IONS, ELECTRIC FORCES, AND THE FORMATION
OF COMPOUNDS

In chemistry, more than 107 known elements react with one
another to form compounds. A compound is a substance that is formed
when two or more elements combine chemically and has properties different from
each of the individual component elements. A compound cannot be
separated simply because the elements are chemically bonded
together. Water (H2O), a compound, is used to put fires
out. However, Hydrogen, an element, and Oxygen, an element, are explosive
in element form. Thus, we emphasize again that compounds' properties
are likely to be very different from the properties of the elements with which
they are formed.
Compounds are formed by combining elements and utilizing
electrons from those elements. There are essentially two things that
elements can do with electrons when they combine. Elements can share
electrons or transfer them to another element. A compound formed by
sharing electrons is called a covalent compound, while a compound formed by
transferring electrons is an ionic compound. The electrons that are
transferred or shared are those on the outside of the atom and are called
Valence electrons.
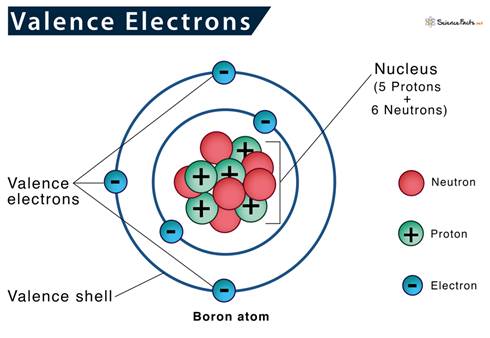
All elements seek to have eight electrons in the outside
level or transfer them to empty the last level. It would be easier
for this element to transfer the two electrons it has rather than find six
more. This element will transfer two electrons, but an element with
seven electrons would find it easier to gain one to equal eight electrons than
transfer seven. Both of these examples are ionic
compounds. When an element gains or loses electrons, it moves from
being neutral to having a charge because the number of protons and electrons is
no longer equal. An element with a charge is called an
ion. If an element loses two electrons, it now has two more protons
than electrons, and that element would have a charge plus 2 (+2). A
positive ion is called a cation. An element that gains two
electrons would now have two more electrons than protons, and this element
would have a charge of negative 2 (-2). A negative ion is called an
anion.
An element with four electrons in its outer shell is in a
unique position since it is precisely in the middle of 0 and 8. The
element would rather not lose or attract four electrons but instead share
electrons. A compound formed by sharing electrons is a covalent
compound. The force that holds compounds together is electrical. The
center of an atom is positively charged, and the outside is negatively
charged. Opposite particles attract, so the negative on one part of
the atom attracts the positive on the other. These attractions are
very short-range forces, but the strength of these bonds is responsible for
many chemical properties. Some of the properties include boiling
point, melting point, and vaporization point, and the stronger the bond, the
higher these points will be.