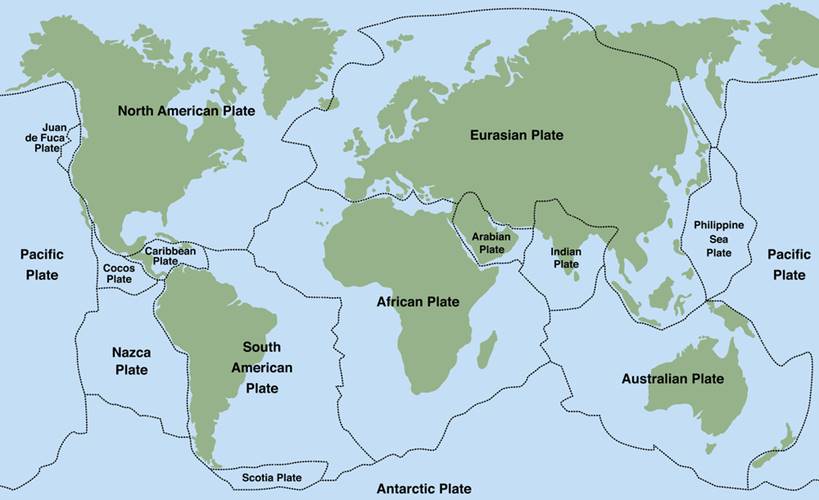
Plate
Tectonics
Introduces
the theory of plate tectonics, which states that the lithosphere is broken up
into tectonic plates that move gradually, causing Earth's features to shift.
Plate
boundaries are often observable in the forms of mountains, earthquakes, and
volcanoes.
There are
three types of plate boundaries, convergent, divergent, and transform,
classified by the direction of the plates' movements.
Introduction
Imagine watching a chick getting out of its
shell. The shell cracks and breaks apart as the chick comes out.
You could glue the shell pieces back together,
like a puzzle, and remake the eggshell, but it would have cracks.

Chick Getting Out of Shell
Look at the cracked egg puzzle and answer the
questions in your science journal.
1. Which piece could
finish the puzzle?
2. How did you figure out
which piece?
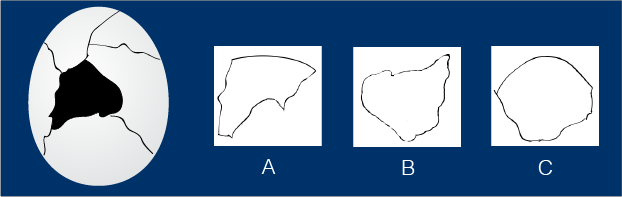
Cracked Egg
Tectonic
Plates
Scientists view Earth as a puzzle, with pieces
that were once together in a supercontinent. Continents drift because Earth's
crust is made up of large tectonic plates—like pieces of a
cracked eggshell that fit together. Tectonic plates are pieces of the lithosphere
that move over the asthenosphere.
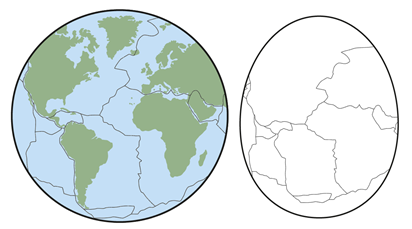
Earth's Tectonic Plates
(Like a Cracked Egg)
Some plates include continents and are
called the continental crust. Others are mostly under the ocean and are
called the oceanic crust.
·
Oceanic Plates
o From the floor of the
ocean
o Thin and mostly made of
dense basalt
·
Continental Plates
o Thicker and less dense
than oceanic plates
o Made of andesite and
granite
Look at the image showing Earth's tectonic
plates.
Earth's Tectonic Plates
Scientists discovered the plate edges by doing
magnetic ocean floor surveys and listening to seismic data. They
found that the seafloor is spreading, and continents have shifted.
In your science
journal,
answer these questions.
1.
Which tectonic plate is located at the bottom of the oceans?
2.
Which tectonic plate is the thick part of the Earth's crust which
forms the large land masses?
3.
Which tectonic plate has a lower density?
4.
Which tectonic plate is thinner and younger?
5.
Which tectonic plates are rarely destroyed?
Plate
Boundaries
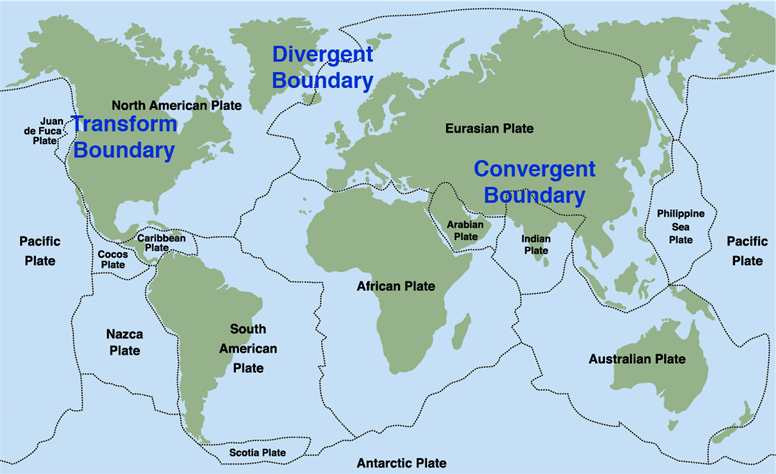
Tectonic Plates Boundaries
One reason tectonic plates
move is that molten rock just below Earth's surface is always moving. Hotter
material rises to the surface, while cooler material sinks towards Earth's
core. Plates move slowly in many directions. At the boundaries where two plates
meet, some plates move toward each other, some move apart, and some slide past
each other. The three main boundary types are:
convergent, divergent, and transform.
