

THE
GEOGRAPHY OF LATIN AMERICA
Unit Overview
Latin America is often
divided into three areas, Middle America, the Caribbean and South America. Middle America consists of Mexico, and seven
countries in Central America, the narrow land that links North and South
America. The islands of the Caribbean, also known as the West Indies, are the Bahamas, the greater and Lesser
Antilles. The largest area of land is in
South America. Brazil is the largest
country in South America. More than half the land and population is Brazilian.
The physical makeup of Latin America is very diverse. There are many large rainforests, with the largest tropical rainforest located in Brazil in the Amazon basin; and the longest mountain range is known as the Andes Mountains.
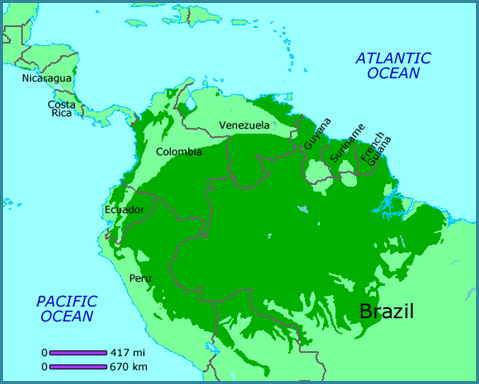
The
Amazon watershed region is the largest area of unbroken rainforest in tropical
America and in the world, as shown in this map of Latin American rainforest.
Note: green area includes tropical forest outside the Amazon watershed, while countries with significant rainforest remaining are labeled. Other significant
areas are in western Colombia and Venezuela, east of the Andes and along the
northeast coast of South America in Suriname, French Guiana and Guyana. Much
smaller areas include parts of Central America, as well as a region along the
southeast coast of Brazil. However, both of these additional regions are severely
deforested, due to a combination of logging, ranching and urban
development. Countries without significant areas are not labeled.
Mountains
There are high
mountain ranges in Latin America; many of the mountains that are in the
Caribbean are actually peaks of underwater mountains. In Mexico, there are two mountain ranges,
Sierra Madre Occidental and the Sierra Madre Oriental. They meet together in Mexico City. No mountain compares to the largest mountain
range, The Andes Mountain. These
mountains stretch over 4500 miles and its highest peak is over 20,000 feet high.
It is in the valley of these mountains
that many people live. People settle
here because the area is rich in mineral and soil resources. However, there are major drawbacks to living
here. The mountain ranges block
communication and people are often isolated. As you will read later on in this unit it
makes trade much more difficult.
Plains and Plateaus
Latin America is a region of the high plateaus. It is here that much farming and grazing takes
place. It is also the most densely
populated area in Mexico. Narrow coastal
plains stretch across the Gulf of Mexico and the Pacific Ocean. In Venezuela and Columbia, people have been
raising cattle for hundreds of years on the fertile plain called the llanos. The llanos runs along the Caribbean coast of
South America. To the south of llanos
is the Amazon River. South of the
Amazon is the heavily forested region called Gran Chacos. In Argentina and Uruguay are treeless plains
called the pampas. It is here where grain and cattle are raised
because there is enough rain that provides fertile soil.

Horses being watered on the Llanos,
in eastern Colombia.
Latin America does
not have many lakes, but the lakes the region does have are large. For example, Lake Maracaibo covers 5,217 miles
and contains one of the world’s most important oil fields.
Natural Resources
Latin American
countries are among the world’s leading producers of natural gas and oil. The oil fields along the coast of Mexico have
helped make Venezuela the 5th largest oil producer in the world. In
addition to oil, coal and natural gas deposits of uranium are found throughout
the region. The rivers and waterfalls
located in Latin America provide the region the potential for hydroelectric
power, using the energy of water to create electricity. In addition to its energy resources, Latin
America also has many mineral resources. Bauxite, which is used to make aluminum, is
found in Jamaica. Mexico is a leading producer of silver. Despite its many resources, Latin America has
not used these resources in a productive manner, mostly because it is expensive
and Latin American countries do not have the money.
