ECONOMIC
GEOGRAPHY OF THE MIDDLE EAST
Unit Overview
The
student will learn about the economy of the Middle East, its climate, land,
water production, and the source of food.
In addition, the student will learn reasons for the growth of
transportation, communication and industry, as well as learning the importance
of oil.
Much
like the culture of the Middle East varies so much; the same can be said for
its economy. The reasons for the
variation can be found in each country’s history or geography. As we discussed in the previous unit, the
growing population has made it difficult for the region to meet the needs of
its people. However, the problem is a
difficult one to solve because each country has a problem unique to
itself. Examples of this can be found
when studying Afghanistan; because Afghanistan has a difficult time feeding its
people since only 15% of its land is suitable for farming. However, when we examine the countries along
the Mediterrean Sea, they can produce enough food and be able to use the
surplus to trade for other things they cannot make on their own. The countries along the Mediterranean Coast
can produce cereal crops, fruits and even dates.
Livestock
The
second source of food comes from the over 300 million livestock, cattle and
sheep, living in the region. However,
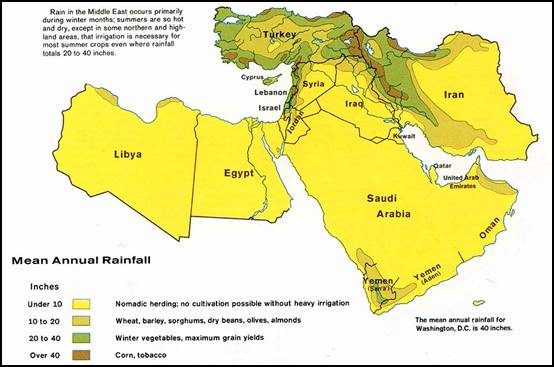
the climate of the region makes this difficult for some countries. By looking at the countries of Turkey and
Saudi Arabia, this becomes very clear.
Turkey has the required rainfall and the land is suitable for grazing or
for the animals to feed, while Saudi Arabia is so much larger one would think
they grow more livestock. But, that is
incorrect to think. The region is almost
all desert, therefore animals are unable to graze. This is the reason why Saudi Arabia can only
produce 10% of the livestock that can be found in Turkey. The effects on geography has a great impact
on a countries economy, these differences cause countries to become
interdependent on one another.
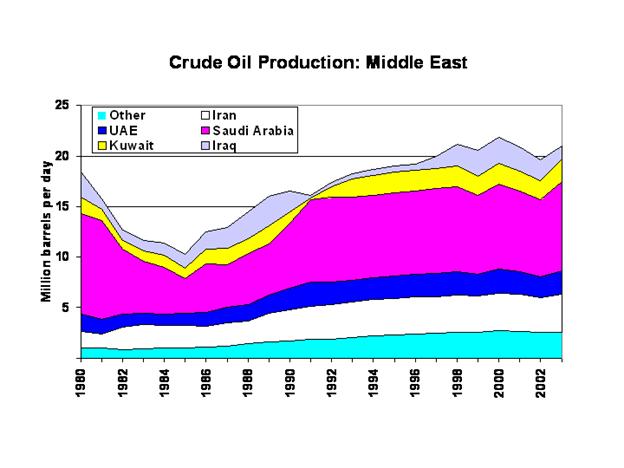
Industrial Growth
What
do you think of when someone talks about the Middle East? Yes, the answer is oil. Oil is the most important natural resource to
be found in this region. As much as 60
percent of the world’s oil is found in the North Africa and Southwest
Asia. However, oil is even more
important than you might think. What
does it take to run a factory? I you answered oil, you are correct, because oil
is needed to help run the machines. This
is why the region has experienced much industrial growth. Iran and Saudi Arabi have created large oil
refineries and shipping industries. Some
countries use oil to create products based on petrochemicals, products’ made
from petroleum and natural gas. Many
of these products you use on an everyday basis, such as fertilizer, plastics,
medicines and paints.
Remember
the era of imperialism; you learned the region is rich in diamonds. The oil industry has helped create diamond
cutting industries. This growth in
industry has improved the standard of living in many of these countries.
