Ohio’s Constitution
Unit Overview
In this
unit, students will identify the difficulties in governing Ohio under its first
Constitution and identify how the Ohio Constitution complements the federal
structure of government in the United States. (CS #16)
Section A: Content Statement 16
As a
framework for the state, the Ohio
Constitution has similarities and differences to the federal Constitution; it was changed in 1851 to address
difficulties governing the state.
Content Elaboration
Similarities
between the Ohio and U.S. Constitutions:
• separation of powers into three
branches (executive, judicial, legislative);
• checks and balances;
• limited government;
• bill of rights;
• popular sovereignty; and
• elections.
Differences
between the Ohio and U.S. Constitutions:
Ohio Constitution
• Citizens can directly vote on laws
through initiative and referendum.
• Judges are elected.
• Legislators are term-limited.
U.S. Constitution
• Legislators vote on laws for citizens.
• Judges are appointed.
• Legislators do not have term limits.
In 1851 a new Ohio Constitution was written which made several changes to improve
governing including:
• Major executive officials and all
judges were to be elected.
• District courts were added.
• Debt limitations were instituted
Let's Practice: Content Statement 16
Under Ohio’s original Constitution, the General Assembly was the preeminent
branch of the government. Key judicial and
executive officers, other than the governor,
were appointed by the legislature and were not elected by the people of Ohio.
The governor, although an elected
official, had few specific powers. The Supreme
Court, which was required to meet once each year in every county, found it challenging
to meet its obligations. Also, the state was burdened with a significant amount
of debt.
The Constitution of 1851 provided that principal
executive officials and all judges were to be elected by popular vote. While the powers of the governor were not
significantly increased, legislative powers to enact retroactive laws were
prohibited, and all laws of a general nature were required to be uniform
throughout the state. District courts
were added to the court system to reduce the burdens upon the Supreme Court.
The new Constitution instituted debt
limitations, banned poll taxes, and
required that tax funds be used only for their stated purpose.
Let's Practice: True
or False
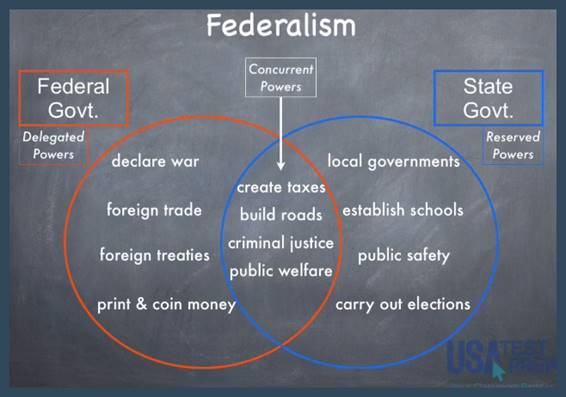
Section C: Federalism
Under our
federal system, the powers of government are assigned as follows:
·
Delegated Powers: powers which the Constitution gives only to
the national government
·
Reserved Powers: powers which were kept by the states and
belong solely to the state government
·
Concurrent Powers: powers shared by both the state governments
and the national government
For example,
Ohio has the power to levy taxes,
define crimes and punishments, determine voting qualifications, and borrow
money. However, there are certain powers
that Ohio is prohibited from exercising.
These powers include declaring war, negotiating treaties, and issuing
money, regulating trade between states, and maintaining a military force.
Like the United States Constitution, the Ohio
Constitution has many of the same principles that form the framework of the
United States government. Both documents
organize government into three separate branches – the legislative, the
executive, and the judicial. In both documents,
each branch is independent of the other two and has defined powers and
responsibilities. Also, both documents
begin with a Preamble that starts with the word. “We, the people.”
Look below
at the chart to study the similarities and differences between Ohio and the United
States Constitution.
|
Ohio’s Constitution |
Ohio and United States Constitution |
United States Constitution |
|
Citizens can directly vote on laws through initiative and
referendum. |
separation of powers into three branches |
Legislators vote on laws for citizens. |
|
Judges are elected. |
checks and balances |
Judges are appointed. |
|
Legislators are term-limited. |
limited government |
Legislators do not have term limits. |
Let’s Practice: Federalism