
THE HUMAN ELEMENT
OF GEOGRAPHY
Unit Overview
This unit will explore elements of determining population statistics of the world, cultural regions and economic systems.
The World Population
There are close to 6.5 billion
people living on the Earth. By the year
2050, the population is expected to grow to 9 billion. You might be surprised to learn that this
increase has not always been in the case.
Between 1800 and 1950, the population of the world has doubled. Why?
The reason for the increase in population is that the Industrial
Revolution occurred.
Few events in history have had as great an effect on people’s lives as the Industrial Revolution that began in the late 18th century.
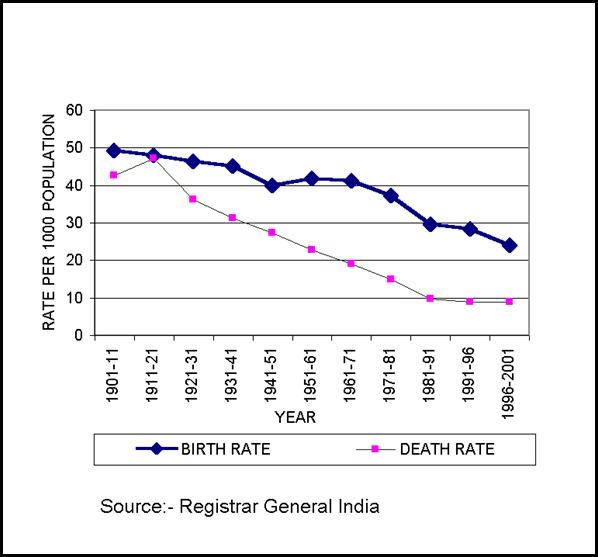
The Study of Demographics
Demography is the study of
populations. We use statistics to learn
about trends in population. The birth
rate is number of births per 1000 per year.
The opposite of birth rate is the death rate. The death rate is the number of deaths per
1000 per year. The natural increase is the difference
between death and birth rates. If there
are more birth rates, we are in a period of population growth. If there are more death rates than birth
rates, the period is known as a negative population growth. If the birth and death rates equal out, the
period is called zero population growth. By knowing the demographics of a nation,
we can determine many things. We can tell if the country is an industrialized
nation, whether it has mass poverty or if it has a solid system of healthcare.
Population Growth
Population growth does present
many challenges for a nation. As the
population increases, it becomes more difficult to ensure the country has
enough food to feed the population and there are enough homes for people to
live in. However, it is not all bad when
we talk of population growth, countries that experience population growth have
high levels of technology and they have quality agricultural systems that allow
them to produce food at a faster pace.
There is good and bad when talking about population growth.
Negative Population Growth
Much like countries that
experience positive growth in their populations, there are many challenges for
those who experience negative population growth. These countries have a difficult time finding
workers to help keep the country going.
How can a country produce goods, if they have no workers to produce the
goods? These countries have to depend on
people from other countries to work in their country. What happens when people from different
countries come in contact with each other?
Sometimes, conflicts do happen.
Those conflicts are the reason why there is a negative population
growth.
Population Density
We use the concept of population
density, which is the average number of people living in a square mile or
square kilometer, to determine how crowded it is in a region. To determine the population of a region we
divide the population by its total land area.
A country like Canada has a very low population density, which means
there are fewer people per square mile.
A city like New York has a large population density, there are more
people living per square mile. In
addition, on the map, countries in Asia have the highest population
density. The map below will help you
answer some questions.
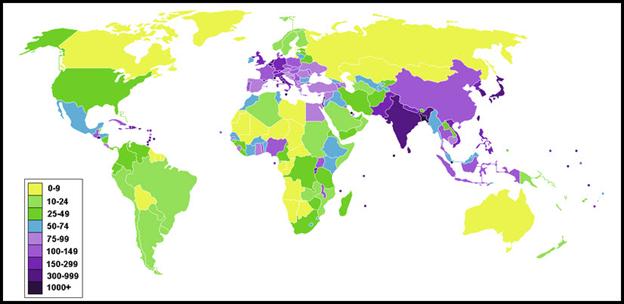
Population density (people per
km2) by country, 2006.”Every day the world’s population grows by approximately
200,000 people. That means every 40 days the planet adds enough new people to
replace the entire population of New York City” Joel E. Cohen
Population Movement
Migration is the movement of
people from place to place. During the Industrial
Revolution, many people moved from rural areas to urban areas (cities). This process is called urbanization. The reason urbanization occurs is the
desire for people to find jobs, we know from our studies in history that the
Industrial Revolution provided these jobs.
