
LOOKING AT THE
EARTH
When
Neil Armstrong walked on the moon, he said the earth was “like a beautiful jewel in the
sky”, because he felt the earth was seen as land and water coming together with huge
swirls of clouds.
How the Earth is Viewed from Outer
Space
The surface of the earth is made of water, land and surrounded by
air and there are many differences between the height and depth of the earth’s
surface. The earth is part of a system
of planets that revolve around the sun.
Apollo 8 mission, astronaut Bill Anders said, “We came all this way to explore
the Moon, and the most important thing is that we discovered the Earth.” The view of the earth from
space has expanded our understanding of how the planet works.
A view of the Earth as seen by the Apollo 17 crew
traveling toward the moon.
The
Solar System
Earth
is part of the solar system, made up of all objects that revolve around the sun
and is the only planet in the solar system known where life exists. The sun is the center and largest object of the
solar system, and the earth is the third planet from the sun. Its great mass, the amount of matter it
contains, keeps objects revolving around it.
Earths Measurement
Earth
is about 93 million miles from the Sun.
The diameter of the earth at the equator is about 8,000 miles and the
distance is shorter at the poles of the equator. Earth is considered one of the smaller
planets, yet it is the largest of the terrestrial planets in the Solar System
in diameter, mass and density.
Water, Land and Air
About
70 percent of the earth’s surface is water.
The ocean, lakes, rivers and other bodies of water are the part of the
earth known as the hydrosphere, which is a key to the water cycle. The other 30 percent of the earth is made up
of land. The land makes up the part of
the earth known as the lithosphere, or the earth’s crust and upper
mantle. The
earth’s crust is the outermost part of the lithosphere and underlying the crust
is the upper mantle, a relatively brittle part of the earth’s interior. When
someone states that everyone and everything live together on the surface, this
is known as the biosphere, the part where life is found. The atmosphere or air surrounds the planet Earth with
a mixture of gases that become thinner and fades into space. Some examples of how the atmosphere works, is
that it absorbs energy from the sun, recycles water, works with climate
control, protects warming of the surface through heat retention and helps reduce extreme temperatures.
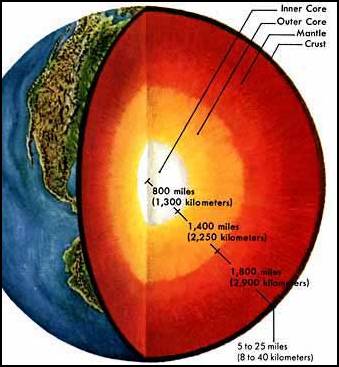
The Structure of the Earth
The
earth is made up of three layers, the core, the mantle and the crust. The core, which makes up the
center of the earth, is divided into an inner core and an outer core
that is a hot metal made up mostly of nickel and iron. The mantle is a layer of dense hot rock that is
the thickest layer of the Earth. The
outer layer, next to the mantle, is the crust.
The crust is a thin layer of rock that floats in the upper mantle and includes
the continents and oceans.
All of your life you have learned that you live on Earth, a planet in the solar system orbiting the Sun with an atmosphere that contains oxygen. But how much do you really know about the various features of the Earth that make it the unique planet that it is?
Click on the Britannica link below to learn more.
School Access ID - vla
School Passcode - student
Internal Forces
As
time went by, the surface of the earth has changed greatly. Even now, you may not be aware of it, but the
surface of the earth is changing as this unit is being read. Plate tectonics or as most scientists would state that
moving plates are large slabs of rock and when plates spread apart, gaps form
in the surface. What happens when the
plates come together? When plates come
together, a trench forms because the plates slide underneath each other.
Have
you ever experienced an earthquake? An earthquake
is a sudden movement in the plates and as these movements change the
surface of the land and the floor of the ocean, they trigger
landslides and occasionally volcanic activity.
Volcanoes are mountains
with lava,
melted rock that rises through the crust of the earth and lava of intermediate composition form something known as block lava, which is when
the lava is too block, then the flow
of the lava is blocked and pressure builds up.