Many types of
climates can be found in Latin America. When traveling through Latin America one will
pass through deserts and rainforest.
There are five climate regions in Latin America.
Vegetation
The natural
vegetation of Latin America consists of rainforests and grasslands. The vegetation varies from one region to the
other. Tropical rainforest are scattered
throughout the region, mostly near the equator. The largest rainforest is located in Brazil
near the Amazon River. This rainforest
covers nearly a third of South America.
The trees in a tropical rainforest grow tall and have broad leaves. The trees form a canopy or covering, keeping
the sun from reaching the forest. There
are few plants growing on the floor of the rainforest. In a rainforest there are a great number of
species of animals that can be found. Many
people consider the rainforests the most beautiful place in the world.
Grasslands and
Deserts
In areas with a
subtropical climate, such as Paraguay and Uruguay, prairie like grasses
grow. Since there is a rainy season we
consider this region a transition region, a region that has the rains of
grassland and the dryness of a desert.
In a desert region very few plants grow, as you might have
expected. That plant life that does grow
here are cacti, prickly green plants that store water.
Vertical Climate
Zones- Much like with the climate, the vegetation differs based on altitude. Earlier we explained about the Tierra Caliente region, this is where a rainforest is found.
Crops such as rice and sugar cane are found here. In the tierra templada, where most people
live, coffee is the chief crop. As you can tell from your surroundings,
Starbucks coffee is very important to their economy. Evergreen trees are found here. In the tierra fria, crops such as potatoes
are grown.
Population
Roughly around 470 million
people live in Latin America, close to 10 percent of the world’s population. The people come from many different background’s,
spanning from North America, Europe, Africa and Asia. There is much diversity in Latin America.
The Native Americans
were the first to arrive in what is now modern day Latin America. They built civilizations long before the
Europeans had arrived. The chief Native
American groups were the Aztecs, Mayas and Incas. As time moved on, Native American culture
would blend with those groups that would conquer the region. However, especially in Mexico, Peru and
Bolivia, Native American cultures remain intact and live in isolated valleys.
Sometime around the 1400s,
the 1st Europeans arrived in Latin America. At first, it was only the Spanish and
Portuguese, but they were soon followed by Italians, British and Germans. Today, Europeans still follow the culture
their ancestors brought with them to Latin America.
In the 1500s,
Europeans needed workers to work on the plantations in Brazil. This would mark the arrival of the Africans. They brought them over as slaves to work on
the plantations. The Africans helped
build the region and their culture remains an important part of Latin America
life.
In the 1800s, the
Asians came to Latin America. They too
worked on the plantations, but unlike the Africans they were not slaves. Today, there is a large population of Asians
living in the Caribbean.
Languages
Most countries of
Latin America speak the language of the country that colonized them. The official language of Brazil is Portuguese
because Portugal colonized Brazil.
