TYPES OF GOVERNMENT—DICTATORSHIP

North Koreans Bowing before the Statues of Kim II-sung
and Kim Jong-I1
Unit
Overview
A
dictatorship is a form of government in which one, strong leader or a small
group of people have all the power. The dictator
controls not only the government but also every aspect of the country’s
society, including education, religion, media and the economy. People often obey this type of leader out of
fear. In this unit, you will learn about
past and present rulers who lead by this method of governing. Let’s get started.
What
is a Dictatorship?
A dictatorship is a form of government in
which one person or a small group of people hold all the power. Dictatorship come from the Latin word dicere, which means to speak in English. Under
this system, one person, the dictator, speaks for everyone. Citizens have no say in how their government
operates. People are expected to do what
the leader orders. The government
emphasizes the importance of loyalty and duty.
For average citizens, civil liberties and political rights are extremely
limited. Dictators do not accept
criticism. They rely on the country’s
military and police officers to enforce their policies. Dictatorships are often
described as totalitarian. This means that the government has control
over all aspects of people’s lives. This
includes schools, churches, television, radio, Internet access, films, books,
magazines and newspapers. If they are
going to exist, all institutions and forms of media must not question the
ruler.
Dictators
achieve power by undermining traditional governments. There are several ways to do this. During periods of unrest or violence, powerful
leaders sometimes take control of a country’s army. Then, they can use force and fear to convince
the citizens to follow them. Dictators also achieves power by offering simple
solutions to complex problems. They can
be very persuasive and know how to create interest and excitement. As a result,
these leaders gain large numbers of supporters, who form a political
party. This often happens in times when
people are desperate for change.
Eventually, the leader and his party have a very large majority. They can ban all other political parties and
change the country’s constitution. Those
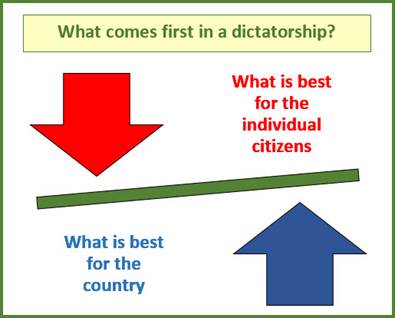
who oppose the dictator’s policies are arrested, imprisoned or killed. Dictatorships put the good of the country
before the good of individual citizens.
Famous
Dictators of the 1930s and 1940s
The
idea of a dictator dates all the way
back to ancient Rome. In times of
crisis, Romans believed in decisive and immediate action. They did not want to waste time debating the
issue. For this reason, they appointed a
dictator for six months. During this time,
he had the power to make and to carry out decisions for solving the
problem. The dictator did not have to
wait for the approval of the Roman Senate to carry out his plans. Of course, not all Roman dictators were
willing to give up their authority after six months. Sometimes, this led to a civil war.

Some
of the most famous dictators in history rose to power in the 1930s and
1940s. Let’s look at some examples. After World War I, Germany faced many serious problems. The treaty that ended the war forced the
country to decrease its army, to give up some of its land and to pay for
damages caused by the war. German
citizens were angry and insulted by these terms. They tried to solve their problems by
printing more money, but this only made matters worse. The National Socialist German Worker’s Party,
or Nazi Party, encouraged people to
blame Germany’s Jewish population for the nation’s difficulties.
The
Nazi Party and its leader, Adolf Hitler,
became more and more popular.
Eventually, Hitler became Chancellor,
one of Germany’s highest government officers.
This enabled Adolf Hitler to outlaw all other political parties and to
control the government. Only newspapers,
books, magazines and films that said positive things about Hitler and the Nazi
Party were allowed to be published. Those who opposed the Nazi Party, along with millions
of Jews, were imprisoned or put to death.
Hitler ruled Germany until his death in 1945 at end of World War II. Today, Germany has a democratic government.

Joseph Stalin was another
dictator who seized power during this era.
He became the leader of the Soviet
Union, which was made up Russia and several other countries. Stalin used secret police to spy on those who
opposed him. He eliminated his rivals by
placing them in prison or by murdering them.
When compared to other countries, the Soviet Union had a small number of
industries and factories. Most people
made a living by farming their own land.
Stalin was determined to turn the Soviet Union into a modern,
industrialized nation. He ordered a
takeover of small forms and combined them into government-owned businesses. The farmers no longer owned their lands. They were forced to work on the farms and in
factories that belonged to the government.
Workers who rebelled were severely punished or killed. Stalin remained in power until his death in
1953. In later years, his policies were
condemned. The city of Stalingrad, which had been named after
him, was once again called Volgograd. Stalin’s name was also removed from public
buildings. In 1991, the Soviet Union
collapsed and became fifteen, independent nations.
North
Korea: A Twenty-first Century Dictatorship
Currently,
several countries around the world are governed by dictatorships. North
Korea, established in 1948, is one example.
The Kim Dynasty has
controlled the nation’s government for three generations. Kim I1-sung
was the country’s first leader. After
his death in 1994, he was followed by his son, Kim Jong-I1, and his grandson, Kim
Jong-un. For this reason, North
Korea is sometimes called a hereditary
dictatorship. Today, Kim Jong-un is
the political, economic and military leader of the country. North Korea’s official name is the Democratic People’s Republic of North Korea. It has a written constitution and holds elections. Nevertheless, North Korea has one of the
world’s least democratic governments.

The Korean National Worker’s Party is the
only political party permitted under the constitution. Kim Jong-Un is the party’s chairman. A few other small parties exist, but they are
controlled by the KNWP. Although the
country holds elections, almost all candidates run unopposed. In other words, there is only one candidate
on the ballot for each office. The North
Korean constitution does mention the freedoms of speech, press and religion,
but people do not actually have these rights.
Citizens who criticize the political system and its leaders are
arrested. The government tries to keep
the ideas and cultures of other countries out of North Korea.
People
have only one source for news, the Korean
Central News Agency. Owned by the
government, it controls the television stations, radio stations and
newspapers. The agency also runs the
nation’s only available internet server.
Just a few, high-ranking officials have access to the world-wide
web. Citizens are not allowed to travel
freely within the country or to visit other countries. Foreign visitors are closely monitored. The
government strictly regulates education.
Click on the graphic below to see how this impacts students.
Review
the three dictatorships that you read about in this unit. Then, click on the graphic below and complete
the worksheet.
Advantages
and Disadvantages of Dictatorships
Like
all forms of government, dictatorships have both advantages and
disadvantages. On the plus side, they
usually provide stable leadership. A
dictatorship operates efficiently in a crisis, such as an unexpected military
attack, a natural disaster or a health epidemic. There is no waiting for another branch of
government to approve a spending plan.
Dictators can take action quickly and are not concerned with keeping the
citizens happy. After all, they do not
have to worry about being re-elected. Because people are threatened with harsh
punishments, dictatorships generally have lower crime rates than other forms of
government.
At
the same time, there are some major disadvantages to living in a
dictatorship. Because there are no
limits to his or her authority, dictators often abuse their power. It is easy for them to imprison or to kill
people that stand in their way.
Dictatorships do not tolerate different points of view. This discourages new ideas, cultural exchange
and advancements in technology. The
system restricts personal rights, and laws can be changed at any time. Eventually, citizens may attempt to overthrow
the dictator. This often results in
unrest, violence and civil war.
Time
for a Quick Review
Before
moving on the Unit 22, review the names and terms found in Unit 21. Be sure you can answer the “Can I” questions
with a loud “yes”.


Additional Resources and Activities
