Extinction
of Living Things
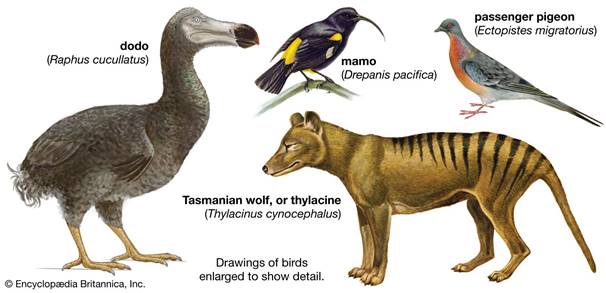
Some
species are made extinct by humans.
What is
extinction?
Extinct means there isn't
any of that type of living thing left alive. It does not exist on the Earth
anymore.
Extinction occurs when the
environment changes and the adaptations of a species are no longer sufficient
for its survival.
Changes may include:
·
Increased competition with other species
·
Newly-introduced predators
·
Loss of habitat
·
Catastrophes
Based on the fossil record, extinction of a
species occurs when the environment changes and the individual organisms of
that species do not have the traits necessary to survive and reproduce in the changing
environment. Most species (approximately 99
percent) that have lived on Earth are now extinct.
In your science
journal, answer the following
questions.
1.
Write down a phrase that has the same meaning as "extinction."
2.
What is a "predator?"
3.
What is another word for "habitat"?
4.
Give two examples of "catastrophes."
Mass
Extinction
Although extinction is an ongoing feature of
the Earth, the fossil record reveals the occurrence of several unusually large
extinctions, each involving the demise of vast numbers of species. These
conspicuous declines in diversity are referred to as mass extinctions; they are distinguished from most extinctions,
which occur continually and are referred to as background extinctions.
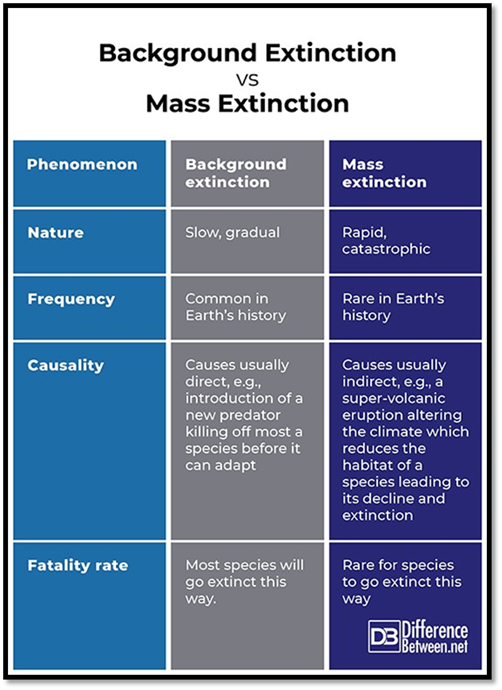
In your science
journal, identify each item as either Mass or
Background.
1.
Rapid.
2.
Most species will go extinct this way.
3.
Common in Earth's history.
4.
Slow, gradual.
5.
New predator killing off a species
The greatest mass extinction in Earth's history
occurred about 266 million to 251 million
years ago. This event is known as the Permian
extinction. The Permian extinction was characterized by eliminating some 95
percent of marine species and about 70 percent of land species. The cause of
the Permian extinction is not known with any certainty.
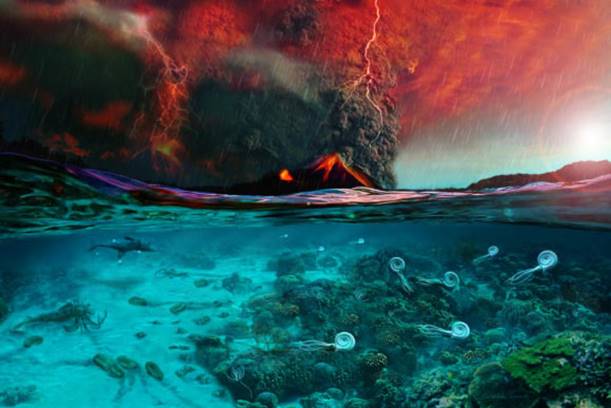