People also migrate to new countries. Why did people want to come to
America? People wanted to come to America for better opportunities, so they
could enjoy the freedoms we have.
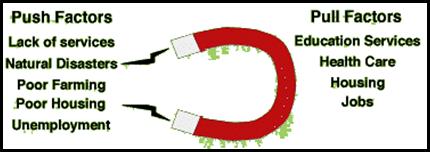
When people leave an area for
certain reason, those are known as push factors. Push
Factors could be anything, perhaps there are no jobs in that area. Reason people migrate to other areas are
called pull factors. Pull factors
may be the amount of jobs that are available.
The diagram below explains push pull factors.
Another example of why people
leave an area is because of Natural disasters, like Hurricane
Katrina, that struck New Orleans in 2005.
The people who lost their homes because of the hurricane had to flee to
other places to find a place to live. As
these people left New Orleans to go to other places, they were called refugees.
Global Cultures
Not only do geographers study
locations, but they also study culture. When we use the term culture, it
means a way of life for a group of people who share similar beliefs and
customs. People may share the same language, music, and religion, but let’s not
forget that government, social groups and economic systems reflect cultures in
many parts of the world. People organize communities by developing their
way of life and they change based on cultures. Today many people are
struggling to maintain their cultures, as we have become a global community.
Elements of Culture
There are five elements of
culture:
1.
Language
2.
Religion
3.
Social
Groups
4.
Government
and the Economy
5. Culture Regions
Language
Language is the key to
everything. It is because of language
that we express ourselves, communicate with others. Even within an individual culture, people may
speak a different language, or a different way of pronouncing words. People who study language are called
Linguists. Linguists organize the
world’s language into language families; these are simply large groups of
languages.
Religion
You have seen how differences
in religion have led to various conflicts.
The attacks on 9/11 are just one example. These attacks are because religious beliefs
are different throughout the world.
People use religion to define
themselves; they celebrate holidays based on what their religion believes. Some of the major religions are Christianity,
which may include Roman Catholics and Protestants or other religions such as
Buddhism, Hinduism, Islam or Judaism.
Social Groups
In your life you there have
been times where you have had to depend on friends to meet your basic
needs. That is why we call it a social
group. Within cultures, there are social
classes. A social class is group of
people ranked tog ether according wealth, education, religion and a variety of
other items. Social groups are members
of the same culture that work together to meet a basic need. Cultures include ethnic groups, people who
share a common language, history or place of birth.
Government and the Economy
Governments share certain
features and similar responsibilities as one another. Each government is responsible for
maintaining security, law and order within its own country and also protects
its people against invasion from a foreign country. They also provide services to those who are
in need.
Governments are organized by
levels of power such as national, state and local levels. As people get broken
down into social classes, governments are also divided up- into levels of power,
and the types of power of leaders. Is it
possible for a national government to solve local problems? Of course not, this
is why governments are broken down into levels.
Societies have economic
systems. Geographers use economics as
way of studying people. Much can be
learned about a group of people by looking at their economic system. They look at the way they use natural
resources to satisfy their needs. Do
they enjoy the freedom of buying and selling as they wish, or does the
government do that for them?
Cultural Regions
To help better understand the
development of cultures, geographers often divide the Earth into cultural
regions. These regions could be based
on economic systems, social groups, languages, religions and governments found
in the region. By studying their history
we see how regions often share many influences.
