic
system.
Describe the lymphatic system's role in protecting against the spread of
disease and cancer.
Promote strategies for maintaining healthy cardiovascular and lymphatic
systems.
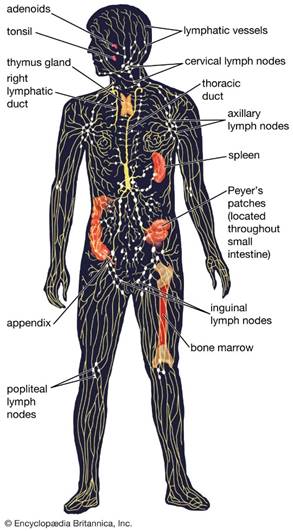
The lymphatic system,
an integral immune system component, regulates bodily fluid levels and
safeguards the body against infectious agents. It comprises a comprehensive
network of minuscule lymphatic vessels, which facilitate the drainage of lymph
fluid from various body regions. Lymph is a transparent, aqueous fluid enriched
with proteins, salts, and other vital substances.
| Click on the image below to watch the video. |
 |
“Science in Progress: The Lymphoid System.” Discovery Education, Discovery Education, 2014, https://app.discoveryeducation.com/learn/videos/5f378659-6854-4c74-a363-b422ba96f934 |
Key constituents of the lymphatic system are as follows:
1.
Lymph: A clear
fluid that circulates throughout the lymphatic system.
2.
Lymph Nodes:
Small, bean-shaped structures that produce and store cells that fight
infection.
3.
Lymphatic Vessels: The network of channels through which lymph flows.
4.
Collecting Ducts: The larger vessels into which smaller lymphatic vessels drain.
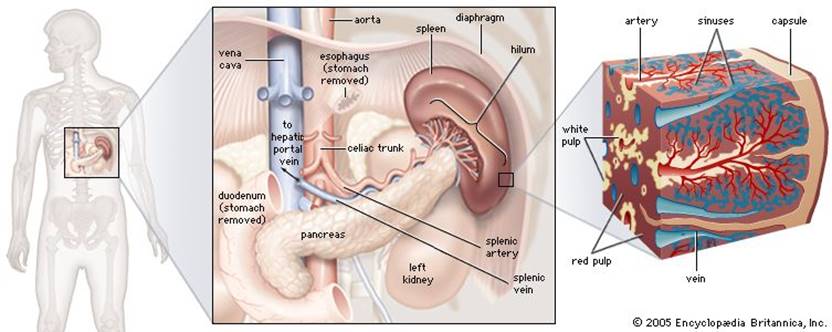
5.
Spleen: An
organ that filters and stores blood and produces white blood cells.
6.
Thymus: A
gland situated in the chest that aids in T-cell development.
7.
Tonsils and Adenoid: Lymphoid tissues are located in the throat and behind the nasal
passages.
8.
Bone Marrow:
The soft tissue where blood cell production occurs inside bones.
9.
Appendix: A
small, tube-like organ attached to the large intestine that has roles in immune
function.
The Role of the Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system is pivotal in fortifying the body
against pathogens, including
viruses, bacteria, and fungi, that can lead to diseases. Within this system,
the lymph nodes serve as filters, trapping these harmful agents. Surgical
lymphocytes, T-cells, and B-cells reside inside the lymph nodes, contributing significantly to the
body's defensive mechanisms. B-cells are responsible for synthesizing
antibodies, unique proteins designed to confine and neutralize infectious
agents, thereby preventing the propagation of infections. On the other hand,
T-cells actively migrate to the site of an infection to participate in its
neutralization.
| Click on the image below to watch the video. |
 |
“Humoral Immune Response.” Discovery Education, FortunaPix, 2018, https://app.discoveryeducation.com/learn/videos/79d00e97-eca8-44bb-8361-0cc427cb6870 |
When an individual contracts an infection, the pathogens
accumulate in the lymph nodes,
resulting in noticeable swelling. For instance, an infection in the throat can enlarge
lymph nodes in the neck region. Consequently, during medical evaluations for
throat-related ailments, physicians often assess for enlarged lymph nodes,
colloquially referred to as swollen "glands," especially when a
patient presents with symptoms such as a sore throat.
| Click on the image below to watch the video. |
 |
“Sick: Here's What Makes Measles So Dangerous.” Discovery Education, Seeker, 2019, https://app.discoveryeducation.com/learn/videos/379a39db-b688-444c-b017-6cdfa4483da6 |
Furthermore, certain immune cells possess the capability to
discern and eliminate cancerous cells due to their aberrant nature. However,
this intrinsic ability might not be sufficient to eradicate cancer. To address
this limitation, recent therapeutic innovations endeavor to harness and augment
the body's immune system's capacity to combat cancer more effectively.
