Geometry Exam II

(The following sections
will be covered in the exam)
Section A: Classify Quadrilaterals
All quadrilaterals are polygons that have four sides
and four angles. Some common types of quadrilaterals are rectangles, squares,
parallelograms, rhombuses, and trapezoids.
Key Vocabulary
Parallel: if two straight lines are parallel, they stay
the same distance from each other, and they never cross or meet
Angle: is a
figure formed by two lines starting at the same point. Angles are measured in
degrees.
Congruent: equal in shape or size
Parallelogram: a
quadrilateral with opposite sides that are equal in length and parallel
Rhombus: a shape that has four straight sides of equal
length but usually does not have right angles
Trapezoid: a shape with four sides of which only two are
parallel
Click
Step by Step to complete the learning module.
Section B: Area of a Triangle
A triangle is a polygon with three sides, and the
area measures the number of square units inside a polygon. Learn this formula,
and you will have no trouble finding any triangle’s area.
Key Vocabulary
Area: the amount of surface in a given boundary,
measured in square units
Triangle: a closed shape with three straight sides and
three angles
Click
Step by Step to complete the learning module.
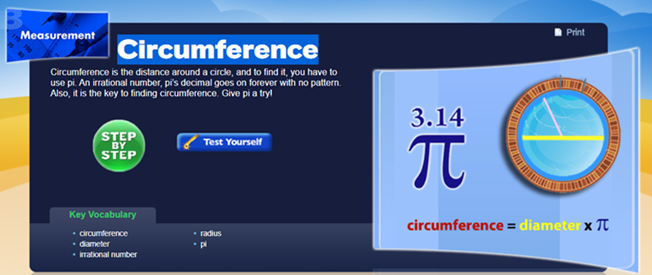
Section C: Circumference
The circumference is
the length of the outer edge of a circle; to find it; you have to use the pi.
An irrational number, pi’s decimal, goes on forever with no pattern. Also, it
is the key to finding circumference. Give pi a try.
Key Vocabulary
Circumference: the outer edge of a circle, or more
precisely, the length of the edge
Radius: a straight-line segment drawn from the center
of a circle to its outer edge
Diameter: a straight line through the center of a
circle, from one side to another
Pi: in math, a symbol for the ratio of the
circumference of a circle to its diameter
Irrational number: a number that never ends or terminates
Click Step by Step to complete the learning module.
Section D: Units of Measurement
There are two major measurement systems of the
U.S. customary system and the metric system. Measurement systems are essential
because they ensure that measurements are consistent. Capacity, length, weight,
mass, and temperature are commonly measured.
Key Vocabulary
Capacity: the amount that a container can hold
Length: the distance from one end of something to the
other
Weight: the force of gravity of an object’s mass
Mass: the amount of physical matter an object
contains
Click Step by Step to
complete the learning module.