Population Density
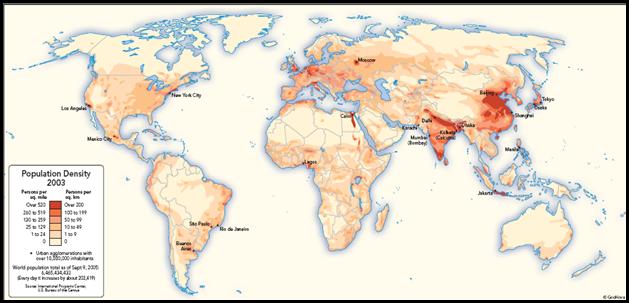
World Population Density
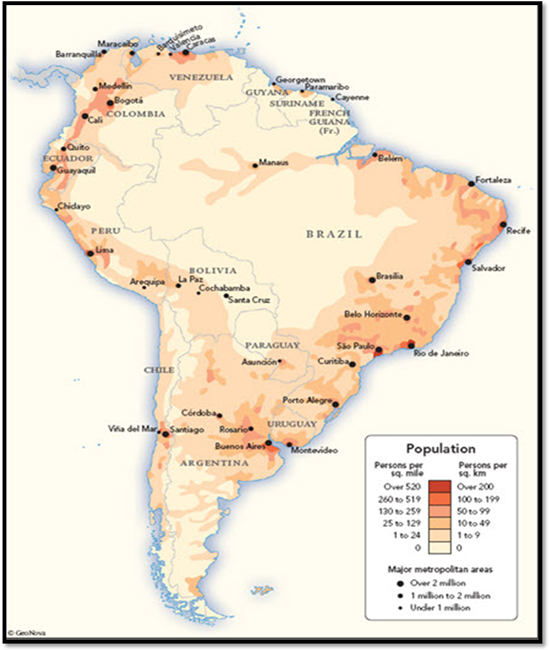
Latin America Population
Density
As with the case in
every region the population is not evenly distributed. Most Latin Americans live only in one-third
of the land. Most live only in two major
areas, around the coasts of South America or in the coastal strip that connects
Mexico and Central America. Two thirds
of the people living in South America live in two regions. The first region stretches from the Amazon
River in Brazil to Buenos Aries in Argentina. The second region is along the coast of the
Andes Mountains, the western side of South America, where Venezuela is
located. The next largest group of Latin
Americans lives in Middle America, the Mexican plateau along the pacific coast
in Central America. In these areas the
land is fertile and has a mild climate.
The population
density varies greatly in Latin America. This can be studied by looking at the
countries of Mexico, Brazil and Ecuador. There are roughly around 90 million people
living in Mexico, that is close to three times the number of people living in
Central America. However, Brazil has a
larger population. Which country has the
higher population density? Even though
Mexico has less people, it is a HIGHER population density. Brazil has more people, but the size of the
country is over three million square miles, while Mexico is only around 750
thousand square miles. That would mean
that Mexico has a population density of around 125 people per square mile,
compared with Brazil which has only 48 people per square mile.
The countries in the
Caribbean are small in land mass, mostly because the land is not suitable for
living or farming. However, these
countries have high birth rates. The
combination of a small land mass and a growing population equal countries with
a high population density. For example, the country
of Barbados has a population density of nearly 1800 people per square mile.
Urbanization
In the past, the
people of Latin America worked and lived in the countryside, but today most live
in urban areas. In the rural areas the
conditions are very poor; you should remember from earlier in the course these
would be called “push factors”. These
are factors that push people away from a certain region. Factors that pull people to a certain region
in order to find a new life, better jobs and better education would be
considered “pull factors”. However,
since many of the people cannot read or write, they rarely find what they are
seeking. This explosion in an urban
population has brought big problems. These problems are the same as every region that experienced urbanization, lack of resources to satisfy the needs of a growing population, little or no money, and often forced people to live in slums. In addition, there are high poverty and crime rates. Since many
cannot get jobs it is almost as if they are coming to the area in order to
escape.
History and
Government
The history of Latin
America is long and often violent. Its
past includes Native Americans, European colonization and their own struggle
for independence.
Native American
Empires
The Native Americans
came to Latin America thousands of years ago; they probably got here by
crossing the Bering Strait. Long before
Christopher Columbus came to America, three major Native American civilizations
had emerged, the Mayans, the Aztecs and the Incas.
The Mayan Empire
The Mayans started
an empire in modern day central Mexico. They
built great cities which featured pyramids and temples. The empire was ruled by priests and nobles.
Their economy was based on trade and agriculture. They were very skilled in mathematics, they
created a number system. They also created a calendar that has 365
days in it. This was based off of their observations of the orbit of the earth around that of the sun.
The Aztec
At first the Aztecs
were a tribe without a permanent home. Finally around 1300, they built a permanent
civilization in the city called
Tenochtitlán .
They grew crops needed for survival, such as beans on chinampas, floating artificial islands. They made these islands by building rafts and covering them with mud
from the bottom of the sea.
The Aztecs were very
skilled in politics, ruled by an emperor. They were very religious and held
many religious ceremonies to guarantee good harvests.