Produced by
white blood cells, antibodies are proteins that help protect the body from
foreign substances like bacteria and viruses.
"Blood
vessel with antibodies." Discovery Education, Paul
Fuqua, 2004, https://app.discoveryeducation.com/learn/player/b4f351ad-c32a-4ec5-a2ed-031f4c813a87.
To Keep the Lymphatic System Strong and Healthy
Certain preventive and maintenance measures are crucial to
ensure the optimal functioning and longevity of the lymphatic system. Firstly, minimizing
exposure to environmental pollutants and potentially detrimental surroundings
is imperative. The reduction of contact with hazardous chemicals frequently
found in everyday products, such as pesticides and certain household cleaning
agents, is equally significant. An excessive buildup of these toxins in one's
system can impede the body's natural ability to filter and eliminate waste
efficiently. Another vital component for the health of the lymphatic system is
hydration. Regular and adequate water intake ensures that lymph fluid can
circulate effectively throughout the body, performing its essential functions.
Lastly, adopting a holistic approach to well-being, which includes a regimen of
regular physical activity and a balanced diet, can significantly bolster the
health and resilience of the lymphatic system.
Aspect
|
Description
|
Environmental Exposure
|
Minimize interaction
with environmental pollutants and harmful surroundings. Avoid hazardous
chemicals, often found in items like pesticides and household cleaners.
|
Hydration
|
Drink an ample amount of water
consistently. Proper hydration facilitates efficient circulation of lymph
throughout the body.
|
Holistic Well-being Approach
|
Adopt a comprehensive
lifestyle approach, emphasizing regular physical activity and a balanced
diet. This will ensure the overall health and efficiency of the lymphatic
system.
|
Lymphatic System:
Protecting Against Disease and Cancer
The human body is a complex and intricate network of systems
working in tandem to maintain optimal health and defend against potential
threats. One of the key players in this defense mechanism is the lymphatic
system, which plays a critical role in protecting against the spread of disease
and cancer. This system, consisting of lymph nodes, lymph vessels, and various
types of cells, works tirelessly to filter out and destroy harmful germs and
abnormal cells. In this section, you will delve deeper into the lymphatic
system's structures, functions, and significance.
The lymphatic system comprises numerous components, one of
the most crucial being the lymph nodes. These small, bean-shaped structures act
as filtration points, trapping germs like viruses, bacteria, and fungi that can
cause illnesses. When an infection occurs, germs collect in the lymph nodes,
leading to swelling – a phenomenon often observed by doctors when checking for
infections, particularly in the throat area.
Lymphocytes: The Body's Protectors
Within the lymph nodes are two main types of lymphocytes:
T-cells and B-cells, which are instrumental in fighting off infections. B-cells
contribute by producing antibodies – specialized proteins designed to trap and
destroy disease-causing germs, preventing the spread of infections. On the
other hand, T-cells take a more direct approach, migrating to the site of the
infection to assist in its eradication.
The Lymphatic System and Cancer
In addition to defending against common germs, the lymphatic
system plays a role in identifying and combating cancer cells. Some immune
cells can recognize these abnormal cells and work to eliminate them. While this
may not always suffice in completely eradicating cancer, it forms the basis for
emerging treatments that aim to leverage the immune system in the fight against
this formidable disease.
Component
|
Function
|
Role in Disease
Prevention
|
Role in Cancer
Prevention
|
Lymph Nodes
|
Filter out germs and
debris from the lymph fluid.
|
Trap and destroy
infectious agents.
|
Swell when cancer cells
are present, aiding in early detection.
|
Lymph Vessels
|
Transport lymph fluid throughout
the body.
|
Facilitate the movement of immune
cells to infection sites.
|
Assist in the drainage of excess
fluids, potentially reducing tumor growth.
|
B-Cells
|
Produce antibodies to
neutralize harmful pathogens.
|
Prevent the spread of
infections.
|
Can produce antibodies
that target cancer cells.
|
T-Cells
|
Attack infected or abnormal cells
directly.
|
Destroy infected cells.
|
Recognize and kill certain types of
cancer cells.
|
Lymphocytes
|
A type of white blood
cell involved in the body's immune response.
|
Crucial for the adaptive
immune response.
|
Can recognize abnormal or
cancerous cells and initiate an attack.
|
In summary, the lymphatic system is vital to the body's
defense mechanisms, contributing to the fight against diseases and cancer. Its
complex network of lymph nodes, vessels, and cells works synergistically to
filter out harmful elements, ensuring the maintenance of a healthy internal
environment. By understanding the structures and functions of this system, you
can appreciate its significance in disease prevention and the promotion of
overall good health.
Application Activity
Click here to complete the Lymphatic System:
Protecting Against Disease and Cancer worksheet.
Interactive Activity
Click the
image below to complete the learning activity on the "Lymphoid System."