What happens when something has too much pressure? When something has too much pressure, it will
explode with great force, the same applies with volcanoes. Volcanoes are mostly known because they are
above sea level, but it is said that the majority of the volcanoes lie beneath
the sea. Internal
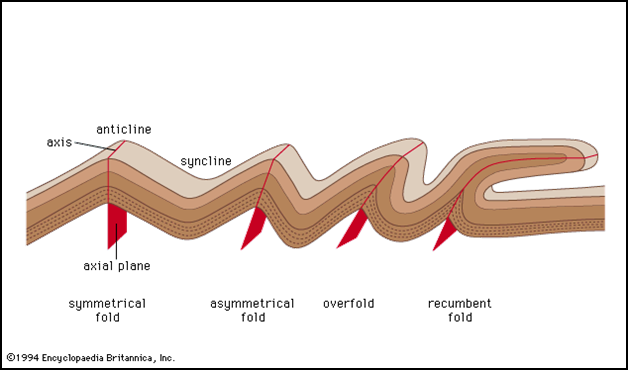
forces can break down surfaces as well. Folds are bends in layers of rock and when the plates
squeeze the surface of the earth and pressure is applied for a long period of
time, the surface slides and the rock bends instead of breaking. Other
internal forces are faults, a
break or a crack in the earth’s crust where there is movement. Faults are usually called a lateral
fault when the movement is along the center of the earth, a normal
fault, when the crust has been extended during a vertical movement or a
reverse
fault, which is opposite of a normal fault during a vertical
movement. Normal
and reverse faults are examples of dip-slip faults, where the movement
along the fault is in the direction of dip. These breaks occur when the land around the fault
cannot fold any more. Have
you heard of the San Andreas Fault in California, when sudden movement along
the fault caused the great San Francisco earthquake and fire? Where
Is It? The figure below
shows the general location of the San Andreas Fault and several other major faults
in California. Read
more information on San Andreas Fault by clicking on the following link PDF
File. Both
volcanoes and earthquakes are the cause of tsunamis, or sea waves that move through
water, with some of the waves being over 50 feet high. Earthquakes
occur when different plates meet each other. Many earthquakes occur in the Pacific Ocean, an area called the Ring
of Fire, a boundary where the plates that should hold the Pacific Ocean
together, meet the plates that hold the continent in place. It
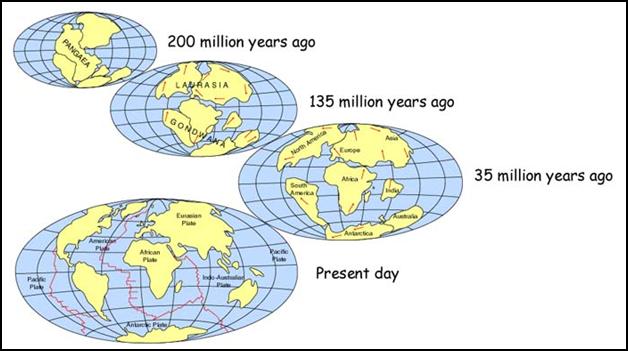
is a common belief that around 240 million years ago all the land masses were
joined together and as the ocean floor and continents spread to their current
places this was known as continental drift. What
is the opposite of internal forces? Yes,
the opposite of internal forces is external forces and they can change the
surface of the earth. We know rocks are
always breaking into smaller pieces. This
occurs through weathering and erosion. Weathering is the breakdown of rocks and minerals at or around the earth’s surface.
There
are two types of weathering, chemical weathering and physical
weathering. The first form,
called chemical weathering, occurs when water combines with minerals to produce a chemical reaction. This causes rocks to disintegrate and disolve over a period of time. Physical
weathering also causes rocks to break down slowly but through processes such as freezing and thawing. Another
force that changes the surface of the earth is known as erosion, which is the wearing
away of the earth’s surface, the most powerful form of erosion is
water. Erosion occurs by means in which
glaciers erode or wear away the terrain, known as land. Glaciers
are large bodies of ice that move across the surface of the earth. The glaciers change the land by destroying
forests and altering the flow of rivers.
Over the past 2 million years, glaciers have moved across the surface of
the earth, naming this period the Ice Age.