The Incas
At about the same
time, the Incas were building a civilization along the Andes Mountains. Much like the Aztecs they had one central
government, under the rule of an emperor.
Since their civilization was built on a desert, they built irrigation
systems to provide the needed water. The
Incas also cut slopes into the Andes Mountains to keep the soil from washing
away, remember soil is important for farming.
The Incas were known for their building skills, having constructed stone
temples that were used as fortresses. In addition, the Inca’s built the first suspension bridges made of rope and wood across deep gorges. They had no written records, and communicated using a quipu, a knotted cord of various lengths and
colors. Different lengths and colors meant different
things.
European
Colonization
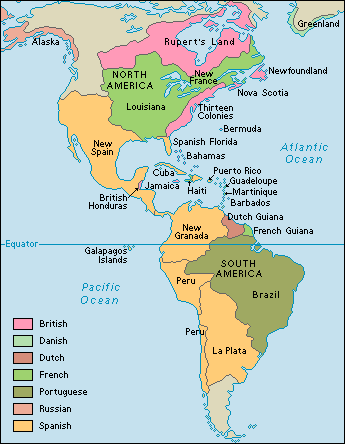
Seeking new trade
routes to Asia, the Europeans came to the Americas. The first two countries to
arrive were Spain and Portugal. In order to prevent conflict, the Pope created
the Line
of Demarcation, an imaginary line that runs from the North Pole to the South
Pole. All lands east of the line
belonged to Portugal; any land west of the line belonged to Spain. Portugal
claimed Brazil, while Spain claimed Central and South America.
Spanish Conquests
The trade routes
became a search for riches, but also to turn the Native Americans to
Christianity. The Spanish conquistadors
or conquerors easily defeated the Native Americans with their far more
advanced weapons. Spain created colonies
from Mexico to Bolivia as a way to mine for gold and silver. They built cities in the same locations as
the Native Americans did.
In the tropics, the
Spanish setup plantations in the highland areas, where the weather is cooler. Cattle
ranchers were established. The Spanish
used Native Americans to work on the plantations and ranches. When the Europeans arrived, they brought with
them diseases, which killed off the Native Americans. The Spanish now in need of new workers,
brought enslaved Africans to replace the Native Americans.
To rule the colonies
the Spanish created viceroys, or
governors to govern the
colonies. This was to make sure Spanish
law was enforced. A new social structure
was also created placing Europeans at the top of society and Native Americans
and Africans at the bottom.
The Portuguese
Brazil was colonized
by Portugal. Brazil had no precious
metals, but what it did have was brazilwood, a tree from which red dyes could be made. However, the land was perfect for raising
livestock. On the coastal lowlands the conditions were ideal for raising sugar
cane. Just like the Spanish did, the Portuguese relied on enslaved peoples to
work on plantations.
Independence
Movements
In the late 1700s,
the people of Latin America began to resent European rule. They were well aware
of the successful revolution that gave the United States independence. After seeing this, they wanted
independence.
The first
country in Latin America to gain independence was Haiti. Under the leadership of Toussaint L’Overture, Haiti overthrew the French and became an
independent nation in 1804. Under
leaders such as Simon Bolivar of Venezuela and Jose De San Martin of Argentina,
most Latin American countries achieved independence. Only Brazil became an independent nation
without experiencing a revolution.
Independence did not
come to the Caribbean Islands, except for Haiti. For example, Cuba did not win
independence from Spain until 1898, during the Spanish-American War.
Dictatorships and
Democracies
The wars for
independence created political and economic confusion, the same happened with
the Eurasian Republics and African Colonies. Leaders wanted to build countries that were
politically stable, but, political control was in the hands of a small group of
people, such as business owners and the clergy. The leaders were known as caudillos, or strong men. Though they promised to solve all the problems
faced by Latin America, they really only cared about the wealthy. It was very much like a dictatorship, governments ruled
my military force.
