The Building
Blocks of Life

A
family welcomes its newest member.
©
Ariel Skelley—Digital Vision/Getty Images
Introduction
Have you ever been told that you have your
mother's eyes? Or maybe your father's hair? Or your grandmother's chin? What do
you think people mean when they say something like that?
Think of characteristics of your mother, father,
or any family member that you share with them.
In your science journal, answer the following questions.
1.
What are some similar traits that you have with a family member?
2.
What are some different traits that you have with a family
member?
3.
What do you mean when people say you look like your father or
mother?
Deoxyribonucleic
Acid (DNA)
Deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA, is a tiny molecule that is the blueprint for all life. To make
the complex organism YOU, you got half of your DNA instructions from
your mother and a half from your father.
All living things,
including things that were once living, contain DNA. Everything from
microscopic bacteria to towering trees, huge blue whales, and small insects contain
DNA. Even woolly mammoth fossils still contain DNA that we can study now,
thousands of years after they died!
Proteins help form cells; each cell stores an organism's
DNA within its nucleus. Complex living organisms can cram so much information,
or genetic material,
inside every cell.
In your science journal, answer the following questions.
1.
What comes to your mind when you hear the word "DNA?"
2.
What comes to your mind when you hear the word "protein?"
Let's explore how DNA is contained in a cell
with a nucleus called a eukaryotic cell by looking at the image below.
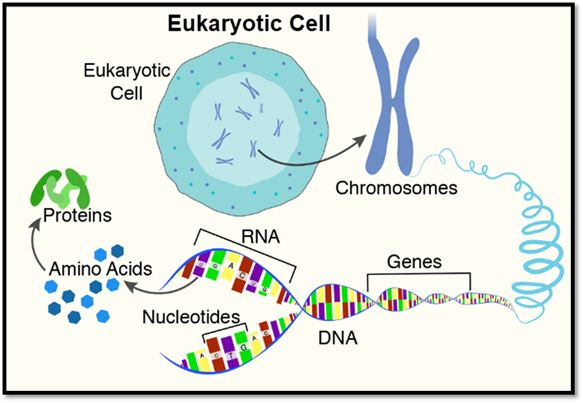
The image above shows the
genetic parts of the eukaryotic cell.
Eukaryotic
Cell
Eukaryotic cells are found in almost
all living organisms. They hold genetic material, or DNA, within the
nucleus.
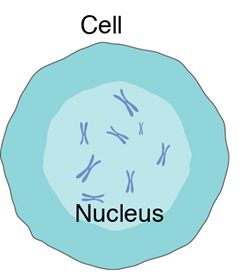
Eukaryotic Cell
Chromosomes
Genes are tightly packed into pairs of
structures called chromosomes. The
job of chromosomes is to help keep the DNA within each cell. The structure of
chromosomes keeps DNA wrapped tightly around a protein called histone.
This complete instruction book of genes, or genome, for a human, contains 23 pairs
of chromosomes, for a total of 46.
Twenty-two of these pairs looks the same in
both males and females. However, the 23rd pair—the sex chromosomes—is
different. Females have two copies of the X chromosome, while males have one X chromosome and one Y chromosome.
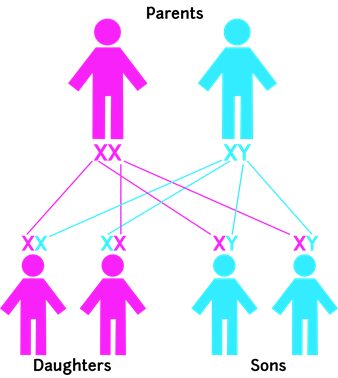
A human embryo gets 23 chromosomes from its
mother and 23 from its father. The genetic
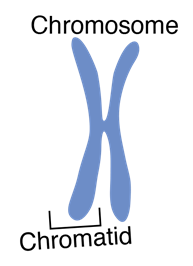
code is passed down from biological parents to offspring. Each chromosome
has two identical strands, called chromatids,
joined together.
Sometimes errors happen when chromosomes are
passed down, and the offspring gets more or fewer chromosomes. This can affect
how an individual looks and behaves. Down
syndrome is one example of a chromosomal condition. Children born with Down
syndrome have an extra copy of chromosome #21, creating a total of 47
chromosomes, and they often have delays in their development.
In your science
journal, answer the following questions.
1.
What is the job of chromosomes?
2.
How is the 23rd pair of chromosomes different for males and
females?
Genes
A gene
is a basic unit of information made out of strands of DNA. It controls how
offspring develop different traits from the mother and father. For example, one
gene could dictate how your eyes look while another may decide how your face is
shaped.
For example, one gene could dictate how your
eyes look while another may dictate how your face is shaped.
Every person has two copies of each gene, one
inherited from each biological parent. Different forms of a gene are called alleles, which is why each person looks
unique. Different alleles, for instance, produce different hair colors, such as
brown, blonde, red, and black.
