 †
†
MOON PHASES,
TIDES AND SEASONS
When the motions of the Earth and the moon are considered, they can be
described separately, but scientists prefer to describe their motions in
relation to each other. The Earth revolves every 364 ľ days around the sun
while rotating every 24 hours on its own axis. At the same time, the moon
revolves every 29 Ĺ days around the Earth and rotates on its axis in 27 ⅓
days. These events cause us to basically see the same side of the moon.
Gravitational attraction keeps the Earth in its orbit around the sun and the
moon around the Earth.
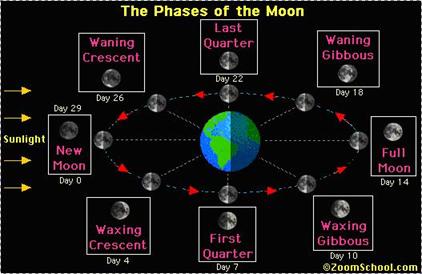
Phases of the Moon
As the moon revolves around the Earth, the shape of the moon appears to change. The varying shapes, lighted by reflected sunlight, are called the PHASES of the moon. When the moon is in between the sun and the Earth, the side of the moon facing the Earth is not lighted. This is the NEW MOON PHASE.
As the moon continues in its orbit around the Earth, part of its lighted half becomes visible. As the size of the lighted portion increases, the moon is WAXING. When the lighted portion of the moon becomes a semi-circle it is in the FIRST QUARTER PHASE. The lighted portion of the moon continues to increase in size until it appears as a full circle. This is the FULL MOON PHASE.
As the moon continues in its revolution around the earth after the full moon phase, the size of the lighted portion decreases so less of it is visible to the Earth. This is called WANING. When the visible portion becomes a semi-circle again, this is the LAST QUARTER PHASE. The moon again moves between the Earth and the sun, and becomes a NEW MOON. The cycle of phases begins again.








For additional information on the Phases
of the Moon click here PDF
File.
Eclipses
![]() †† Eclipses and Conclusion (01:37)
†† Eclipses and Conclusion (01:37)
For additional information click here PDF
File.

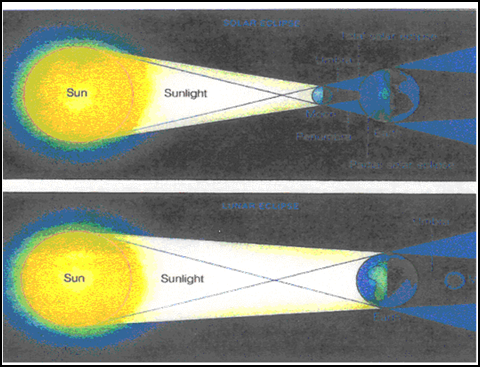
All the bodies moving around the sun cast long shadows into space. When one planetary or satellite body passes through the shadow of another, an ECLIPSE occurs.
There are two types of eclipses which are named depending on which body, the sun or the moon is blocked. The first is a SOLAR ECLIPSE. A solar eclipse happens when the new moon comes directly between the sun and the Earth. The small inner part of the shadow is called the UMBRA. Only those in this portion of the Earth in this part of the shadow see a TOTAL SOLAR ECLIPSE. The larger, outer shadow is called the PENUMBRA. Those who view an eclipse from this part of the shadow see only a PARTIAL SOLAR ECLIPSE. Since the orbit of the moon is tilted in relation to the Earth, an eclipse occurs only when the new moon is directly between the Earth and sun. This is a rare occurrence and never lasts more than seven minutes.
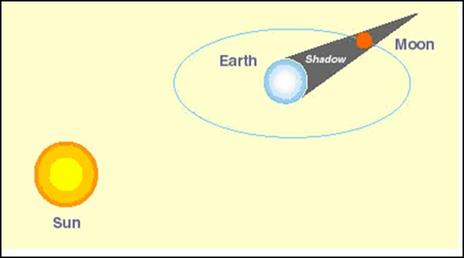
The second type of eclipse happens when the Earth comes directly between the sun and the full moon. This is called a LUNAR ECLIPSE and takes place when the moon passes through the Earthís shadow. When it passes through the umbra, the eclipse is total. When the moon passes through the penumbra a PARTIAL LUNAR ECLIPSE occurs. Since the shadow of the earth is much larger than the shadow of the moon, lunar eclipses may last several hours.

