
PLANT STRUCTURES
Unit
Overview
Pollination,
fertilization, and germination are three processes that help explain to the
reproduction of plants. Plants make life on Earth possible. Plants grow just
about everywhere in the world. Plants supply man with important materials to be
used for food, medicine, clothing, and other life necessities. Plants make
their own food by way of photosynthesis. It is important to know that the plant
kingdom has five different types of organisms. The group that this unit will
focus on is seed plants. The following four plant types are as important but
seed plants are the most common in our surroundings. There are also algae
plants which are mostly one-celled green plants. Moss and liverwort plants grow
low to the ground and have no roots, stems, or leaves. Ferns are a bit larger
than the moss and liverwort group. Ferns do have roots, stems, and leaves.
Since seed plants make up the biggest part of the plant kingdom, this unit will
take a closer look at different types of seed plants.
|
VOCABULARY |
|||
|
monocot |
dicot |
vascular |
nonvascular |
|
pollen grains |
germination |
fertilization |
roots |
|
factors |
stems |
leaves |
Flowers |
|
reproduction |
seeds |
|
|
The fourteen vocabulary words
above are throughout this unit. Be prepared to know what the words mean so that
you can understand how the words are used in the unit. Below are some
definitions you can practice to help you understand the words better.
VOCABULARY DEFINITIONS
· monocots are flowering plants with one seed leaves
· dicots are flowering plants with two seed
leaves
· vascular means relating to the system of vessels for carrying
water and nutrients to plant parts
· nonvascular means no vessels to carrying
nutrients and water to plant parts
· pollen grains are the powdery substances given off
from the male part of a flower for fertilizing
· germination is when a plant begins to grow and
put out shoots of plant growth
· fertilization is when a plant develops a new individual
part when introduced to the male flower part; when a plant is able to produce
seed
· reproduction is the action of copying or to make
again
· roots are the plant part that normally
grows below the ground that acts as a support and collects water and
nourishment for the plant
· factors are the influence that contributes to a result
· stems are the main body or stalk of a plant or shrub; it
supports the fruit, flower, or leaf
· leaves are a flattened, typically green, structure of a plant
that is attached to a stem and is the chief area for photosynthesis and
transpiration
· flowers are the seed-bearing part of a plant that consists of
reproductive organs surrounded by brightly colored petals and green sepals
· seeds are the flowers part where reproduction
occurs and this is where the plant is capable of developing another plant
Seed plants are the
plants that make up the majority of the plant kingdom. The parts of a seed
plant are the seeds, flowers, stems, leaves, and roots. Try to think of all of
the different kinds of plants that you know. Do not be surprised if most of
them are seed plants. You need to be aware of the parts of seed plants. We
enjoy eating many of them. When you eat salad you are eating the leaves of a
seed plant called lettuce. When your mom packs your lunch and gives you celery
and carrots to munch on, you are eating stems (celery) and roots (carrots) of
seed plants. The salted nuts that you enjoy for a snack when watching
television is the actual seed part of a plant. Now that you understand that
seed plants are not just for beauty but also are essential foods, it is
important to know how this all happens. You need to keep the next three plant
words in your memory: germination, pollination, and fertilization.
Germination is the growth
period of a seed. A seed germinates when two factors are present. Water and
temperature are the conditions that allow for germination to take place. A seed
has a seed coat. As the tiny plant grows it will break through the seed coat
and will start to develop roots, stems, and leaves. As the plant continues to
germinate, flowers and new seeds develop.
Pollination of a seed
plant is a process that requires the help of some insects. Insects will gather
food from plants as they travel from one flower to another. There is a plant
part called the stamen (male part) that will hold pollen grains. As the insect
moves around to other flowers, pollen grains brush off onto the pistil (female
part) of the flower. Also, pollination can happen by the pollen grains being
moved by the wind. If the wind blows pollen grains around and they land and
stick on the female part of the flower then the pollination process has begun.
Most of the time grasses and trees get pollinated by these grains getting blown
around.
Fertilization of a plant
can only begin after pollination takes place. Pollen grains allow for a
tube to grow from each grain. This happens when the grains stick to that part
known as the pistil. The tubes grow downward from the pistil. As the tubes
continue to grow through the pistil, they continue until they enter the ovary.
It is here where the male sperm cells get released and join the female egg
cells. Once this happens the fertilization process begins. It is here in the
ovary that seeds are formed. Some of the other changes that happen are three of
the plant parts begin to dry up–the pistil, the stamen, and the petals. As the
ovary grows so do the seeds and this allows the ovary to be a fruit. This is
where the seeds are contained. An example of a fruit is an apple.
We need to mention the
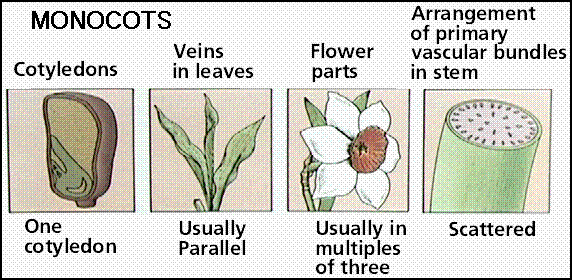
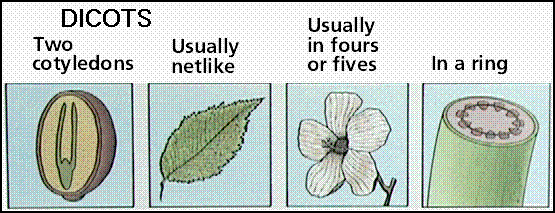
two groups of flowering plants. They are monocot and dicot. Since flowering
plants get their seeds from the flowers, they are put into these two smaller
groups. Monocots make seeds with one seed leaf. The leaf has parallel vein
patterns. Onions are monocots. A dicot makes seeds with two seed leaves. The
leaf has a net like vein pattern. A dicot can be trees, shrubs, and some
flowers. Not only are these two groups different because of their seed leaves
but the tubes within the stems are not the same. The tubes in monocots are
scattered and the tubes in a dicot are circular.. The
monocot plant has leaves that are narrow and long with veins that do not cross.
The opposite is true of a dicot. They have broad leaves with veins branching
out and sometimes crossing. Counting the flower petals will also help to show
the difference between the two types of flowering plants. Monocot flowers have
either three, six, or nine petals. Dicot flower petals have four or five petals
or any number of petals that can be divided by four or five.
Examples of Monocots and Dicots
(above) Monocots on the left;
dicots on the right
Knowing about seed plants
is very important because of the importance of their value in our world. Many of
the plants structural parts are used for food, or making our world look pretty,
or for products that can be made to help us live a better life. Flowering seed
plants help to make the world go round!
