
TYPES
OF PARAGRAPHS
Depending on the purpose for writing, a writer must develop one of the four types of paragraphs: expository (to explain or inform), persuasive (to persuade), descriptive (to describe), or narrative (to tell a story).
The Persuasive Paragraph
 The
persuasive paragraph is an attempt by the writer to convince the audience
(readers) to agree with an opinion on a debatable issue or to perform a
specific action. The writer uses details, facts, or examples to form his
argument. The argument should be a direct, precise, logical presentation of the
issue. The persuasive paragraph answers “why” questions – Why should the reader
agree? - Why should the reader do what the writer asks?
The
persuasive paragraph is an attempt by the writer to convince the audience
(readers) to agree with an opinion on a debatable issue or to perform a
specific action. The writer uses details, facts, or examples to form his
argument. The argument should be a direct, precise, logical presentation of the
issue. The persuasive paragraph answers “why” questions – Why should the reader
agree? - Why should the reader do what the writer asks?
The purpose of this type of writing is to convince the reader to accept a particular point of view or to take a specific action. If it is important to present other sides of an issue, the writer does so, but in a way that makes his or her position clear. The unmistakable purpose of this type of writing is to convince the reader of something. In well-written persuasion, the topic or issue is clearly stated and elaborated as necessary to indicate understanding and conviction on the part of the writer.

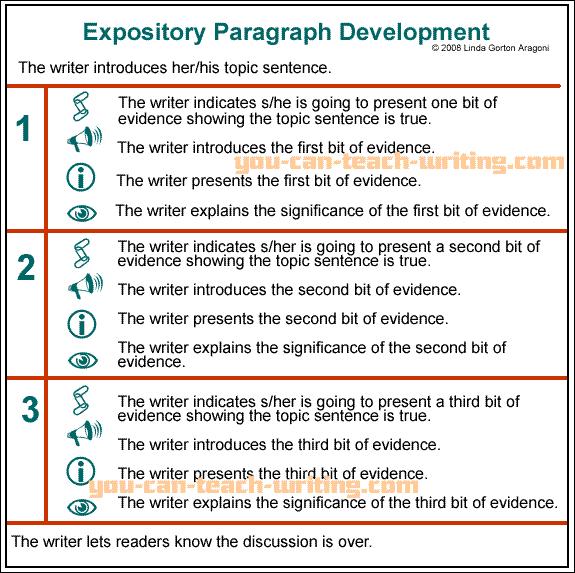
The Expository Paragraph
 The
expository paragraph is a paragraph that explains or informs. The writer must
identify the topic and the purpose for writing. The information is arranged in
the order which best develops the topic. Details, facts, examples incidents,
similarities, differences, etc. are included to explain the topic.
The
expository paragraph is a paragraph that explains or informs. The writer must
identify the topic and the purpose for writing. The information is arranged in
the order which best develops the topic. Details, facts, examples incidents,
similarities, differences, etc. are included to explain the topic.
Sample
Expository Paragraphs
Today the P.E. teacher talked with our class about
physical fitness. In fact, she said it is important to exercise at least an
hour every day. Exercise doesn’t have to be a chore. For instance, riding a
bike is great exercise. Roller-skating is, too. So, find an activity you enjoy
and get some exercise!
I made a plan for getting enough sleep at night. After I
eat supper I play for a while. Then I take a warm bath. When I finish bathing,
I put on my pajamas and climb in bed. Finally, I read a good book. Reading
makes me sleepy and I usually fall right to sleep.
It is important to stay clean. If you don’t take regular baths germs can grow easier in cuts or sores. In fact, sometimes you have to use medicine to kill the germs. Also, if you don’t take regular baths you might not smell so good. As a result, your friends might not want to play with you. Staying clean helps you stay healthy and happy.
What
to consider when writing an expository essay:
- What process are you trying to explain? Why is it important?
- Who or what does the process affect?
- Are there different ways of doing the process? If so, what are they?
- Who are the readers? What knowledge do they need to understand this process?
- What skills/equipment are needed for this?
- How long does the process take? Is the outcome always the same?
- How many steps are there in the process?
- Why is each step important?
- What difficulties are involved in each step? How can they be overcome?
- Do any cautions need to be given?
- Does the process have definitions that need to be clarified?
- Are there other processes that are similar and could help illustrate the process that you are writing about?
- If needed, tell what should not be done or why something should be done.
- Expository papers are often written in the second person (you), but some teachers prefer that you avoid this.
The Descriptive Paragraph
The descriptive paragraph is a piece of writing that develops a “picture” of one idea by using sensory (ones that appeal to the senses) or concrete (ones that represent things seen or touched) details. The topic sentence reveals the main impression of the topic by using only those details that enhance the single idea.
A Descriptive Essay is used to create a vivid image of a person, place, or thing. It draws on all of the senses, not merely the visual. Its purpose is to enable the reader to share the writer's sensory experience of the subject. For instance, see the picture of Old Faithful erupting. You could describe what you see for the reader.