|
|
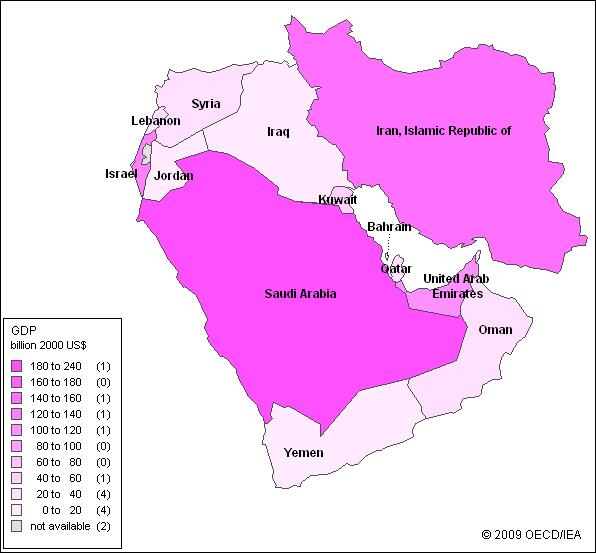
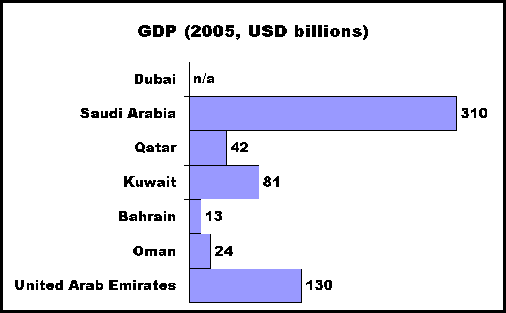
Service Industries
Just
as the name says, the service industry includes banking, insurance and
tourism. In the country of Bahrain the service
industry accounts for as much as 60% of the gross domestic product or GDP,
the value of goods and services created in a country in any given year. The map below will give you some idea
of the GDP in the Middle East. As
we said, the Middle East is the cross roads to the world. What would you think the biggest service
industry is? Yes, tourism, mostly
because of its close proximity to Europe.
In addition, the monuments, pyramids and other religious sites draw
millions of people each year. However,
like we said earlier, this does not apply to all the countries in North Africa
and Southwest Asia. Some countries have
governments that discourage tourism because there are human rights violations. Also, in some countries there is so much war
and violence that discourages tourism, which is another example of the
diversity of the region.
|
Map Energy Indicators - Middle East - Gross Domestic Product 2006 |
|
|
Transportation and Communication
The
systems of communication and transportation are growing rapidly; most of the
development that is happening is going along the Mediterranean coast, because
it provides easy transportation for goods and services. Roads are used to connect the major cities with
oil fields. The countries with the most
roads are Iran, Turkey and Egypt. However, in some areas, there are not as many
roads because of the mountains and deserts, therefore making roads in these
areas very expensive. But, there is
increasing number of vehicles, so road construction is a priority.
Even
though roads are not built in many countries, life still must continue. The addition of railroads and airlines has
allowed this to happen. Railroads now
connect many urban areas with seaports and industrial areas. After World War II, the area benefitted from
the development of airlines, on benefit is that this is the area of the
crossroads between east and west.
Another benefit is that trade has also increased so much in Europe,
North America and Asia. A third reason
for the development of air travel is total size of the area; air travel has
made travel time shorter. A new method
of transportation was essential and without air travel how would goods get
exchanged with North America?
The
physical landscape has required the development of pipelines to transport
oil. Obviously, trucks cannot drive
through deserts and mountains, and in those areas you cannot just get rid of
the mountains. Pipelines have been
developed to allow the oil to flow through the mountains and deserts and at the
end of the pipeline tanker trucks await to take the oil to the seaports, or
refineries or where ever oil is needed.
How
do we communicate with others? Yes,
through cell phones and television. The
use of phones and television has become a major means of communication. However, telephone communication is somewhat
difficult because of the mountains and deserts.
|
|
|
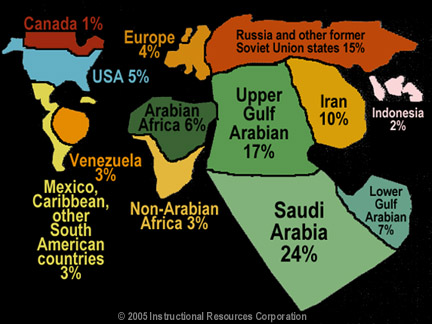
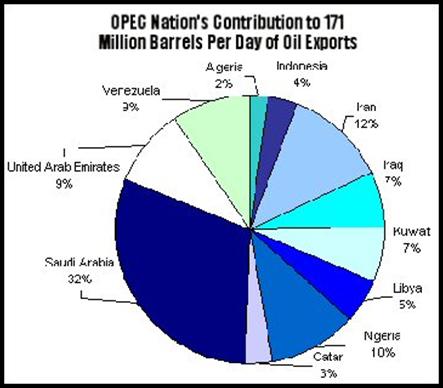
A graphic map of world oil reserves,
showing the importance of the Gulf reserves. Saudi Arabia's control of nearly
a quarter of the world's petroleum assures its place in global affairs into
the next century. Traditionally the most influential member of OPEC (the
Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries), Saudi Arabia demonstrated its
ability to manipulate the price of oil in the 1980s. |
Interdependence
The
geography of the land has created wealthy and poor countries. Though, it has created a system of
interdependence in which the wealthy countries help the poor countries. They have given loans to poor nations so
schools and hospitals could be built.
