Aerobic
and Anaerobic
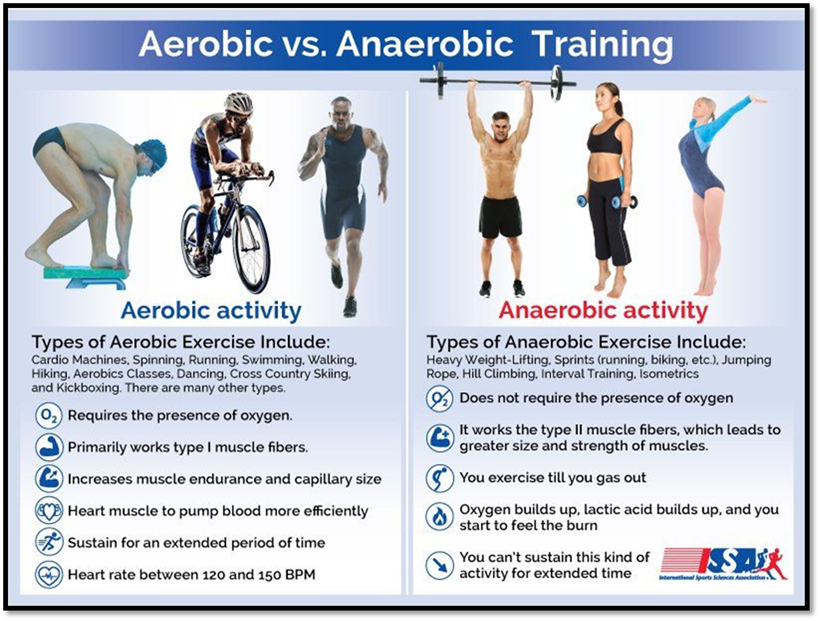
Aerobic exercise is any cardiovascular conditioning or “cardio.” During cardiovascular conditioning,
your breathing and heart rate increase for a sustained period of time. Examples
of aerobic exercise include swimming,
laps, running, or cycling.
Oxygen is your primary
energy source during aerobic workouts.
You breathe
faster and deeper during aerobic exercise than when your heart rate is at rest.
You’re maximizing the amount of oxygen in the blood. Your heart rate increases
blood flow to the muscles and back to the lungs.
Aerobic
exercise can offer numerous benefits for your health, including reducing
your risk of a heart attack, type 2 diabetes, or stroke.
Other
benefits of aerobic exercise include:
- can
help you lose weight and keep it off
- may
help lower and control blood pressure
- may
increase your stamina and reduce fatigue during exercise
- activates
immune systems, making you less likely to get colds or the flu
- strengthens
your heart
- boosts
mood
- may
help you live longer than those who don’t exercise
Anaerobic
Anaerobic exercises involve quick bursts of energy and are performed at maximum effort for a short
time. Examples include jumping, sprinting,
or heavy weight lifting.
During
anaerobic exercise, your body requires immediate energy. Your body relies on stored energy sources rather than
oxygen to fuel itself. That includes breaking down glucose.
Benefits
of anaerobic exercise
Anaerobic
exercise can be beneficial if you’re looking to build muscle or lose weight. It
can also be beneficial if you’ve been exercising for a long time and are
looking to push through an exercise plateau and meet a new goal. It may also
help you maintain muscle mass as you age.
Other
benefits include:
- strengthens
bones
- burns
fat
- builds
muscle
- increases
stamina for daily activities like hiking, dancing, or playing
Fitness
NFL
PLAY 60: Huddle up and Get Moving!
Complete all the exercises by
watching the video above to complete your Fitness Logs.
Below is a chart of other exercises you
can complete for your Fitness Logs.
Name and Description of Physical Activity
|
Picture
|
Type of Physical Activity
|
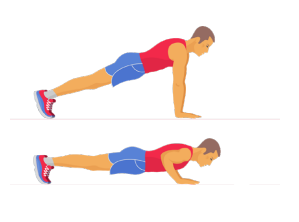
Push-up: an activity in which a person
lies facing the floor and, keeping their back straight, raises their body by
pressing down on their hands
|
|
Strengthening
|
Plank: an activity that involves
maintaining a position similar to a push-up, but usually without any movement
|
|
Strengthening
|
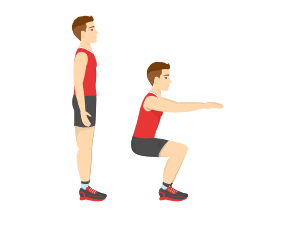
Squat: An activity that requires
squatting toward the group with the back of the knees at a 90-degree angle
|
|
Balance/Flexibility
|
Jumping jack: a jump is done from a standing
position with legs together and arms at the sides to a position with the legs
apart and the arms over the head
|
|
Balance/Flexibility
|
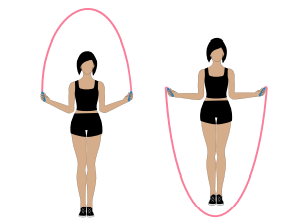
Jump rope: An activity that requires jumping
straight up into the air and back down, as if jumping over a rope.
|
|
Balance/Flexibility
|
High knees: An activity in which a person lifts
their knees as high as possible, alternating left and right
|
|
Aerobic
|
Kickers: An activity in which a person jogs
in place, hitting their behind with their feet
|
|
Aerobic
|