Industrialization
came to Latin America in 1940. With
industrialization came new wealth, but as you would expect the new wealth only
made the wealthy wealthier and the poor even poorer. The military governments
were opposed to change, and the cries for democracy, government ruled by the people would
become louder, except in Cuba, where there was a communist government under the
control of Fidel Castro. By 1970, the
economic problems still remained and that caused for increased demands for
democracy. By the early 1990s, new
democratic governments began to replace the old, harsh political systems,
except in Cuba.
Cultural Geography
of Latin America
The long and diverse
history of Latin America is the foundation of its culture. Beginning with the
Native Americans, each group that settled here had an impact on the region. As
these people came together, their cultures came together as well.
Religion
When the Spanish and
Portuguese came to Latin America, they brought with them Roman
Catholicism. The Catholic religion
remains a strong influence today. The
role of the Catholic Church has changed over time. At first, the priests came to convert the Native
Americans to Christianity. Not long
thereafter the Church became involved in politics, and became wealthy. When the independence movements started, did
the Church side with the wealthy or the poor? They sided with the wealthy. When these independence movements became
successful, the Church became committed to helping the poor and the suffering.
The Church also became active in the areas of land reform, education and
healthcare.
Healthcare and
Education
Healthcare and
education are serious problems for Latin America, while the situation is
improving, much needs to be done. Advances in medicine have led to better
health services, improved diets and better sanitations. This has all played a
role in Latin Americans living longer. The
infant mortality rate is decreasing and there are fewer diseases. However, in
many poor areas the advancements have not been experienced yet. In some places malnutrition, a badly balanced
diet, is a major problem. Malnutrition
can be caused by poor nutrition, not enough food.
Education
Education in Latin
America is a problem. The literacy rate, the percentage of people that
can read or write, is low. There are too few schools and many
unqualified teachers. Many children cannot attend schools because they need to
make money for their families. However,
advancements are being made. All
children now go to school for free for 12 years. In the past, only the wealthy went to school. In the country where changes are happening,
the literacy rate is over 90 percent! The challenge is to get all countries to
experience the changes.
The Arts
When the Europeans
were in power, it should come as no surprise that art was dominated by European
standards. Today, Latin American art
reflects its diversity. Since the Native
Americans arrived first, they produced the first art forms. They left a legacy of wood carvings and
paintings. They built temples decorated
with murals and mosaics.
When the Europeans
arrived all art was about the Europeans. When the Africans arrived, they brought with
them song and dance, such as one of the popular dances in America, the
“samba”. After the independence
movement, Latin American artists began mixing Native American art with that of
European art.
Leisure Activities
Latin American
places a high value on family ties. They
value their freedom and their cultures.
Their long history is a reason for this. Latin Americans belong to extended families, aunts and
uncles and other relatives besides their parents, brothers and sisters. Many social events occur in ones home.
Negatively, their quality of life
depends on their place in the social class. The problem is, a large gap still exists
between the rich and the poor.
As far as sports, Latin
Americans enjoy futbol, or soccer, it is seen as a way of life. In the last two
decades baseball is becoming very popular.
The Economics of
Latin America
Latin America
consists mostly of developing countries, countries that are in the process of becoming
industrialized.
Agriculture is the
foundation of the Latin American economy. Most countries in the region export,
or send things to other countries for sale, and their products come from
what the land can produce for them, this is called cash crop, a crop produced to
sell or trade. Brazil and Columbia are the world’s largest producers of
coffee. The physical landscape is
responsible for this, because
the volcanoes have fertile slopes, combined with the warm, moist climate that
makes the conditions for growing coffee terrific.
In the tropical
coastal areas, bananas are the key cash crop. Brazil and Ecuador are the
world’s leading producer of bananas. Brazil,
along with Cuba, is the world’s leading producer of sugar. This is why Latin America is so important to
the United States, because they produce the
products we use on a daily basis, products that our physical geography does not
allow us to grow.
Most Latin American
countries base their entire economy on just one cash crop. For example, the entire economy of Ecuador is
based on bananas. This is called specialization,
production of one product, but one produced well. A problem with specialization is if a
drought, a flood or a disease out break would occur, that would damage a crop, the
national economy would be in serious danger. The second problem with
specialization is that these countries use most of the land to grow cash crops,
and that leaves little land to feed a growing population.
