Equations with Variables
on Both Sides

Unit Objective
●
To solve equations with variables on both sides
Key Vocabulary
● Variable - a symbol (usually a letter) standing
in for an unknown numerical value in an equation or an algebraic expression. In
simple words, a variable is a quantity that can be changed and is not fixed.
● Solution - any value of the variable that
satisfies the equality. (It will be the answer to the equation)
● Constant term - a term without a variable. It is
simply just a number.
Solve with Variables on
Both Sides
To solve equations with variables on both sides,
collect the variable terms on one side and the constant terms on the other.
Example 1: Solve 15 – 2x = -7x. 15 – 2x = -7x Write the equation.
|
 |
Let's practice.
1) -3x
= 2x +20
 |
2) 2.5y – 6= 4.5y – 1
 |
Use the Distributive Property to Solve an Equation
Example 1: Solve -2(x – 5) = 6(2 – 0.5x). -2(x – 5) = 6(2 – 0.5x) Write the equation.
|
Let's practice.
1) 6(4
– z) = 2z
 |
2) 5(w – 2) = -2(1.5w – 5)
 |
Solving an Equation with No Solution
Example 1: Solve 3 – 4x = -7 – 4x. 3 – 4x = -7 – 4x Write the equation.
|
Let’s practice.
1) 2x + 1 = 2x – 1
 |
Solve an Equation with Infinitely Many Solutions
|
Solve |
Let’s Practice.
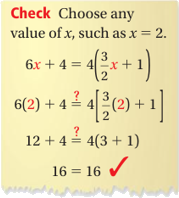
1) Solve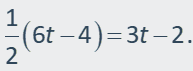
 |
Modeling in Real Life
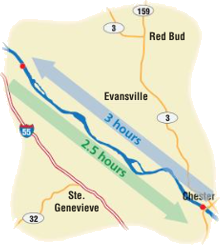
Example 1: A boat
travels x miles per hour upstream on the Mississippi River. On the
return trip, the boat travels 2 miles per hour faster. How far does the boat
travel upstream?
|
x(3) = (x + 2)(2.5) Write an equation.
The
boat travels 10 miles per hour for 3 hours upstream. |


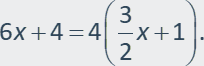
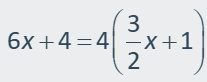

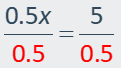
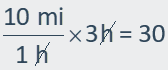 miles upstream.
miles upstream.