There are two types of glaciers sheet and mountain glaciers. As the name suggests sheet glaciers are long
sheets of ice that are most common in areas that are difficult to access or at
high elevations, Antarctica is covered by sheet glaciers. Mountain
glaciers occur when snow falls on the mountains and turns into ice. Let
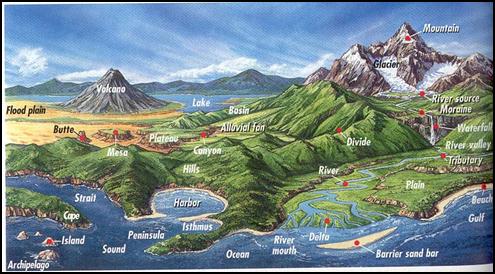
us begin talking about the various types of land on the earth. The natural features of the earth are called
landforms, which help people locate specific places with specific features to
help influence where they settle. Geographers
divide the land into seven large landforms, which are known as continents. In the western hemisphere, North and South
America are found. Europe, Africa, Asia
are found in the Eastern Hemisphere. As
mentioned earlier, Antarctica is found on the southern end; it is under an
enormous sheet of ice with Asia being the largest continent and Australia being
the smallest. Within
the continents, there are four major types of landforms: mountains, hills, plateaus
and plains. When you notice that land rises above the rest
of the land these are mountains. You may
have heard them called the highlands because they are the highest
landform. A
plateau is higher than the land that surrounds it consisting of at least one
steep side called a cliff, while plains are flat. Hills also rise above the land, but they
differ from mountains because they are more rounded and lower. There are several types of landforms. Have
you ever noticed Are
landforms only on land? Of course, not,
there are many different landforms on the ocean floor, which is the most widespread surface feature of Earth. Did you know the continents often expand
underwater? When the plate tectonics
expand, move away from the ridges and carry continents, this expansion and
movement is called a Continental drift.
As mentioned earlier, on the ocean floor one can find mountains that
have formed because the Earth's surface is formed of
different plates, which slide into one another or drift apart.
While looking at the picture, refer back to the content to see the
different landform explanations. Water As
stated earlier, water makes up 70% of the surface of the earth. Unlike landforms, the amount of water remains
mostly the same. One source of
freshwater is called ground water, which lies beneath the surface of the earth
and as the groundwater finds openings in the land surface emerges as freshwater
springs. Eventually, the water reenters
the ocean, where the water cycle started.
Lakes, streams and rivers are examples of freshwater. People are known to use ground water through
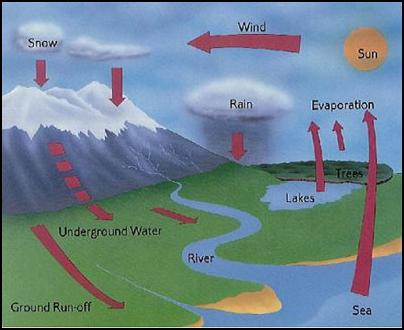
wells. The Water Cycle
The water supply
remains constant because of the water
cycle. This process is the movement
of water from the ocean to the air, then to the ground, and back to the ocean. The water cycle remains a vital method for
supporting life on land, and is a primary factor in the erosion of surface
features over geological periods. For additional
information on the Water Cycle, click on PDF
File. The process
begins with evaporation or the change of water into gas. By the heat from the sun, the vapor
rises from the ocean into the air, causing moisture. When the clouds become too full of moisture,
the moisture is returned to the earth in the form of rain or snow. Because of gravity, the water flows downward
towards the ocean. The amount of water
that evaporates is about the same that falls back to the earth. Most of the
water found on the earth is salt water, usually referring to
water from the sea or oceans. The large
body of salt water is divided into four oceans:
Atlantic, Pacific, Indian and Arctic Oceans.
Smaller bodies of water include gulfs, seas and bays.
The Mediterranean Sea is the world’s largest sea, surrounding three
continents Europe, Asia and Africa.
Roughly, around
95% of the water is saltwater and we know that we cannot drink saltwater. Why you might ask? One reason we should not drink saltwater is
that a person would become dehydrated quickly.
Soon, we will have to find new ways of changing seawater to freshwater
to meet the needs of people. Currently,
about two percent of the water is available for drinking. Lakes, Streams and Rivers Natural Resources Elements
from the earth that are not made by man, but can be used by the people are called natural resources. People must develop natural resources and that
is why the earth relates to human life because the earth helps produce what
humans need to survive. The earth
creates oxygen, produces soil for farming and along with plants and animals,
the earth forms part of the food chain.
