Scientific
Tools
Click Image to view the video
(username: masloski7511 password: lemon6753)
Introduction
This lesson introduces students to the various
tools of the science lab--from
beakers to Bunsen burners and balances. Students will discover the name of each
tool, how it helps scientists observe, measure, experiment and/or collect data
and how to use it correctly in the lab.
Vocabulary
1.
balance
noun
an instrument for
measuring weight.
The chemistry students
used a balance to weigh the copper.

2.
beaker
noun
a cylindrical glass
container often used in science labs. They have flat bottoms and a lip for
pouring.
The scientist used a beaker to
pour out the liquids in the experiment.

3.
flask
noun
a glass bottle with a
narrow top, often used in science labs.
It is hard to pour liquid
into a flask because the opening is so small.

4.
microscope
noun
a scientific
instrument with a magnifying lens or lenses used for inspecting very small
objects.
We looked at the cells
under a microscope and could see each individual cell
wall and nucleus.

5.
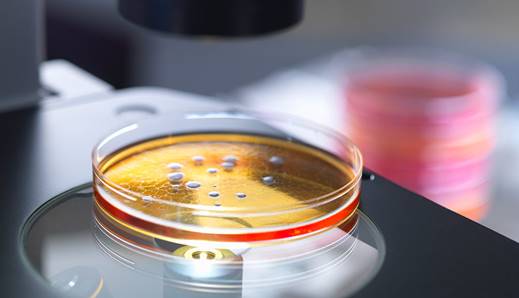
petri
dish
noun
a shallow glass dish
used in science labs for growing bacteria and other microorganisms.
In biology, we examined
germs that were living and growing in a petri
dish.
6.
specimen
noun
something or part of
something that is taken as an example of the whole thing or category.
The
scientists chose this specimen of bacteria because
it is resistant to medication.
Synonyms example, representative, sample

7.
stopper
noun
something that is used
to close a bottle, drain, tube, etc.
The water spilled from the
bottle because the stopper had fallen out.

8.
test
tube
noun
a thin glass tube
often used in science labs. They are closed at one end.
The test tube filled with sulfuric acid was standing up straight
in a holder so that it wouldn't spill.

9.
thermometer
noun
an instrument used to
measure temperature.
I checked the thermometer to see how hot it was outside.

10.
tongs
noun
a tool with two arms
that are connected at one end or in the middle. They are used for picking up
and holding small objects.
When I make jewelry, I
use tongs to pick up the small beads.

Scientific Tools
Scientists use special tools to do their work. They gather data,
or information, as they seek to learn about the world. In order to solve problems,
they must record data that is accurate and organized. This is an important part
of the scientific method. Scientists may use these tools in a
laboratory or anywhere that they perform their work.
Science Notebook
Scientists carefully record questions, illustrations,
descriptions, data, and their conclusions in science notebooks.
They may organize data into tables and graphs. When scientists conduct
experiments, they must write down the steps that they followed and the
materials that they used. This will allow the scientists to repeat the
experiments and test the results. All of the information in a science notebook
can be used later to draw conclusions about a problem.
Lenses
Scientists use different types of lenses to examine
objects that are very small or very far away. The lenses magnify objects so
that they appear larger and closer than they really are. A magnifying glass is
a simple example of a lens that scientists use. Other examples include telescopes, binoculars,
and microscopes. All have one or more lenses.
Measuring Tools
A science laboratory must have tools for measurement.
Examples of measurements include temperature, distance, time, volume, weight,
and mass. In addition to the different measurements, there are different
standards of measurement. The two most widely used are the English system and the metric
system. Scientists use the metric system.
Temperature
Temperature measures how hot or cold an object is. It is
measured with a thermometer. Most thermometers show temperature readings in
units of Fahrenheit and Celsius. Scientists use the Celsius scale to measure
temperature.
Distance
Scientists may measure distance with a metric ruler, meter stick,
or measuring
tape. Centimeter and millimeter units are used for measuring the length
of small objects. Longer distances are measured in meters and kilometers.
Time
Scientists must keep track of how long it takes for things to
happen during an experiment. Stopwatches and clocks are
important tools for measuring time.
Volume
Volume is the amount of space that something takes up. The volumes
of solids and liquids are measured in units called milliliters and liters.
Weight
A scale measures the pull of gravity as weight.
The kilogram unit is commonly used to measure weight. Very light objects are measured
in grams or milligrams. The weight of an object differs depending on where it
is located in the universe. For example, the weight of an object on Earth is
greater than the weight of the same object on the moon. This is because the
pull of gravity on the moon is less than it is on Earth.
Tools to Deal with Data
Calculators and computers help scientists
analyze data. Computer programs can be used to organize and store data.
Scientists often use graphs to organize and present information so that it can
be easily shared and understood. Scientists also use tables and maps to
show the results of studies.
Laboratory Safety Tools
A science laboratory can be a dangerous place if rules are not
set and followed. Some basic rules are to wear protective
clothing, keep the lab clean and organized, never eat in a lab, always put
things back where they belong, and gather all the needed materials before
beginning an experiment. Scientists often wear safety glasses in a
laboratory to protect their eyes from chemicals. They may also wear lab coats,
aprons, or gloves when dealing with harsh materials.