Cultural Change
Cultures change for many
reasons. They could be internal changes such as new technologies being
introduced. If you are taking the course, new technologies have influenced how
you educate yourself. These changes
could also be external such as changes resulting from war and trade. When new knowledge spreads from one culture
to another, it is called cultural diffusion.
The Agricultural Revolution
Cultural Diffusion has been a
major factor when we look at how the world had developed. Many humans had no home, they often moved
from place to place. These people are called nomads. Why did they move from
place to place? They moved from place to place to find food. As the climate warmed, these people began to
settle in cultural hearths. Cultural
Hearths are the centers of civilization where ideas can be spread and
practiced. Think of these as market places.
These early Cultural Hearths all had mild climate and fertile land for
farming.
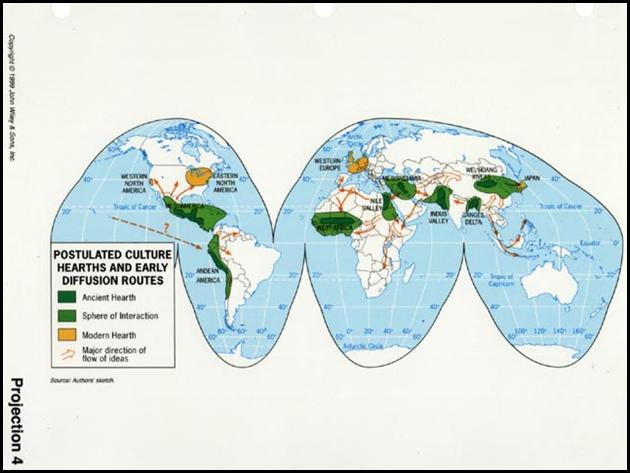
The rise of cultural hearths
led to having a surplus of food. Why is this important? What happens when you have more than you need
of something? When there is more than
what is in demand, people trade for something one does not have enough. This has led to the rise of cities. As you read earlier in this unit, governments
must be broken down, creating the need for local governments.
What can happen when cultures
come in contact with each other? There
can be conflict. We know that
differences in beliefs have led to many wars.
People have migrated or moved from region to region to avoid these
wars. Some migrated because there are
more opportunities in other cultural hearths.
What happens when people migrate?
They bring with them their cultures and new ideas. This is how the process of cultural diffusion
works.
Industrial and Informational Revolutions
As people continued spreading
ideas, people began to learn about revolutions in technology. As you probably have studies in World History
the world has gone through an Industrial Revolution. The idea of the Industrial Revolution is that
we now can mass-produce products. This
allows people to buy more of what they need and at cheaper prices. Many people moved from their farms to cities
(where factories were located) this has led to even more exchanges of cultures
and ideas.
Political and Economic Groups
As countries have become
interconnected, we have the seen the rise of Unions (such as the European
Union, a political and economic union of twenty-seven member states, located primarily in Europe)
that use the strength of their economy to help countries with weaker
economies. Today, there are over 200
countries that vary in their size, natural resources, and population.
Levels and Types of Government
Each government has its own
characteristics. Some countries have
what is known as unitary systems. This means that all powers are given to the national
government and there are no local governments.
Other countries like the United States have three levels of governments.
The Federal
System powers are divided between national, state and local
governments. The national government is
the most powerful level.
All governments belong to one
of the three major groups:
- Autocracy- Rule by
a single person
- Oligarchy- Rule be a few people
- Democracy- Rule by many people
There are many forms of
autocracies. One such form is a Totalitarian government, in which
the decisions of a single person determine how the government will be run. In a totalitarian government the ruler
controls every aspect of a person’s life, sometimes called a dictatorship.
A Monarchy is the second
form of an autocracy. In a monarchy the
leader has the title of King or Queen.
There are two types of monarchies:
- Absolute
Monarchy- Where the
ruler has complete and unlimited power
- Constitutional
Monarchy- The
leader has limited power.
An Oligarchy is where the
government is ruled by a few people. The
group could be made up of military or social leaders. There are some freedoms for the people. However, the group in charge determines what
those freedoms may be.
