ENVIRONMENT

Humans
depend on the environment for all of their survival needs. We need the
environment for food, water, air, shelter, fuels and many other resources. Many
times, as we live our everyday lives, we affect the quality and availability of
many of these important resources. Studying the relationship between humans and
the environment full of resources is referred to as environmental science. Environmental Science examines the
environment, the impact of human activity on the environment, and the solutions
to environmental problems. Environmental science does not involve just biology
and ecology, but also other sciences such as chemistry, zoology, geology, and
geography.
|
Human
Population |
|
|
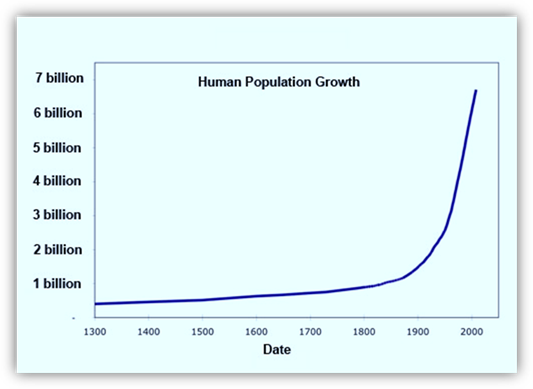
Since about the year 1800, the
human population of the world has been increasing exponentially. Much of the
reason for the dramatic increase in the world-wide population is not so much
about more humans being born, rather it is more about humans surviving and
living longer as a result of science and technology. Some of the main factors
that allowed for this rapid increase in the human population of the world
include dependable food supplies, improved public health, and medical
advances. |
|
|
|
|
|
Dependable
Food Supplies |
Humans have developed reliable
methods of mass producing and processing foods. In the last 200 years humans
have developed more efficient and reliable ways of producing crops. Some of
the technologies developed include genetically engineered plants to withstand
environmental variables, chemicals (such as fertilizers and pesticides) to
assists in the growth of crops, and machinery that increases the speed of
harvesting the crops. |
|
Improved
Public Health |
Science and technology has
supported humans with ways of providing safe drinking water to the public and
ways of isolating and treating sewage. |
|
Medical
Advances |
Science has improved human health
by developing technologies to be proactive to potential health dangers, in
addition to, technologies to treat existing health disorders and diseases.
Some of the ways humans are proactive include education in nutrition and
exercise, use of vaccinations, and use of health screenings. Humans have also
developed medicinal treatments, therapies, and surgical procedures for
conditions that do exists. |
We depend on
the environment and the environment is affected by everything we do. Since we
live in this interconnected global ecosystem and rely on it for our resources
to live, it is very important for us to understand and take care of the
environment. Our goal through environmental science is to understand the
environment, so that we do the least damage and disruption to it, in addition
to, preserving the resources it provides for us.
Resources
Since we, as
humans, rely on Earth’s many natural resources, it is important for us to
understand the nature of these resources. Earth’s resources are categorized
into two possible groups: renewable
and nonrenewable.
|
Renewable
Resources |
|
|||
|
A renewable resource is a natural resource that can be replaced at
about the same rate at which it is used. Some renewable resources can be
replaced almost immediately, while others may take a little more time. Some
say if the resource can be replaced within 100 years it is classified as a
renewable resource. |
· Solar energy · Wind energy · Geothermal · Hydropower · Biomass |
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
Nonrenewable
Resources |
|
|||
|
A nonrenewable resource is a natural
resource that is used much faster than nature can produce them. In
general, nonrenewable resources take well over 100 years to be replaced.
Fossil fuels are nonrenewable resources that are formed from the remains of
organisms that lived a long time ago. Fossil fuels require millions of years
to form. |
· Fossil Fuels (Coal, oil, natural
gas) · Minerals · Metal ores |
|
||
|
|
|
|||
Environment
Issues
Now we will look at how human
activity is affecting the resources of the Earth that we rely on in order to
live and survive. As we pollute the air and water not only do we disrupt and
possibly destroy those resources, but we also disrupt our own health. Air
pollution causes respiratory problems, diseases, and cancers. Water pollution
may also cause problems as in diseases and cancers among our body systems.
Habitat destruction also creates problems by way of disrupting the entire
ecosystem for all organisms.
Air
Pollution
Most air
pollution is caused by human activity. We pollute the air by releasing carbon
dioxide (CO2), sulfur dioxide (SO2), and nitrogen oxides
(NO2 and NO3) into the air every time we burn fossil fuels.
As the
concentration of sulfuric and nitric acids increase in the atmosphere, acid
rain begins to form. Recall the water cycle, when condensation occurs in the
atmosphere, precipitation follows. As precipitation with these acids fall as
acid rain, the acid rain will damage forests and bodies of water. The forests
and bodies of water that are damaged will then affect all living organisms
associated with them.