Tides
Due to the close proximity of the moon
to the Earth, there is a gravitational attraction between the Earth and the
moon. This was first discovered in the late 1600ís by Sir Isaac Newton.
According to
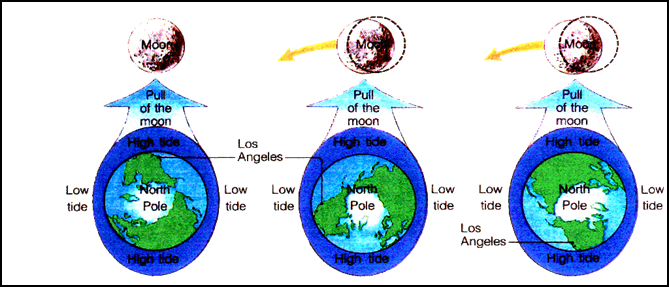
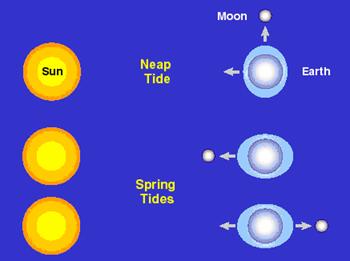
THE TIDES
During the full moon and new moon phases, the sun and moon are directly in line with the Earth. This causes higher than normal high tides called SPRING TIDES.
During the first and third quarter phases of the moon, the
moonís gravitational pull is partially cancelled by the sunís gravitational
pull. This causes high tides to be lower than normal. These are called NEAP
TIDES.
For additional information on Tides
click on this link PDF File
Seasons
Because the Earth is tilted on its axis, a different portion of the Earthís surface is exposed to varying intensities of the sunís rays as it revolves in its orbit around the sun. These changes in the angle at which the sunís rays strike the earthís surface and changes in the amount of daylight is what causes the SEASONS.
When the North Pole is tilted away from the sun, the sunís rays fall on the Northern Hemisphere at a lower angle. This tilting causes there to be fewer hours of daylight. The sunís rays also deliver less heat to the Earthís surface because they must travel through more of the atmosphere before reaching it. With the weaker the sun and fewer hours of daylight the WINTER season takes place. At the same time, the Southern Hemisphere is tilted toward the sun and the sunís rays fall at a higher angle. This causes there to be more hours of daylight and more heat is delivered to the Earthís surface. This is the SUMMER season.
On June 21st or 22nd of each year, the sunís rays strike the Earth at a 90 degree angle along the Tropic of Cancer. At this point in the Earthís orbit, the North Pole points toward the sun. This day is the SUMMER SOLSTICE, also known as the first day of summer. The Northern Hemisphere experiences the most hours of daylight on that day. On December 21st or 22nd of each year, the sunís rays strike the Earth at a 90 degree angle along the Tropic of Capricorn. The North Pole is now pointing away from the sun. This day is the WINTER SOLSTICE, or the first day of winter in the Northern Hemisphere. The least hours of daylight are experienced on that day.
On September 22nd or 23rd of each year, the sunís rays strike the Earth at a 90 degree angle along the equator. This day is the AUTUMNAL EQUINOX or first day of fall in the Northern Hemisphere.
On March 21st or 22nd of each year, the sunís rays once again strike the Earth at a 90 degree angle along the equator. This day is the VERNAL EQUINOX or the first day of spring in the Northern Hemisphere. During both equinoxes the hours of daylight and darkness are equal because the North Pole points neither toward nor away from the sun.
![]() † Spring the Summer Solstice (01:44)
† Spring the Summer Solstice (01:44)
For additional information on Equinox and Solstice click on the PDF File.

|
Winter Solstice Ė First day of Winter |
|
Vernal (Spring) Equinox Ė First day of
Spring |
|
Summer Solstice Ė First day of Summer |
|
Autumnal Equinox - First day of
Fall |