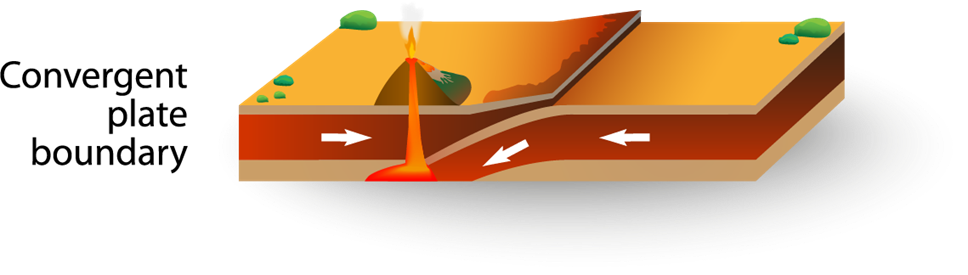
Convergent Boundary
Plates bump into each other. The thicker plate
goes over the top of the thinner plate in a process called subduction. The
thinner plate begins to melt, which makes magma go over the plate. An example
of this type of boundary is the Himalayas mountain range connecting the Indian
and Eurasian tectonic plates. These plates are colliding and have been doing so
for 40 or 50 million years—which is why the mountain range rose. Tsunamis can
form when subduction at convergent boundaries causes an earthquake in the
ocean.
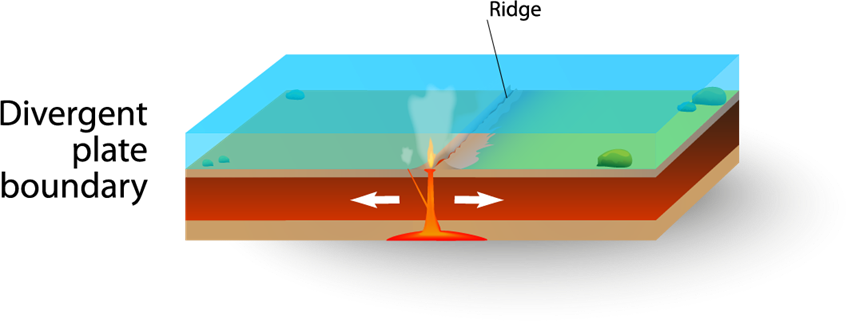
Divergent Boundary
Plates move apart, making a rift between them.
On land, this rift can cause an earthquake. In the ocean, magma flows into the
rift and hardens, making more crust on the seafloor. This is called seafloor
spreading. Iceland has a divergent boundary formed from the Mid-Atlantic Ridge.
The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is usually beneath the ocean, but Iceland is one of the
few places above the ocean (and you can stand on it). Millions of years ago,
Iceland formed from the eruptions of volcanoes at the ridge.
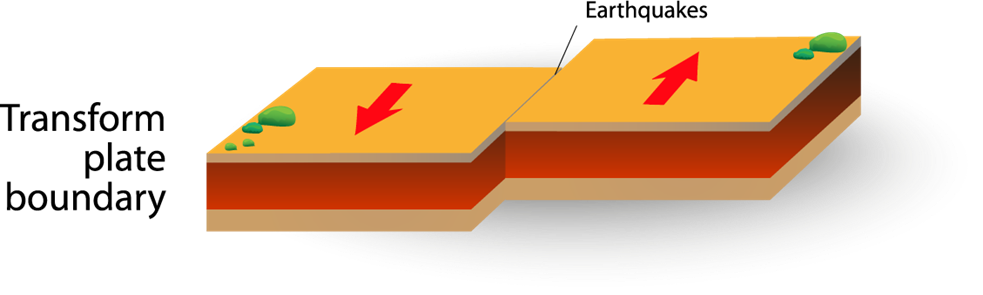
Transform Boundary
Plates slide next to each other. Transform
boundaries are usually found in the ocean but can be on land. Two plates
sliding against each other can make a lot of energy—so much so that sometimes
it makes an earthquake. This happened on land in 1906 at the San Andreas Fault
south of San Francisco, California, where a huge earthquake collapsed
buildings, started fires, and killed over 600 people.
In your science
journal, identify the plate
boundary.
1.
A thicker plate goes over
the top of a thinner plate at this boundary.
2.
This type of boundary
makes more crust on the seafloor—called seafloor spreading.
3.
The San Andreas Fault in
California is at this type of boundary.
Let’s Practice