Latifundia
and Minifundia
In the past many Latin Americans lived and worked in the countryside,
today that has changed. Today only about one-third of the people are campesinos,
those who live and work in the countryside. The farms campesinos work on are
divided into two classes, latifundia, a large farm owned by a family
or business that produces a large number of crops for sale. or a minifundia,
a small farm that produces food for a family or small village. The only thing these two types of
farms have in common is that the campesinos that work on them are all poor.
Industry
Everyone in Latin America recognizes the need to industrialize. Some are doing this at a faster rate, just
like with education and healthcare than others. Today service industries, business that produces a
service rather than a good, have grown sharply in the last two decades.
Mexico made great progress in becoming an industrialized nation. Among the goods produced in Mexico are
automobiles and electrical goods. In
fact, many American companies have created factories in Mexico to take
advantage of the low cost labor. Workers
in Mexico will work for much lower wages than American workers.
Brazil, like Mexico, has increased its industrial production. Like
Mexico, Brazil has many natural resources, a large workforce, solid systems of
transportation and a government that promotes the growth of industry.
Industrial
Development
Not every country in Latin America has been able to industrialize. In order to industrialize a country must have
money. Many countries in Latin America
do not have the money needed to build factories. Since there are no factories, foreign
companies have been unwilling to setup businesses. These countries also have unstable
governments and a foreign country will not invest in a country that has no
stability in its government. To
complicate matters even more, even if they could get stability in their
governments, these countries have a lack of manpower and few natural resources
needed to industrialize.
Trade
or Interdependence
Because many Latin American countries are dependent on cash crops, they
are unable to produce everything they need. As a result, most countries depend on trade
with foreign nations. Another reason for
interdependence is their desire to become industrialized. The region depends on outside sources for the
raw materials and other things needed to industrialize. This has led to major money problems.
Transportation
and Communication
The physical geography of Latin America, mostly because of the
mountains and other physical barriers, has made communications less
developed. Also, communication systems
cost money; and as you read earlier, many Latin American countries have little
money.
Roads
and Bridges
The building of roads and bridges has been slow and very difficult. For
example, the Andes Mountains are a barrier in which one cannot build a road or
a railroad through. Some nations like Argentina have developed highway systems.
On the flip side, countries like Brazil have few paved roads. Advancements are being made. A new series of roads known as the Pan-American
highway is under construction in Brazil. Its primary purpose is to increase the
development of the Amazon River Basin.
Railroads are used as a way to make up for the lack of paved roads. In
the Caribbean Islands, this only increases the problem because the railways
systems are very poor, as well.
Waterways
In certain parts of Latin America, waterways are the only way to
transport goods and services. A perfect example is the Amazon River Basin, which
produces the waterway needed for the transportation of goods and services. Some waterways have been built my man to help
with the transportation of goods and services, an example of how humans have
altered their environment. An example of this is the building of the Panama
Canal, which made it possible for ships to travel between the
Atlantic and Pacific Oceans without having to travel around South America.
Air
Travel
How does one travel when there are no roads or rivers? Yes, one flies over the unpaved roads.
Airlines provide fast travel over the rough geography of mountains and
forests.
Communication
Just like the vegetation and mountains have made it difficult to build
roads, it has made communication just as difficult. Millions of people use telephones to
communicate with each other. What may be
surprising to you is that many people have no phones. In fact, in some countries in Latin America
there are only 5-10 phones for every hundred people. Many countries are using televisions and radio
to communicate. It may be surprising for
you to learn that not every country has its own television station. Also, only ten percent of the people have
televisions. The major means of
communication comes from newspapers, yet in some countries the low literacy
rate has made newspapers useless.
Latin
American Environment
An ecosystem is a complex variety of life in a delicately balanced
environment. When humans
interact with their environment, such as by building roads, that changes the
ecosystem more than any other living organism does. No where in the world is this truer than in
Latin America. In Latin America, the
disruption of the environment is occurring all over.