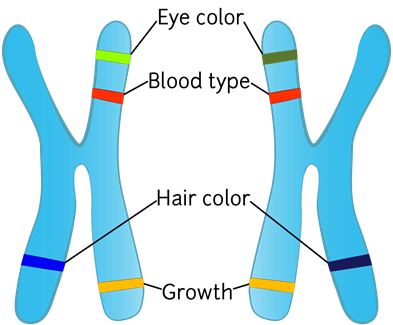
Gene Alleles
In your science journal, answer the following questions.
1.
What is a gene?
2.
Why does each person look unique?
DNA
DNA is the hereditary material in humans and
almost all other organisms. It contains the instructions for developing,
growing, and reproducing. If all the DNA from one human cell were unraveled and
put on end to end, it would be about six feet long.
DNA is made of four types of bases: adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G),
and thymine (T). These bases go
together to form base pairs. The sequence of base pairs in each part of the DNA
molecule is called a gene, and genes decide how organisms will develop.
Most DNA is in the nucleus of cells throughout
an organism.
DNA has two important properties:
- DNA
can be copied
- DNA
can store information
The double helix shape of the DNA molecule
looks like a twisted ladder. Because of this shape, DNA can make exact copies
of itself and pass biological instructions from old to new cells. The
information stored in DNA is needed for building and maintaining all parts of
an organism.
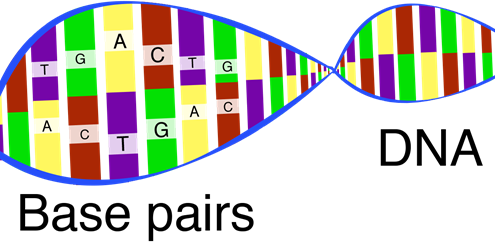
DNA
In your science journal, answer the following question.
1.
What are the two important properties of DNA?
RNA
Ribonucleic acid, or RNA, is a single-stranded molecule that acts like a messenger to
move genetic information stored in the DNA in a cell to other parts of the
cell. RNA gives parts of the cell the blueprints for building proteins.
The structure of RNA is similar to that of DNA.
But instead of having A, C, G, and T, RNA has A, C, G, and U. RNA has uracil
(U) instead of thymine (T).
RNA molecules carry genetic information using
the A, C, G, and U codes. RNA makes a copy of part of the DNA, and this strand of
RNA has a unique code that parts of the cell can read to create different
proteins. This process is called transcription.
RNA
In your science journal, answer the following question.
1.
What are some differences between RNA and DNA?
Nucleotides
The basic building block of DNA is called a nucleotide. Each nucleotide comprises six molecules: one sugar molecule, one
phosphate molecule, and one of four bases (A=adenine, T=thymine, C=cytosine,
and G=guanine). The order of nucleotide bases (A, T, G, and C) along the DNA
strand is like a recipe that tells the organism how to develop itself,
including all of its cells, tissues, and organs. This constitutes the genetic
code.
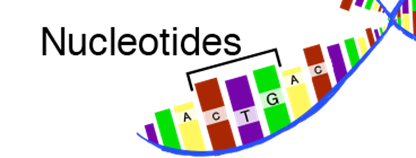
Nucleotides
In your science
journal, answer the following
questions.
1.
What are four types of bases found in nucleotides?
2.
How is the order of these bases like a recipe?
Amino
Acids
Proteins are the most common
substances in humans and other animals, and they are needed to build and repair
cells and tissues. Amino acids form proteins. Different combinations of amino
acids make up different proteins.
There are 20 types of amino acids, and they can
be put into many different orders. For example, the protein pepsin is a chain
of about 320 amino acids. Antibodies are made of different combinations of
amino acids to fight different bacteria and viruses.
Humans can naturally make 10 of the 20 amino
acids in their bodies. To get the other ten amino acids, people can eat foods
with proteins that have these amino acids.
Amino Acids
In your science
journal,
answer the following question.
1.
What role do amino acids play in your body?
Proteins
Proteins are necessary for most life on Earth.
They can be thought of in two different ways—as nutrients (which you can get from food that contains protein) or as
large molecules that do many jobs
within an organism.
Proteins are made of amino acids. Amino acids can be formed into proteins inside cells,
and they help carry out tasks under the direction of genes.
Without proteins, which do most of the work in
our bodies, most organisms would not be able to function correctly. The body
uses proteins to build and repair itself. Pepsin is a protein that helps your
body digest and breaks down food. Antibodies are proteins your immune system
uses to fight bacteria and viruses that can make you sick.
Proteins are the most common substances in humans
and other animals and are even found in plants. Proteins in foods help the body
build bones, muscles, skin, and blood. The body breaks down proteins found in
animals or plants into amino acids, then reuses the amino acids to form
different proteins

Proteins
In your science journal, answer the following questions.
1.
What do proteins do?
2.
What are some specific examples?
Let's Practice