
THE FIVE ELEMENTS OF MUSIC

The Five Elements of Music
Melody

Melody: A succession of single pitches or tones perceived by the mind as a unity.
* Melody is what we remember!
* Melody is what we whistle & hum
* The Most Direct appeal to the Listener
Tone = The Sound
Pitch = The Highness or Lowness of a Tone
We describe melody in three ways: Range, Shape, and the Way it moves.
Range = Distance between the melody’s lowest and highest tones.
Shape = The direction the melody takes as it moves upward or downward or remains static.
Interval = The distance between two pitches.
Type of Movement:
Conjunct = Melodies that move by small intervals in a joined connected manner
Disjunct = Melodies that move in disjointed or disconnected intervals.
Phrase = Unit of meaning within a larger structure.
Cadence = The resting place of the phrase.
Phrase = Sentence/Cadence = Period
Rhythm

Rhythm = The orderly movement of music in time.
Beat = Basic unit of length
* Beats can be accented or strong
* Beats occur in regular intervals
* Beats can occur every other beat, or third, fourth.
* These groupings are called Meters.
* They are marked off in Measures.
Metrical Patterns:
Duple Meter = Two beats to a measure
* Marches
Listening Example: (Stars and Stripes Forever)
Triple Meter = Three beats
* Dances/Waltz
Listening Example: (The Blue Danube)
Quadruple = Four Beats
* Common Time – Most music is written in common time!
Listening Example: (Born to be Wild)
Syncopation = Accent is shifted to the weak beat
Upbeat = Last beat of the measure
Downbeat = First beat of the measure
Offbeat = The weak beat of the measure
Polyrhythm = Many rhythms
Nonmetric = No meter
Harmony
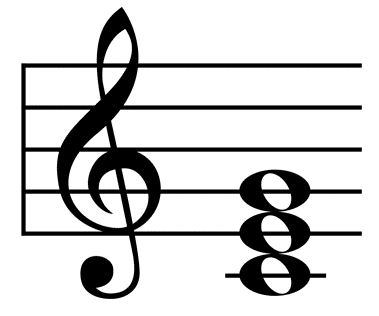
Harmony = The movement and relationship of intervals and chords.
Chord = Three or more tones(pitches) occurring at the same time or together.
Scale = Collection of pitches arranged in ascending or descending order
* Syllables or numbers
Do Re Me Fa So La Ti Do
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Listening Example: (Scale)
Consonance = Two notes played together with a pleasing sound.
Dissonance = Two notes played together with an unpleasant sound.
Listening Example: (Consonance and Dissonance)
Musical Texture
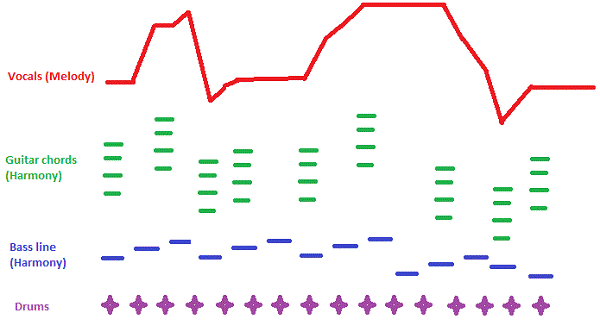
Types of Texture:
Monophonic = Single voice
* Simple texture
* One line
Heterophonic = Two or more voices simultaneously elaborating the same melody
* Improvisation/Jazz
Polyphonic = two or more melodic lines are combined.
* Counterpoint: One musical line set against another
Homophonic = Single voice takes over the melodic line/Others accompany.
Listening Example: (Row Row Row Your Boat in all four textures)
Musical Form
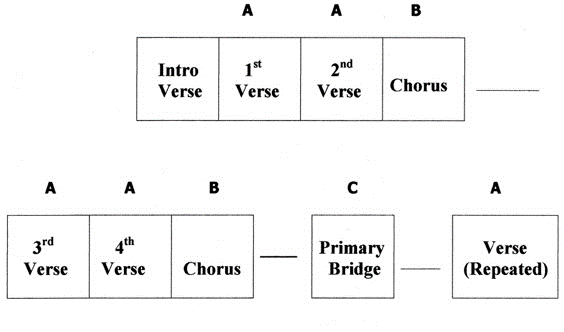
Form = The structure and shape of a work or musical piece.
Types of Musical Form
Repetition and Contrast:
Repetition = Fixes the material in our mind and provides for unity and variety.
Contrast = Sustains our interest and feeds our need for change.
Listening Example:
Theme and Variation = some aspects of the music are altered but still recognized.
Listening Example:
Improvisation = Music created during performance rather than pre-composed.
Listening Example:
Motive = Musical idea or cells of musical growth.
Call & Response = Single leader/group responds.
Listening Example:
Tempo Markings = Indicate the character of the music as well as the pace or speed.
Dynamics = Indicate the degree of loudness or softness of the music.
 |
| Unit 2 History of Music Key Vocabulary (Puzzle) Worksheet |
| Unit 2 Cornell Notes Worksheet |