Figure 1Image credit: Dawid
Adam Iurino / PaleoFactory,
Sapienza University of Rome
An illustration depicting
the onset of the end-Permian mass extinction.
Animal Extinction
The dodo once lived on
Mauritius, an island in the Indian Ocean. Europeans took control of the island
in the 1500s and began to hunt the bird. By 1681 the dodo was extinct.
Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.
The dodo bird is an example of how human
impact may contribute to extinction. The dodo bird was first seen around the
1600s on an island in the Indian Ocean. It was a flightless bird with a stubby body and tiny wings. Fossil records
suggest that the dodo bird evolved from a bird capable of flight. When an ancestor of the dodo bird land on the
Indian Ocean island, it found a habitat with plenty of food and no predators.
It did not need to fly and eventually evolved into a flightless bird.

Dodo bird was flightless (could
not fly)
Cause
The dodo bird was extinct less than 80 years
after its discovery. Some of the birds were eaten by Dutch sailors who
discovered them. Also, domestic pigs and cats destroyed their nests built on the
ground. The main cause of their extinction was the human destruction of their habitat.
Reason
One reason the dodo bird may have become
extinct is the lack of genetic variation. As a species population gets smaller,
its genetic variation may decrease.
Natural selection requires genetic variation. A small population may be more
susceptible to extinction than a large population if their environment changes.
If the genetic variation is not present, the population may not have enough favorable
adaptations to survive environmental changes. Scientists study extinctions like
the dodo bird in the hope of preventing future extinctions.
In your science journal, answer the following questions.
1.
What does flightless mean?
2.
Did the dodo bird ever fly?
3.
Did the dodo bird have any predators before humans came to the
island?
4.
What happens when the species population gets smaller?
Plant
Extinction
When the first living things appeared on Earth
more than 3 billion years ago, the environment was much different from how it
is today. Only simple life-forms composed of a single cell were present. These
organisms had to carry out their life
processes without oxygen, though the early Earth atmosphere did contain
large quantities of nitrogen, carbon dioxide, methane, and ammonia. Scientists
believe that very slow chemical reactions in the shallow seas of primitive
Earth were the only source of food to fuel early ecosystems.

A fossil formed from part
of an extinct treelike club moss of the genus Liriodendron.
Louise K. Broman—Root Resources/Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.
The evolution of the first plants initiated
many changes in Earth's environment. Photosynthesis,
how plants, algae, and some bacteria use light energy to make food from carbon
dioxide and water, produced molecular oxygen (O2), which supported
future life forms that relied on aerobic respiration. Plants and other
photosynthetic organisms themselves provided food for the animals that evolved
later. During the long course of plant evolution, fossil plant
material accumulated to form the fossil fuels upon which modern society
depends.
Over the more than 400 million years of the
evolution of plants, many different species have appeared. Certain species
disappeared or became extinct as new forms arose that were better adapted to
Earth's changing environment. This evolutionary change process has produced a
diverse array of plant species today. Recently, rapid environmental changes,
caused primarily by various human activities, have killed or threatened some
plants, and scientists and conservationists are working hard to protect endangered species from extinction.

Figure 2. Photograph: Marco Longari/AFP/Getty
Images
One of the biggest factors
threatening plant species is the destruction of habitats,
including farming, such as
palm oil production (pictured) and cattle ranching.
In
your science journal, answer the following questions.
1. Did the first plants
that lived on Earth use oxygen?
2. Describe
photosynthesis.
3. What are fossil fuels?
4. Give two examples of how
humans can be the cause of plant extinction.
Let's Practice