Plot
The plot is
the literary element that describes the structure of a story.
Reading Literature (11-12.3)
Analyze the
impact of the author’s choices regarding how to develop and relate elements of
a story or drama.
Let’s Practice: Key Terms
Section A: Plot Structure
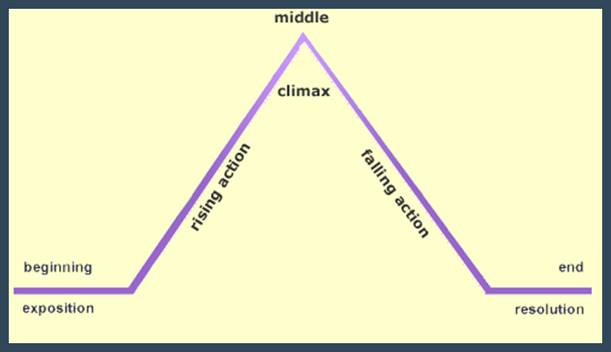
The plot is the literary element
that describes the structure of a story.
It shows the casual arrangements of events and actions within a story. The most basic and traditional form of the plot
is pyramid-shaped. Gustav Freytag has
described this structure. Freytag used
the five-part design shown below to illustrate a story’s plot.
Plots can be
told in chronological order, flashback, and media res (middle of the story)
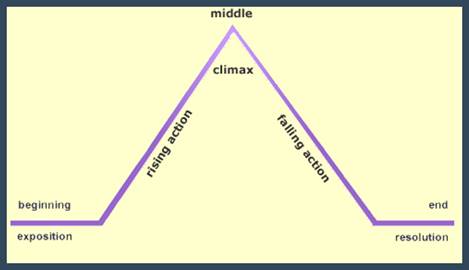
Plot Components
Ø Exposition
o The start of the story, the situation before the action starts
Ø Rising Action
o The series of conflicts and crisis in the story that leads to
the climax
Ø Climax
o The turning point, the most intense moment – either mentally or
in action
Ø Falling Action
o All of the action which follows the climax
Ø Resolution
o The conclusion, tying together of all the threads
Let’s Practice: Plot
Section B: Elements of a Plot
A story’s
plot is the events that make up that story.
The plot explains the “why” of a story and draws the reader into what’s
happening. Within the plot, characters
perform actions that make up the story.
Three main elements support the events of the story.
Ø Characterization
o The author make choices for the character
o The author describes how the character is portrayed through
actions, dialogue, appearance, and motivation
Ø Setting
o The time and location that the story takes place
Ø Conflict
o The dramatic struggle between two forces in a story
o Without conflict, there is no plot
o Protagonist à story’s main character
o Antagonist àa character who opposes the protagonist
These
elements above, along with the events of the plot, are essential parts of every
literary story.
Let's Practice: Elements of a Plot
