COURSE OVERVIEW
In this course, students will have the opportunity to study the interaction of people and cultures, as well as natural and physical environments in the major areas of the world. The course is designed to familiarize students with the world and how they, along with their community, can play a role in the development of the world. Students will also study and develop an understanding of various regions of the world and will focus on several geographic topics in each region. In addition, students should develop an understanding of how physical geography impacts the way humans live and interact with their world and how humans have changed the world’s physical geography. As citizens our lives are greatly impacted by the rest of the world and this is our opportunity to learn about many of these places and issues.

LOOKING AT THE
WORLD
Unit
Overview
Geography is the study of
the earth and the way people live and work.
Geography also includes locations of places and their relationship
between people and their environments. Geographers
are those who study geography.
1. Location
2. Place
3. Human Environment/Interaction
4. Region
5. Movement
The theme of location is concerned
with answering the question “Where are we?”
Geographers can study the location and distribution of almost every
surface of the earth. The absolute
location of a place is its exact location on the globe.
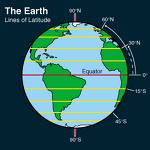
The
equator is an important line that circles the
earth midway between the North and South poles, dividing the earth into hemispheres or halves. The northern hemisphere includes all
land and water between the Equator and North Pole, while the southern
hemisphere includes the land and water between the Equator and the
South Pole.
The
second set of imaginary lines includes lines of longitude or meridian
lines, stretching from pole
to pole and measure east and west of the Prime Meridian. The Prime
Meridian is the starting line, which lies at 0 degrees. Places east of the Prime Meridian up to 180
degrees are east longitude and places west of the Prime Meridian up to 180
degrees are west longitude. One must
indicate if a location is east or west longitude, if not they may be in the
wrong part of the world.
Place
When we talk about place,
we are talking about what it is like there.
Every place on the earth has its own physical features. We can describe the
land, plants, and animal life. Just like
its physical features, every place also has a different element that can best
describe a place. For example, Florida
is known for its warm weather year round, so an element of Florida is its warm
weather. How do we describe a
place? The first way we describe a place
is by something the place is known. No
one place in the world is the same. Places
can be defined by religion and cultural backgrounds.
Physical and Human Interaction with the
Environment
What
is important to know in geography is the relationship between Physical
and Human Interaction with the environment. As you can see for yourself, all places have
both desirable and undesirable elements.
Ask yourself what attracts you to a certain place. Geographers are interested in how people
adapt and change to their environment.
For example, people never lived in the desert, but because of
irrigation, people are now changing the desert into farmland.
Region is an important
theme in geography. Geography can divide the world based on physical features
such as plant and animal life; regions are areas with similar
characteristics. Those characteristics
could be climate, landforms, religion, or even politics. There are three types of regions:
1. Formal Regions
2. Functional Regions
3. Perceptual Regions
A formal
region is a region that has one common characteristic. For example, the Corn Belt is the area that
spreads from
A perceptual
region is a region that is based on a feelings rather than data. For example, this may be thought of as
stereotyping, but some people believe that everyone from Texas is a cowboy.
Another
important theme is movement. This theme answers the question of how people and
places are connected. Throughout history, there have been movements of large
groups of people from one place to another, this is called migration.
People migrate for many different reasons, better land, religious/political
freedom and the chance to earn a better living. Movement is a daily part of our
lives. We use various means of transportation to move from one place to
another.
Geography
is used to study politics, economics, and cultures. Geographers study culture to see how
the ways of people affect the physical makeup of the earth. We use geography to study the relationship
between the physical environment and social structures.