The Amazon River Basin covers nearly 2 and half million square miles. It is the world’s largest rainforest. In
recent years people have become concerned about deforestation, the tearing down
and clearing away of the rain forests. We
estimate that 10 percent of the rainforests have been damaged.
There are several reasons why this is occurring, first, the Pan-American
Highway you read about earlier takes up large amounts of the rainforest so new
roads can be built. Secondly, in order
to feed a growing population, parts of the Amazon Rainforest have been cleared
out to make way for permanent farms. In
the past, farmers relied on a method of farming known as slash and burn farming, where
they cut down all the plants, strip the trees of its bark and set them on fire.
The ash from the fire deposits
the soil into the ground so it could become fertile, but, in two or three years
the soil is no longer fertile and crop production drops. The farmers most now find a new place.
Slash and burn techniques are also used to create cattle ranches
because grass grows well in burned soil. However, that only lasts a limited amount of
time. Another activity that has led to
the deforestation of the rainforest is commercial logging. Much profit is made from the selling or
trading of timber.
Deforestation, according to many scientists, have unknown long term
damage that may be impossible to overcome. In order to help slow down the effects of
deforestation, a policy of reforestation, the replanting of trees when
deforestation has occurred, is being pushed. However, reforestation is not occurring at a
fast enough pace because the demand to develop the resources of the Amazon
River is increasing.
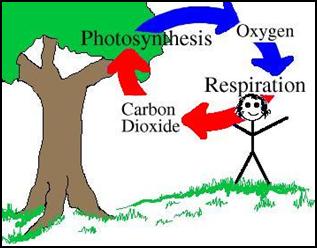
There are many problems that deforestation brings, not everyone can agree on all of them. Deforestation is leading to the decrease in the oxygen cycle because trees take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen. If there are fewer trees the oxygen cycle can become unbalanced. The reason is that there would be fewer trees to take in carbon dioxide.
Another concern is that by cutting down the rainforests, you are
reducing the amount of shade the trees and plants create. This in turn is causing the temperature of
the earth to rise. Deforestation will also lead to many species of plants and
animals to become extinct. We have
learned in many parts of the world, Asia being one, that the forests provide
much needed medicines. If deforestation
continues at the current pace, the plants will become extinct; the region will
not have access to the needed medicines.
No one knows what the effects will be. Latin Americans are now trying to use the
resources of the Amazon River Basin. Laws
are being pushed to control fishing, mining and logging. This will, however, have a negative impact on
the economy because these industries provide jobs. It is a double edged sword.
Population
Growth
Cities in Latin America have experienced a boom in population growth.
Mexico City is home to nearly 25% of Mexico’s population and the
second-greatest population of any city in the world! With this boom come new challenges, many you
have read about earlier. The most
serious challenge is that of poverty. Many people left their rural farms hoping to
find jobs in the city. However, the
cities were overcrowded and jobs were few and far between. Mexico City had an
unemployment rate of nearly 50 percent!
The second challenge is that of housing. The number of people living in urban areas far
exceeds the number of houses and apartments available. This has led to the rise of slum cities, in
Argentina these are called villas miserias. In these cities houses are made of cardboard,
where there is no running water or electricity. You may think of these as Hoovervilles that popped up in the United States during
the Great Depression. In urban areas,
pollution is a constant challenge because rapid urban growth has caused a great increase in the amount of pollution from automobiles, and factories. The
air is so bad that many people cannot even go outside!
The leaders of Latin America are aware of the problems of the cities and are actively trying to solve them. The government is asking businesses to move outside of the cities to create more space and to promote tourism, which will create jobs. They are trying to improve farming and are asking farmers to move back to the rural areas. To solve the problems of air pollution, a new subway system is being built and to help purify the air, trees are being planted.
The problems of Latin America are plenty, and it will take sometime to
solve. The problems seem to feed off one
another and this makes things even more difficult to solve.
 |
| Unit 17 Main Points Worksheet |
| Unit 17 South America: Human geography Article and Quiz |