COMPUTING WORK WAGES

Unit Overview
In this unit you will learn how to compute hourly pay, regular pay and overtime pay. The unit will conclude with finding the time worked.
Hourly Pay and
Salary
Many people are paid a certain amount of money for each hour they work. This
amount of money is called the hourly rate. A regular work week is usually 40
hours, and the money received on payday is called wages. To find your wages, multiply
your hourly rate by the number of hours worked.

Some people are paid a fixed amount of money regularly no matter how many hours they need to complete their job. This money is called salary. People who are paid salary are usually not paid overtime. Professional workers and supervisors in most businesses are among the employees who are paid salary.
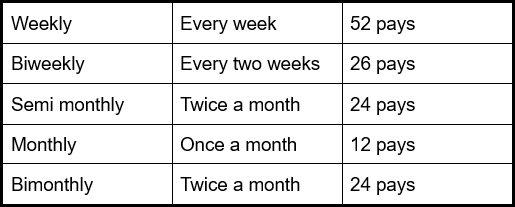
The length of time between pay paychecks is called a pay period. Salaried workers are
paid regularly, but the pay periods may differ from job to job. The table below
presents this information.
Regular Wages and
Overtime
 People
who are paid by the hour are paid extra for hours they work in addition to
regular hours. This is called overtime and refers to the number of hours
worked over 40 hours during a week. Overtime pay is usually one and one-half
times the regular hourly rate, and for special overtime, employees
sometimes receive double time which means 2 times the hourly rate.
People
who are paid by the hour are paid extra for hours they work in addition to
regular hours. This is called overtime and refers to the number of hours
worked over 40 hours during a week. Overtime pay is usually one and one-half
times the regular hourly rate, and for special overtime, employees
sometimes receive double time which means 2 times the hourly rate.

Employees who work both regular hours and overtime hours may compute their total wages by using subtraction, multiplication, and addition.

Time Worked
Employees’ wages are based on the time that they spend on the job. A weekly
timecard is made up for the times for each working day of the week. To use
these logs, the worker records the times in and out and then subtracts to find
the total hours worked.

The later time might need to be renamed before you can subtract the earlier time. Study the example below.

 |
| Unit 2 Calculating Wages Worksheet |
| Unit 2 Computing Gross Pay Worksheet |