An
example of countries becoming interdependent on each other can be found with
the formation of OPEC, Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries. These countries work together to set
and control oil production and prices.
In the 1970s, OPEC used the problems in the Middle East to place an embargo,
or stopping the oil shipments to the United States so it could raise
the price of oil. Recently, the price of
oil has dropped because of the economic problems and because of newer
technology that has allowed countries to become less dependent on oil.
People and Their Environment
In
the first unit, we learned that 70% of the world is covered by water. One is wrong to think there is enough water,
because 97% of that water is salt water.
And, salt water is not suitable to drink because if one drinks saltwater
they will become dehydrated. By 2050,
about 50 billion people are expected to be living on the earth. There will be no additional water available,
so people will need to share and conserve.
Providing
water for the people of North Africa and Southwest Asia is very difficult. Only the Nile, Tigris and Euphrates Rivers
have freshwater. Turkey, Egypt,
Syria and Iraq have good access to freshwater, since they draw from aquifers,
(underground layers of rock and gravel that contain water). Libya is trying one of the most
ambitious methods to obtain water. The project, known as The Great Human Made
River, carries water from two large aquifers that are located beneath the
Sahara Desert and irrigates farms areas near the Mediterranean Sea. However, the Great Human Made River idea is very expensive. This obviously is not the answer for the
poorer countries in the Middle East.
Some nations have started using a process known as desalination (the removal the
salt from sea water). Desalination uses distillation to
remove the salt by boiling seawater.. Kuwait was the first state to adopt seawater
desalination and has produced over 3.4 billion gallons of freshwater. The Middle East continues to play a leading role in the desalination industry and produces 60% of the world's total output. To read more information about the seawater desalination, click on the PDF.
Environmental Concerns
 The new
technologies, along with the wars that have been fought have had severe
consequences on the environment. For
example, the building of dams and the need for hydroelectricity have had major
consequences, just as what happened with the construction of Aswan High
Dam. With the Aswan High Dam being
funded with the help from the Soviet Union, this became an expression of
political tension in the 1960's.
The new
technologies, along with the wars that have been fought have had severe
consequences on the environment. For
example, the building of dams and the need for hydroelectricity have had major
consequences, just as what happened with the construction of Aswan High
Dam. With the Aswan High Dam being
funded with the help from the Soviet Union, this became an expression of
political tension in the 1960's.
In
order to control the flooding of the Nile River, to improve irrigation, to
create hydroelectricity and to help the fishing industry, Egypt began the
building of the Aswan High Dam. The Dam
was successful in creating the power Egypt needed, but, it came at a
price. If you remember the floods of the
Nile created soil suitable for farming. If a dam blocks the floods how does the
land become fertile? It does not, so the
Egyptians were forced to use the expensive fertilizers to maintain the
soil. This increased the costs of
farming, and people had to pay higher prices.
The dam also prevented the salt water from being washed away. If that were not enough, the livestock were
damaged as well. Parasites lived in the
Nile and when it flooded the parasites would be washed away towards the sea.
Now, there is a dam, so the parasites just remain there and many livestock have
died from diseases caused by the parasites.
Today, Egypt is still trying to overcome the negative effects of the
dam.
Persian Gulf War
The
Persian Gulf has been the home of many conflicts, most recently the two wars
fought between the United States and Iraq.
In 1990, Iraq invaded oil rich Kuwait for control of the oil. The United States, with the help of the
United Nations helped drive Iraq out of Kuwait. Though, it came at great
expense as Iraq burned a large number of Kuwait’s oil fields, they also dumped
a large number of oil into the Persian Gulf and the affects are still being
studied.
As
you read, this region is a region that is very diverse. Diversity can be found in the lack of
consistency in areas suitable for farming and industry. This lack of consistency has led to many
nations becoming interdependent on one another.
This has led to the creation of many new roads and improvements in
communication.
The
increase in population has forced the region to make difficult choices. In
order to provide water for the people, they have had to modify their
environment. Continuing conflicts as the
Persian Gulf War have provided consequences that are still unknown.
A
quick glance at countries data is in the following chart.
|
Table: Chart Study |
|||||
|
Country |
Population |
Growth
Rate |
Literacy
Rate |
Imports |
Exports |
|
Egypt |
58.9 |
2.3 |
48% |
Food |
Petroleum |
|
Iraq |
19.9 |
3.7 |
60% |
Machine
vehicles |
Fuels,
energy |
|
Israel |
5.4 |
1.5 |
92% |
Consumer
Goods; polished diamonds |
Machinery
Chemicals |
|
Kuwait |
1.3 |
3.3 |
74% |
Manufactured
Goods |
Petroleum |
|
Saudi Arabia |
18 |
3.2 |
62% |
Machinery |
Petroleum |
 |
| Unit 10 Main Points Worksheet |
| Unit 10 Dams |