RIGHT TRIANGLE TRIGONOMETRIC RELATIONSHIPS
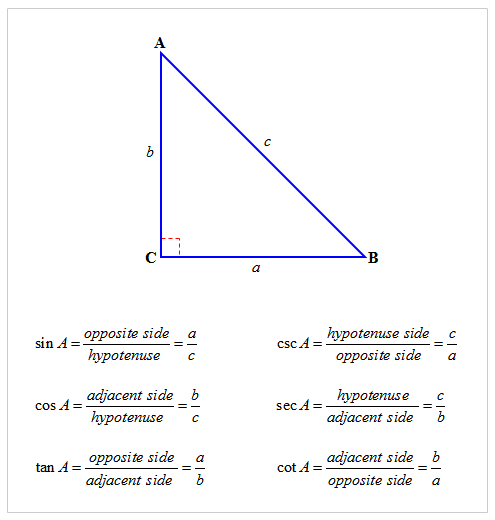
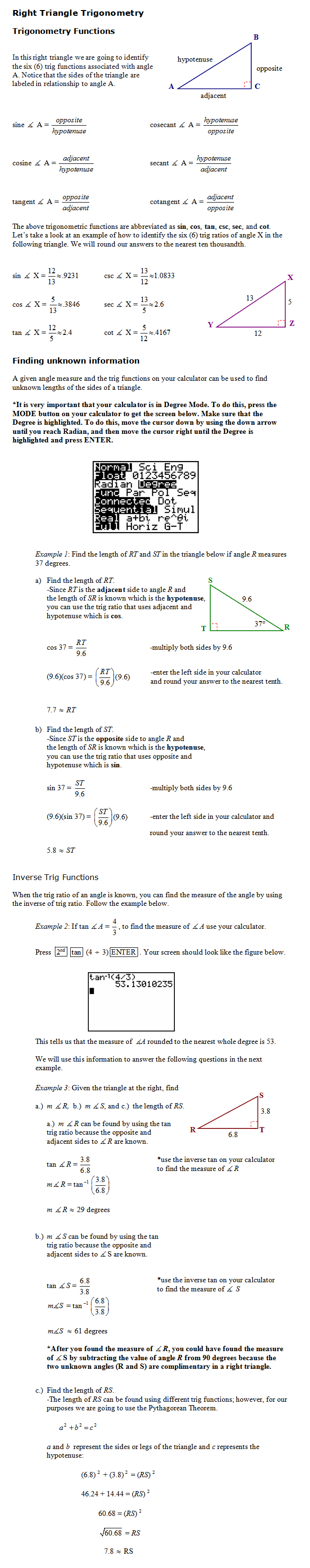
Right triangle trigonometry is the study of the acute angles in a right triangle and the relationships between the angles and the sides of the right triangle. The relationships are related through trigonometric ratios. The Sine(Sin) of an angle is equal to the ratio of the length of the opposite side to the length of the hypotenuse. The Cosine (Cos) of an angle is equal to the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the length of the hypotenuse. The Tangent (Tan) of an angle is equal to the ratio of the length of the opposite side to the length of the adjacent side. A phrase that helps to remember the three basic trigonometry relationships is "Soh Cah Toa".
|
"Soh" |
"Cah" |
"Toa"
|
| |
|
|
|
Sin=Opposite/Hypotenuse |
Cos=Adjacent/Hypotenuse |
Tan=Opposite/Adjacent
|
Each of the three basic trigonometric functions has an inverse. Cosecant (Csc) is the inverse of Sin, Secant (Sec) is the inverse of Cosine, and Cotangent (Cot) is the inverse of tangent.
 Six Trig Functions (12:13)
Six Trig Functions (12:13)