Democracy means rule by the people. The power of the ruler comes from the
consent of its people. This may sound
similar to the ideas of the Enlightenment because it is where the idea
came. There are two types of democracies,
Representative democracy and Direct democracy.
Representative democracy is where people elect representatives to make
decisions for the people and the other type of democracy is Direct democracy in
which people meet in small groups in communities to make decisions for the
betterment of those involved.
Click here to read more about “The Enlightenment”. On this website, it states, “today the Enlightenment is often viewed as a historical anomaly, a brief moment when a number of thinkers infatuated with reason vainly supposed that the perfect society could be built on common sense and tolerance”.
Types of Economies
Each nation creates an economic
system that answers a basic fundamental question. The question is in three parts: what
to produce, how and who should produce it, and who will buy and consume it?
Let us examine the four types of
economic systems:
1.
Traditional
Economies
2.
Market
Economies
3.
Command
Economies
4.
Mixed
Economies
Traditional Economies
In the traditional economic system, that
fundamental economic question (we will refer to this throughout the unit) is
answered by persons’ beliefs, religion, customs or even a family’s
history. In a traditional economy a
business could be private (like a family car dealership) that gets passed down
from generation to generation.
Therefore, in a traditional economy, the people usually do what their
family has been doing. These types of economies are often found in Asia, Africa
and Latin America.
Market Economies
In a market economy the fundamental question
is that the government does not decide what to produce, how it should be
produced and who will consume it. That question
is answered by the people and only the people.
You may have heard it called capitalism or the free market system. In this system private businesses have the
right to decide. We say the United States is a market economy.
Command Economy
On the opposite end of a market economy, is
the idea of a command economy, in which the government has total control of the
production, sale, and consumption of products.
It is the government and only the government that answers that
fundamental economic question. There are
two different systems of a command economy.
1. Communism - Encarta’s Online Encyclopedia’s definition
is that communism is a system of social
organization in which all economic and social activity is controlled by a
totalitarian state dominated by a single and self-perpetuating political party.
2. Socialism
- Encarta’s Online
Encyclopedia’s definition is that socialism is an economic
and social system under which essential industries and social services are
publicly and cooperatively owned and democratically controlled with a view to
equal opportunity and equal benefit for all.
A mixed economy is one that combines features
of a traditional, command and market economy. In this system, there are still privately
owned businesses, there are still opportunities to buy and sell stock. However, there is government intervention
that does the thing people cannot do for themselves. An example might be welfare; this is what
happens when someone cannot afford the basics?
Government will supply the people with the money they need to
survive. Another example would be social
security or disability; this makes sure people have money as income, even if
they cannot work.
Resources and Our
Environment
As we become more
interdependent on each other, our natural resources are traded around the
world. However, there are cases in which
we have misused our resources and caused pollution.
Resource Management
We learned in previous units
that the Earth provides the elements necessary for life to survive. These are not made by man, but by the Earth.
These are called natural resources. We
learned the resources that can replenish are called renewable resources and
those that cannot be replaced are called non-renewable resources. We have to remember that our natural
resources must be managed to ensure future needs. Natural resources are very valuable and improve
everyone’s lives. We must learn to use
our resources wisely if we wish to keep our balance of life with the Earth.
Economies and World Trade
Those countries that have
different levels of economic development have become more interdependent
through trade. As you can tell from the
map below, countries specialize in economic activities that are best suited to
their resources or locations. As you can
see on the map, the Middle East and Northern Africa have the world’s largest
oil supply.
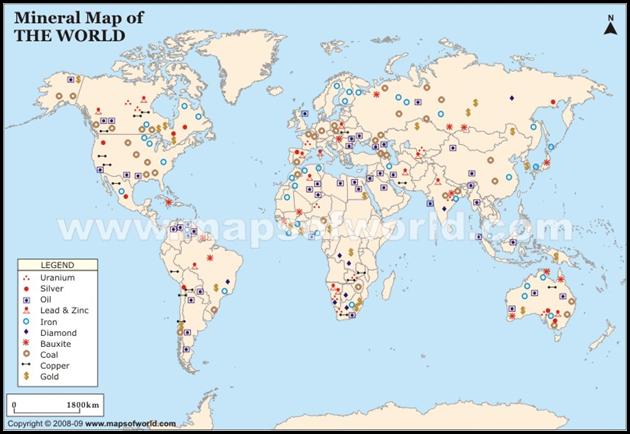
Geographers classify the
economic activities of the world into four types.
