PARTS OF AN ATOM AND CHARGE OF ATOMIC
PARTICLES

You have a cube of sugar in your hand, which you break into
smaller pieces. You then grind those pieces into even smaller pieces
and dissolve the smaller pieces in a glass of water. In the glass of
water, the sugar can no longer be seen, yet, by tasting the water, it is
evident that the sugar is still there. It has not been destroyed or changed to
another form of matter. Sugar is a compound made of 3 elements (Carbon,
oxygen, and hydrogen). Find these three elements C, O, and H on the periodic
table.
In science, the smallest particle that can exist and still
have the element's properties is called an atom. Science has developed many
models throughout our scientific history to describe or illustrate the makeup
of an atom.
Each atom comprises smaller particles—electrons, protons, and
neutrons. These are called subatomic particles. At the center of an atom is a
nucleus. The nucleus consists of protons and neutrons. Protons carry a positive
electrical charge, while neutrons carry no electrical charge. Together, protons
and neutrons are called nucleons. Surrounding the nucleus is a cloud of
negatively charged electrons.
Scientists believe that subatomic particles—protons,
neutrons, and electrons—are themselves made up of smaller substances. The
substances are called quarks and leptons.
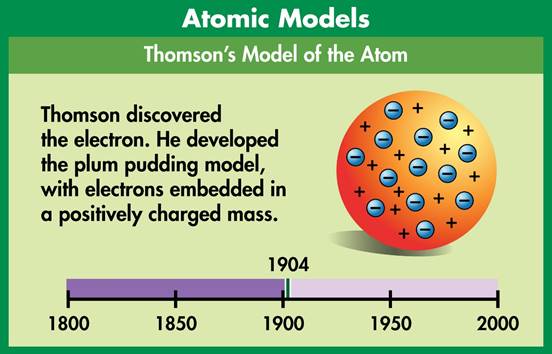
The currently popular model was developed in 1926 and is
called the electron cloud model. In the case of an atom, models are used
to describe or illustrate something too small to see. Models can
also be used to describe or illustrate something too large to view. An
example of something too large would be a model of our solar
system. We cannot see all of the planets in our solar system when we
look at our sky, so a model allows us to grasp conceptually what our solar
system looks like.
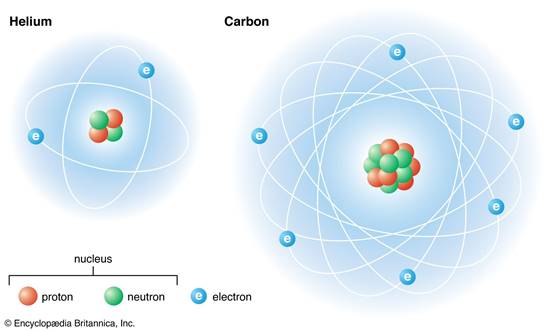
All atoms have the same essential parts. These are a nucleus,
and at least one particle called an electron. The nucleus contains protons and
neutrons.
The model of an atom shows the center of an atom as the
nucleus, which contains two particles: the proton, a particle with
a positive charge, and the neutron, a particle with no charge. Both
protons and neutrons have mass, and their mass in the nucleus represents nearly
all the mass of the atom. Since the nucleus contains particles with no charge
and particles with a positive charge, a nucleus has an overall positive charge.
Most of the atom is space. Ernest Rutherford discovered this. Because the atom
is too small for us to see, we use a model to understand better how it works.
If the atom was the size of the Astrodome, the nucleus could be represented by
a marble placed on the pitcher's mound.
The number of protons in a nucleus is called the atomic
number. Carbon has an atomic number of 6 which means that it has 6
protons in the nucleus, sulfur (S) has 16 protons, and lead (Pb) has 82
protons. The proton number is what makes each element unique.
An atom is electrically neutral. Therefore, if the
center of an atom is positive, there must be a negative atom area. There
is a region outside of a nucleus called the electron cloud, which contains
particles called electrons. Electrons have no mass, and they have a
negative charge. Using our previous example of Carbon, it is known
that the atomic number is six, and we also know the number of protons
determines the atomic number, so Carbon has 6 protons. Since an atom
must be neutral in charge, it must contain the same number of electrons and
protons; therefore, Carbon has 6 electrons, sulfur 16 electrons, lead 82
electrons
Atoms do have mass even though they are minimal. The
atom's mass is in the protons and neutrons. A proton has one mass;
this is called an atomic mass unit. A neutron has one mass; this is
called an atomic mass unit. Electrons are so small they have a
mass too small to consider. Atomic mass is the sum of the number of
protons and neutrons. Everything is made of atoms. Your body is made
of atoms. When you stand on a scale to measure your weight, you measure the
mass of all your protons and neutrons.