
Unit Overview
In this unit, students will be able
to:
·
Identify regular
polygons, as well as their individual interior angles.
·
Determine
missing angle values in polygons.
Key Concepts
·
Regular
polygons
·
Interior angle
sum of a polygon
·
Remote
Exterior Angle Theorem
Ohio’s Learning Standards
·
8.G.5 Use
informal arguments to establish facts about the angle sum and exterior angle of
triangles, about the angles created when parallel lines are cut by a
transversal, and the angle-angle criterion for similarity of triangles.
Calculators
·
Here is a link
to the Desmos scientific calculator that is provided for the Ohio State
Test for 8th Grade Mathematics in the spring.
·
You are
strongly encouraged to use the Texas Instruments TI-30XIIS handheld scientific
calculator. It is extremely user
friendly.
Polygons
·
In a previous unit, you learned this
information
·
Example A Table and images:
 |
·
Notice that
for the interior angle sum:
o It increases by 180° for ever side added, and
the number of triangles that
the polygon can be broken up into is 2 less than the number of sides
o If n = number of sides and S = sum of
the interior angles of a polygon, then
§ S = 180(n – 2) → 180 multiplied by 2 less than the number of sides
·
REGULAR POLYGON
→ see Example A set above
o Every side is equal (congruent) and every angle is
equal
o
Example B Set → irregular polygons
 |
§
For the rhombus, all sides are congruent (symbolized with
the same dash), but not all angles are congruent
(the opposite angle pairs are congruent, marked by the same single or double arcs)
§
For the hexagon, some sides and angles are congruent, but
not all.
o
Determining individual
interior angles of a regular polygon:
§
Sum of the interior
angles ÷ number of angles
§
Example C Set:
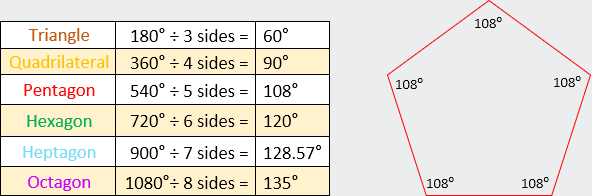 |
o
Determining missing
angles polygons in polygons: set up algebraic equations and solve
§
Example
D Set: solve
for the variable.
 |
 |
 |
||
5 sided figure: pentagon |
Right triangle |
Trapezoid Sum of angles = 360° 62+5x+12+122+58=360 5x+254=360 -254 -254 5x=106 ÷5 ÷5 x = 21.2 |
Further explanation and practice on polygons:
Let’s Practice:
Remote Exterior
Angle Theorem:
 |
Here is why this
theorem works: ∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180⁰
→ sum of the
angles in a triangle = 180°
∠D
+ ∠C
= 180⁰ → ∠D
and ∠C together
make a straight line = 180°
Thus, ∠A + ∠B = ∠D
Example E set: Determine the value of the variable(s):
 |
 |
Long method:
2nd: x + ? = 180 → they make a straight line |
y + 142 = 180 → they make a
straight line
-142 -142
x = 38
x
= 47
|
Short method → use the Exterior Angle Theorem OR
use interior angles: x = 180 – (95+38) =
47
sum of two remote
interior ∠s = external ∠
∠66
+ ∠44 = ∠x
110° = x
External
Angle Sums for Polygons → always =
360°
| Proofs: Triangle | Quadrilateral | Pentagon
|
||
 |
 |
 |
||
| all ∠s – interior∠s = exterior ∠s | all ∠s – interior∠s = exterior ∠s | all ∠s – interior∠s = exterior ∠s
|
||
| 540° – 180° = 360° | 720° – 360° = 360° | 900°– 540° =
360°
|
For further
explanation and practice on remote exterior angles:
Let’s Practice:
