The Cold War
(1945 - 1991)
American Policy of Containment
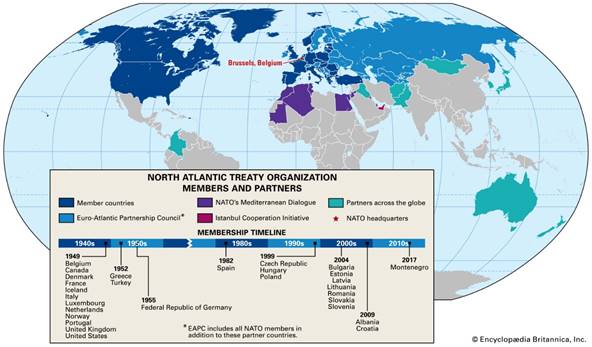
Figure 1 North Atlantic Treaty Organization: members
and partners. Image. Britannica LaunchPacks, Encyclopedia Britannica,
8 Feb. 2020.
The original 12 members of NATO were Belgium, Canada, Denmark,
France, Iceland,
Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, the United
Kingdom, and the United States.
|
|
Content Statement #23
The United
States followed a policy of containment during the Cold War in response to the
spread of communism.
Content
Elaborations
1.
The policy of containment
began in the late 1940s to halt the spread of communism in Europe and Asia, and
expanded to other parts of the world over the next several decades.
2.
Reasons for implementing the policy
of containment included:
a.
the fear of Soviet expansion
in Europe;
b.
the rise of communism in
China; and
c.
the spread of communism
throughout Latin America and Asia.
3. Containment
policies and international alliances included:
a.
the Marshall Plan;
b.
the Truman Doctrine; and
c.
the North Atlantic Treaty
Organization (NATO).
4. In
Asia, the policy of containment was the basis for U.S. involvement in the
Korean and Vietnam Wars.
Section A:
Policy of Containment
The “Cold
War” is the name we give to the era of political, military, and economic
tension between the Soviet Union and the United States. Beginning at the end of
World War II- and ending in the early 1990s- this tension involved Communist
and Capitalist ideological clashes throughout the world. However, situations in
Europe, Asia, and Latin America became the most hostile.
|
“The
Cold War”
|
|
It began in 1945 |
|
Capitalism v. Communism |
|
United States v. Soviet Union |
|
Germany was
divided into two countries: · East Germany à supported
by the Soviet Union · West Germany à supported
by the United States |
|
NATO àthe United
States and Allies |
|
Warsaw Pact àthe Soviet
Union and Allies |
The policy
of containment began in the late 1940s to halt the spread of communism in
Europe and Asia, and expanded to other parts of the world over the next several
decades. Containment is a strategic
foreign policy pursued by the United States beginning in the late 1940s to
check the expansionist policy of the Soviet Union.
|
“Policy
of Containment” |
|
Containment is keeping
something harmful under control |
|
The United States adopted a
foreign policy called Containment Policy. |
|
This policy used strategies to prevent the spread of communism. |
|
The policy was adopted as a reaction to the Soviet
Union expanding its communism throughout Europe, Asia, and Latin
Americans countries. |
Let’s Practice: Matching
Game
Section B: Reasons for
Containment
The threat
of communist invasion or takeover in the decades after World War II was the
main reason for American “Containment Policy.”
Below are
three areas of communist expansion:
|
“Three
Fears of Communist Expansion” |
|
1.) The
fear of Soviet expansion in Europe ·
Eastern and Central Europe o Germany: East Germany
(communist) and West Germany (non-communist) |
|
2.) The
rise of communism in China ·
Chinese Communist Revolution · Chinese Nationalist relocated to Taiwan |
|
3.) The
spread of communism throughout Asia and Latin America ·
Korea o North
Korea (communist) and South Korea (non-communist) ·
Vietnam ·
Cuba o Communist Revolution led by Fidel Castro |
Let’s Practice: Fill in
the Blanks Game
Section C: Policies and Alliances
President
Harry S. Truman pledged that the United States would help any nation resist
communism to prevent its spread. His policy of containment is known as the Truman Doctrine. The Truman Doctrine demonstrated
that the United States would not return to isolationism after World War II, but
rather take an active role in world affairs.
To help
rebuild after the war, the United States pledged $13 billion of aid to Europe
in the Marshall Plan. The US
government feared that a hungry, devastated Europe might turn to communism. The Marshall Plan proved enormously successful, helping to
rehabilitate European nations that accepted the aid.
Tensions
between the United States and the Soviet Union came to a head in 1948, when the
Soviet Union blockaded Berlin, and the United States led a year-long airlift to
supply citizens stranded in the western zone of the city. Realizing that conflict with the Soviet Union
might escalate into war, the United States joined the North Atlantic
Treaty Organization (NATO) defensive alliance. It ramped up security
measures at home with the National Security Act.
|
“Containment
Policy” |
|
|
Truman
Doctrine
|
Marshall
Plan
|
|
President Truman introduced the “Containment Policy.” |
Europe was devastated by World War II |
|
To stop the spread of communism going to non-communist
countries |
The Marshall Plan gave European countries economic aid to
rebuild their countries |
|
Congress asking for $400 million economic and military aid to
support non-communist countries |
This aid was given to support Western European countries that
were democratic allies |
|
The “Truman Doctrine” shaped American policy for the rest of
the Cold War |
Result: Western
European countries had an economic boom, and it strengthens ties with the
United States |
|
NATO
|
|
North Atlantic Treaty Organization – a military alliance |
|
Created to be a counterweight to Soviet Union armies in
central and eastern Europe after World War II |
|
An armed attack against one or more of them in Europe or North
America shall be considered an offense against them all |
|
Charter members included:
United States, England, France, Canada, Belgium, Denmark, Iceland,
Italy, Luxembourg, Norway, and the Netherlands. |
Let’s Practice: Matching
Columns Game
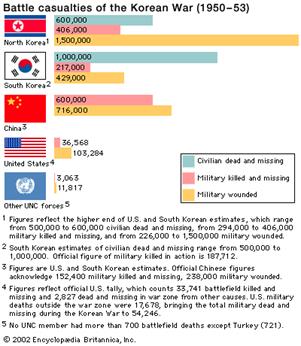
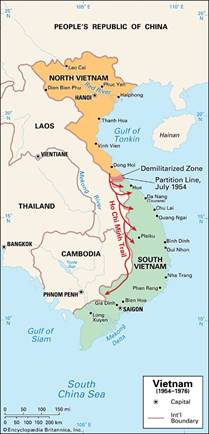
Section D: Korea and
Vietnam
In Asia, the
policy of containment was the basis for U.S. involvement in the Korean and Vietnam wars. Containment through military intervention was
the basis for the Korean and Vietnam War.
|
Korean
War
|
|
Japan ruled Korea until 1945, and the northern half was being
liberated by the Soviet Union and the southern half by the United States |
|
United Nations intervened with creating a resolution that
split Korea in half at the 38th Parallel. |
|
Vietnam
War
|
|
United States' involvement in Vietnam was because of the
“Domino Theory.” |
|
Domino Theory states that if one Southeast Asian country fell
to communism, then all of Southeast Asia would fall like a domino effect. |
Let’s Practice: Unscramble
Word Game