Picture of Old
Faithful
Descriptive writing portrays people, places, things, moments and theories with enough vivid detail to help the reader create a mental picture of what is being written about.
Things
to Consider as You Write Your Descriptive Essay
- Think of an instance that you want to describe.
- Why is this particular instance important?
- What were you doing?
- What other things were happening around you? Is there anything specific that stands out in your mind?
- Where were objects located in relation to where you were?
- How did the surroundings remind you of other places you have been?
- What sights, smells, sounds, and tastes were in the air?
- Did the sights, smells, sounds, and tastes remind you of anything?
- What were you feeling at that time?
- Has there been an instance in which you have felt this way before?
- What do you want the reader to feel after reading the paper?
- What types of words and images can convey this feeling?
- Can you think of another situation that was similar to the one you are writing about? How can it help explain what you are writing about?
- Is there enough detail in your essay to create a mental image for the reader?
The Narrative Paragraph
The narrative paragraph is a piece of writing intended to tell a story, real or imaginary. The narrative paragraph may entertain, or it may make a point. Narrative paragraphs do not always contain topic sentences. Details in a narrative paragraph are obtained by using the Who? What? When? Where? Why? How? method of questioning and should be arranged in chronological (the order in which they happened) order.
A Narrative paragraph tells a story. It has character, setting, and action. The characters, the setting, and the problem of the narrative are usually introduced in the beginning. The problem reaches its high point in the middle. The ending resolves the problem.

The purpose of this type of writing is to recount a personal or fictional experience or to tell a story based on a real or imagined event. In well-written narration, a writer uses insight, creativity, drama, suspense, humor, or fantasy to create a central theme or impression. The details all work together to develop an identifiable story line that is easy to follow and paraphrase.
The narrative approach, more than any other, offers writers a chance to think and write about themselves. We all have experiences lodged in our memories which are worthy of sharing with readers. Yet sometimes they are so fused with other memories that a lot of the time spent in writing narrative is in the prewriting stage.
In this stage, writers first need to select an incident worthy of writing about and, second, to find relevance in that incident. To do this, writers might ask themselves what about the incident provided new insights or awareness. Finally, writers must dredge up details which will make the incident real for readers.
Principles
of Writing Narrative Paragraphs
Once an incident is chosen, the writer should keep three principles in mind.
- Remember to involve
readers in the story. It is much more interesting to actually recreate
an incident for readers than to simply tell about it.
- Find a generalization
which the story supports. This is the only way the writer's personal
experience will take on meaning for readers. This generalization does
not have to encompass humanity as a whole; it can concern the writer,
men, women, or children of various ages and backgrounds.
- Remember that although the main component of a narrative is the story, details must be carefully selected to support, explain, and enhance the story.
PRACTICE EXERCISE- read each of the
following paragraph topics and determine which type of paragraph would be
suitable for the topic. Write P for persuasive; N for narrative; E for expository; and D for descriptive.
 Now answer questions 1-15
Now answer questions 1-15
No matter what type of paragraph, the writer must remember to use the steps of the writing process. Thoughts, details, ideas, etc. must be in logical order and tied to the topic sentence. In addition, the rules of grammar, spelling and punctuation must be applied. The more one writes, the better the writing becomes.
|
5 Steps to the Writing Process |
|
Prewriting: Organize
your thoughts before you begin to write. Brainstorm, list, talk about it,
draw it out, put a graphic organizer together. |
|
Drafting: This is the
‘sloppy copy.’ Get the words down on paper without an undue concern for
mechanics. Free flow your ideas on paper. |
|
Revising: The process
of refining the piece of writing. Reorganize your writing. Does it make sense?
Does it convey the meaningful purpose it was meant to when started? |
|
Editing: This is the
step where you correct your spelling errors, mechanical, and grammatical
errors. This is a developmental process. |
|
Publishing: This is
now prepared in final form. Now ready to share the writing with others. |
APPLICATION
EXERCISE/REVIEW-
Re-write the following paragraph, correcting
all errors. It may be necessary to rearrange or to re-write the sentences.
![]() Now answer question 16
Now answer question 16