GEOGRAPHY MATTERS: MIDTERM

Unit Overview
So far in this course, we have studied the geography of the Western Hemisphere, its geographic features, early history, cultural development and economic change. Our geographical focus included the study of contemporary regional characteristics, the movement of people, products, ideas, and cutural diversity. In this unit, we will briefly review and test these concepts.
Themes of Geography
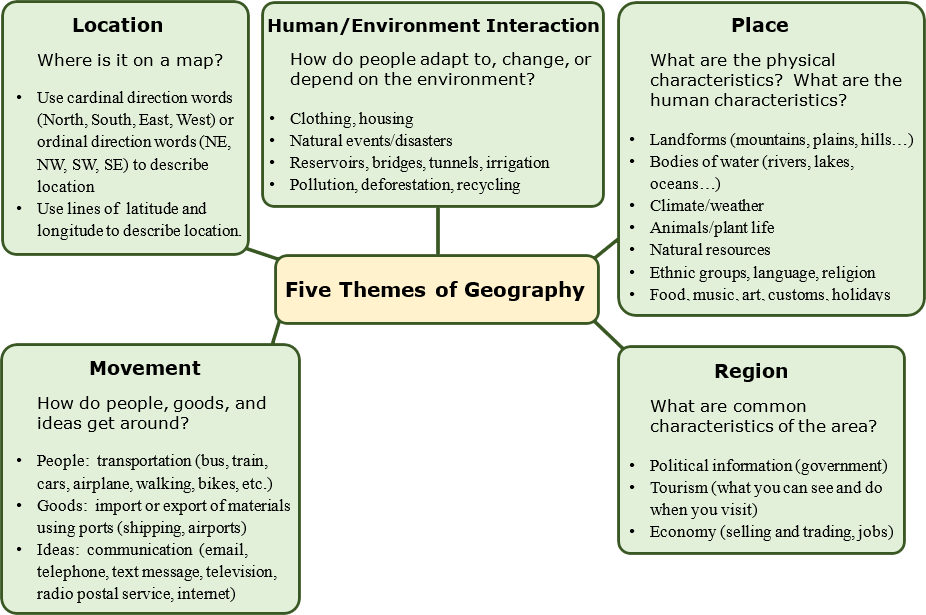
To understand the past and the present of the United States, it is important to study geography and history. Geographers (experts who study the Earth) have developed five themes, or topics, to show the connection between geography and history.
One of the five themes is Human-Environment Interaction. People interact with their environment. They build ditches to bring water to the desert so they can grow crops, known as irrigation. They cut down trees. The changes people create in their environment bring benefits. However, changes can also cause problems, such as pollution.
Another theme is Movement. People travel from place to place to get what they want and need. The first people who came to the Americas were hunters following animal herds. Much later, people came to the United States in search of freedom. When people move, they meet new people. They exchange goods and ideas. The movement of goods and people links the United States with all parts of the world.
A third theme is Location. Location describes the point on Earth's surface expressed by means of a grid (absolute) or in relation (relative) to the position of other places. Geographers begin to study a place by finding where it is, or its location. A location can be
specific (for example, it can be stated as coordinates of longitude and latitude or as a distance from another place) or general (it's in the Northeast). There are two types of location:
1. Absolute location describes the place's exact position on the Earth.
2. Relative location explains where a place is by describing places near it.
Next theme is Place. Place includes a location's physical and human features. Differences might be defined in terms of climate, physical features, or the people who live there and their traditions. The physical features of a place would be explaining that the climate is hot or cold or that the land is flat or hilly. The human features of a place are described by explaining how many people live there, what types of work they do, or what they do for fun.
The final theme is Region. A region can be defined by a number of characteristics including area, language, political divisions, religions, and vegetation (for example, grassland, marshland, desert, rain forest). Therefore, there are many different types of regions (i.e. cultural regions, economic regions, political regions, etc.). On maps, geographers use color and shape or special symbols to show regions.
Now answer the questions!