A globe
is a scale model of the earth. Why do we
use a globe? The earth is round and
since globes are round, a globe will provide the most accurate description of
geography. Maps are printed
representations of the earth. It is hard
to show the earth as being round on a map, so that is why a flat map distorts the earth’s
features. However, the advantage of
using maps is that maps can show small areas in detail. There are two types of maps, political
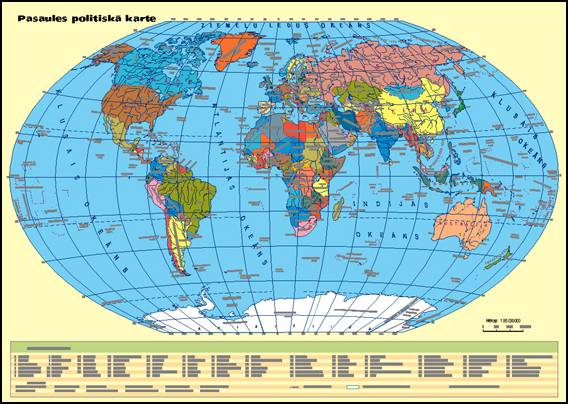
maps and physical maps. A political
map is a map that shows political boundaries of countries, states, and
cities. The diagram below is an example
of a political map, which helps show how countries are networked or linked
together, as well as showing the boundaries, capitals, and roads.
The
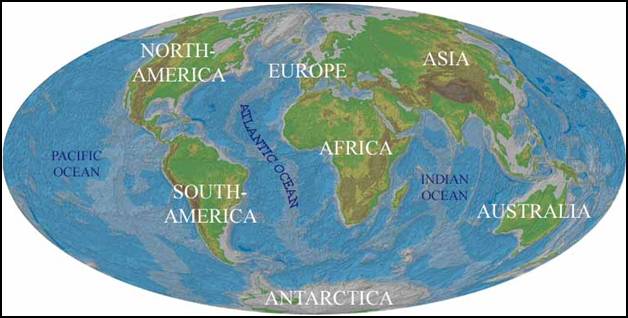
second type of map is called a physical map, which shows the location of natural features such as mountains
and rivers. An example of a physical map
is below showing the location and topography, or a shape, of the
earth’s physical features. These physical
features are important because they help explain the development of a
country. For example, mountains may act
as a barrier to transportation, so a country has to use rivers for goods to
travel in and out of the country.
Physical maps also allow us to see relief, or the differences, in
elevation or height in landforms.
By looking at maps,
we can learn much about
a country. A thematic map is a map
that contains a single idea. There are
maps that show climate, vegetation, and economic activities.
1.
1. Qualitative
Maps
2.
2. Flow-Line
Maps
Qualitative
Map #1
Qualitative
Map #2
The
second type of a thematic map is a flow-line map that illustrates the
movement of people and animals, while also showing the movements of the
glaciers and hurricanes. The map
pictured below is a flow-line map.
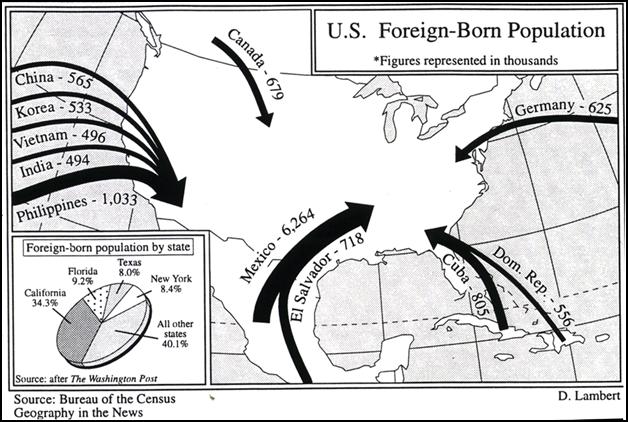
Just
like in your lives, technology has changed the way maps are made. Cartographers now use GIS or Geographic Information Systems, a system that receives information from a variety of sources
including satellite images and statistics.
That is also how a Global Positioning System (GPS)
systems work. GIS systems are like the
GPS systems people now have in their cars; they provide directions when you are
traveling.
Geography
is the study of the location of people and places and the patterns in which
they are arranged on Earth.
Physical
geography focuses on the physical features and processes of Earth.
Human
Geography focuses on the political, economic, or cultural characteristics of
human populations.
An
important element in geography is the interaction between people and their environment.
Geographers try to understand how the Earth’s physical environment shapes are
shaped by human activities.
To
understand geography you need to understand how maps work, but globes are the
most accurate depiction of the Earth.
Flat
maps show projections that distort the Earth’s features in some ways.
 |
| Unit 1 Main Points Worksheet |
| Unit 1 Geography Themes |