- Primary
economic activities- Directly using natural resources
- Secondary
economic activities- Using the natural resources from the Earth to produce
something to sell or trade
- Tertiary
Economic Activities- These activities provide services to people such as
medical and legal services.
- Quaternary
economic activities- These activities produce and distribute information.
These economic activities also
include industrialization or the spread of industry. Those nations that have industry are called
developed countries. Those countries that are working towards industry are
known as developing countries.
World Trade
As we have said before the
unequal distribution of the Earth’s resources have led to world trade. Countries that cannot produce what they need
turn to trade. The rule is one always trades what is has more of for things
they have less of. The idea of world
trade is important because many countries have what we call subsistence
farming. In subsistence farming one
produces only what it needs to survive.
The rest of what they need comes from farming, but there is little or no
profit for the farmer.
Another consideration could
include the cost of making something. For example, why make it yourself, when
it may be cheaper to trade for it. When
a country sends a product to another country that product is called an export.
On the opposite end when a country brings in a product from another country, it
is called an import.
Trade is not that easy. There
are many barriers to trade. Governments
may charge a tariff or tax on things imported.
They could also create a quota or limiting the number of goods one can
import. These barriers are all designed
to create jobs in their own countries. If we could only import 10 foreign cars,
how would everyone else get a car? We
would have to make our own, that would create the need for workers. In recent years countries have attempted to
remove these barriers. The United States
entered into agreement known as NAFTA, or the North American Free Trade Agreement. According to an article in Encarta Encyclopedia, NAFTA is
a pact that calls for the gradual removal of
tariffs and other trade barriers on most goods produced and sold in North
America. North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) became effective in
Canada, Mexico, and the United States on January 1, 1994. Read more in the PDF File.
People and the Environment
The gains in technology have
been great. They also have had negative
impacts. Pollution of water, land and
air threatens the health of all living things.
Forests are being destroyed, species are disappearing, and deserts are
growing. The safety of nuclear power
plants and nuclear waste and the methods of disposing them have caused
additional concerns.
Pollution
Pollution is the contamination
of the environment, including air, water and soil. It is harmful as well to plants
as well as other animals. Factories and
automobiles send fumes and gasses into the air.
These could cause respiratory diseases.
We pollute water with the use of fertilizers and pesticides we read
about earlier. These substances can lead
to cancers or even death. For this
reasons, many nations have created rules for air and water quality. These byproducts are the price we pay for the
quality of our lives.
EPA,
the Environmental Protection
Agency, is an Independent agency of the United States
government, responsible for protecting the environment and maintaining it for
future generations. It was established in 1970.
Read more on
protecting our environment by clicking on an EPA (Environmental Protection
Agency) article from Encarta Encyclopedia PDF
File.
Additional information on how
the United States Environmental Protection Agency writes regulations can be
found by clicking on the EPA website https://www.epa.gov/laws-regulations or
click on the PDF File.
The Ecosystem
As you have
read, our ecosystem is in danger. We
must learn to use our resources wisely if we wish to keep our balance of life with
the Earth. To read more about the human
impact on our natural environment, click on PDF File.
In
Summary
Demography is the study of
populations. The results of the study
explain changes in society and how it has affected people.
Population can be measured in
terms of density, or the average number of people living in a square mile or
square kilometer.
The five elements of culture
are language, religion, social groups, government and economy and culture
regions.
There are four types of
economic systems, which are Traditional, Market, Command and Mixed Economies.
We have to remember that our
natural resources must be managed to ensure future needs.
Those countries that have
different levels of economic development have become more interdependent through
trade.
Careless use of resources is
a threat to our environment.
 |
| Unit 4 Main Points Worksheet |
| Unit 4 Population Growth |