We use the earth to make our lives easier. Can you heat your home without coal? No, coal is what is called a fossil fuel,
which is taken from the earth.
Worldwide, coal is the largest source of fuel for converting energy to
electricity and carbon dioxide emissions.
In addition, the earth has many minerals that are made from non-living
things. Value of Resources Does
everyone value everything the same? Of
course, not, people in some regions of the world may value resources more than
in other regions of the world. Location
is one way we value resources differently.
In the Middle East, they do not value oil as much we do in the United
States. The value of resources may
change if the United States becomes less dependent on oil. We
still must find ways to manage our resources so future generations have access
to them. If people are able to grow these
resources, they are called renewable resources because they are
replenished or reproduced easily and can be renewed if maintained and not sold
too quickly. Examples of renewable
resources are the forests, plant life and grasslands. If we are unable to replace, remake or
regenerate a resource, like many found in the earth, such as fossil
fuels, these resources are known as non-renewable resources. Examples of non-renewable resources
are coal, natural gas and oil. The
distribution of resources will influence how countries relate to one another,
because goods are limited and countries have become interdependent on each
other. Countries in the Southeast are
dependent on the United States for wheat; in turn, we are dependent upon them
for part of our oil supply. This
interdependence on each other has led to many conflicts because rulers believed
their countries need the resources other countries have. Unit Summary The
earth is made up of water, land and air. The land makes up the lithosphere,
while the air makes up the atmosphere.
Sections of the earth crust move which causes continents to move away.
External forces such as wind and gravity helped shape the surface of the
earth by a process called erosion. Landforms
are the physical makeup of the earth with the major types of landforms being
mountains, hills, plains and plateaus.
Water is both a physical feature and a resource and is limited and
controlled by the water cycle. The
natural resources are not divided up evenly among the countries of the world
requiring countries to become interdependent on each other. There are two types of resources, renewable
resources that can be replaced, and non-renewable resources, which cannot be
replaced.
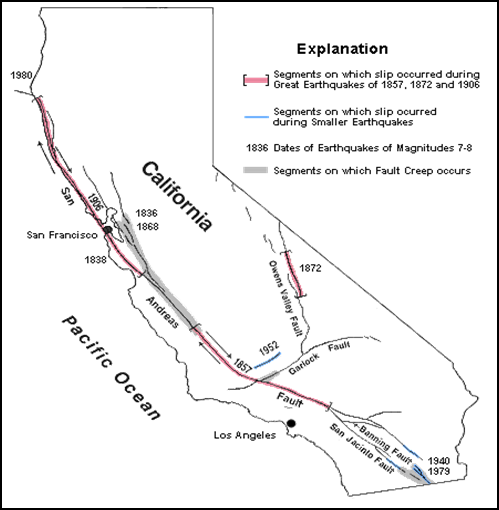
The San Andreas Fault system and other large faults
in California: different segments of the fault display different behavior.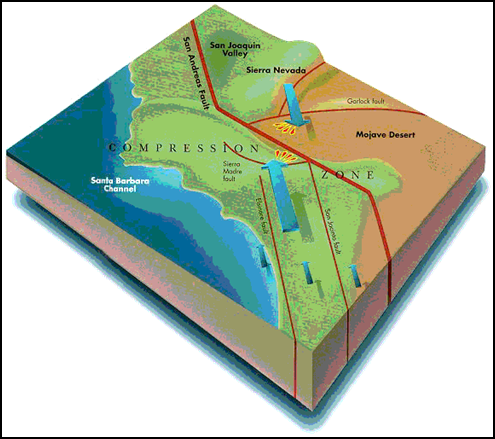
There are
smaller bodies of water found on our earth.
Lakes are bodies of water surrounded by land, not
part of the ocean,
larger and deeper than a pond,
and are usually fed by a river. Streams
are flowing natural waters, regardless of size and are an important instrument
of the water cycle. Smaller
streams, sometimes called creeks, flow through lakes and together, lakes and
streams form rivers, which are large natural streams. Rivers have been
important for farming because river valleys and plains provide fertile soils;
in addition, they have also been important for travel, transportation, trade
routes and an energy source. Today
rivers are still used to power hydroelectric plants and their water turbines.

Unit 2 Main Points Worksheet
Unit 2 Water Cycle