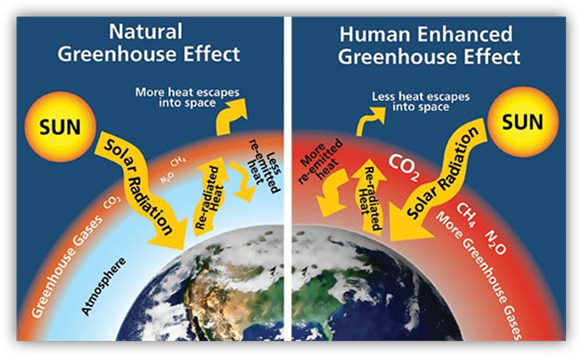 As
the concentration of carbon dioxide increases in the atmosphere, it increases
the temperature of the atmosphere. This idea of carbon dioxide concentration
increasing in the atmosphere relates to the greenhouse effect. The greenhouse effect is the warming of Earth’s atmosphere by way of greenhouse
gases and water vapor in the air that absorb and reradiate the sun’s radiation.
The greenhouse effect is not a bad thing. The greenhouse effect is needed
and has been needed to maintain Earth’s temperature for all life on Earth. The
problem is that human activity has been releasing more carbon dioxide into the
atmosphere than can be
As
the concentration of carbon dioxide increases in the atmosphere, it increases
the temperature of the atmosphere. This idea of carbon dioxide concentration
increasing in the atmosphere relates to the greenhouse effect. The greenhouse effect is the warming of Earth’s atmosphere by way of greenhouse
gases and water vapor in the air that absorb and reradiate the sun’s radiation.
The greenhouse effect is not a bad thing. The greenhouse effect is needed
and has been needed to maintain Earth’s temperature for all life on Earth. The
problem is that human activity has been releasing more carbon dioxide into the
atmosphere than can be 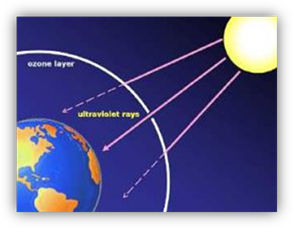 naturally handled, according to the
carbon cycle which you learned in Unit 29. This increase in the greenhouse gas,
carbon dioxide, creates a greater impact in the greenhouse effect on Earth’s
temperature. Many believe this increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide is
responsible for global warming.
naturally handled, according to the
carbon cycle which you learned in Unit 29. This increase in the greenhouse gas,
carbon dioxide, creates a greater impact in the greenhouse effect on Earth’s
temperature. Many believe this increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide is
responsible for global warming.
Another gas that is released into the
atmosphere is chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs). CFCs are human-made and are used as
coolants and propellants. As CFCs are released into the atmosphere, they damage
the ozone layer. The ozone layer in Earth’s atmosphere is necessary, because it
protects Earth and all life on it by blocking most of the sun’s ultraviolet
(UV) rays.
The following video describes the greenhouse effect and its impact on Earth’s atmosphere over time. This program explains the basic process of the greenhouse effect and its importance in regulating temperature by trapping and radiating heat energy through gases; water, carbon dioxide, and methane. It discusses the impact of civilization on the atmosphere in regards to fossil fuels, nitrous oxide, chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), and ozone. Lastly, the program outlines the debates over global warming within the scientific community and considers such alternative energy sources as natural gas and solar, wind, and nuclear power. This program provides straightforward, easy-to-understand answers about the greenhouse effect and its impact on Earth’s atmosphere.
|
Water
Pollution |
|
|
Most water pollution is caused by
human activity. The use of insecticides, pesticides, fertilizers, industrial
waste, oil spills, and landfills are some of the factors that contribute to
water pollution. The contamination usually begins on the surface then,
following the water cycle, percolates into the groundwater or serves as
runoff into bodies of water. All living organisms require water. So it is
easy to understand how once a water supply becomes damaged how it will affect
all living things associated with that ecosystem. One common ecosystem example used
for water pollution is the event known as an algal bloom. An algal bloom is excessive
growth of algae in a body of water. When fertilizers run into a body of
water, for example when fertilizers runoff from a farm into a pond, there is
an increase in nutrients in the body of water. This increase in nutrients now
provides a great opportunity for an algae population to exponentially grow.
This excessive growth, or algal bloom, will then begin to deplete the oxygen
out of the water through growth and decomposition. Removing oxygen out of the
water will then begin to kill the other organisms, such as fish, in the
water. |
|
|
|
|
|
Soil
Damage |
|
|
Damaging the soil does more than
just disrupting plant growth for our immediate consumption as in eating crops
out of a garden. Understanding food webs will help you understand the extreme
importance of soil. You know that all food webs begin with producers. The
majority of the terrestrial food webs require plants as producers. Plants
require soil and the nutrients within it to survive. If there is no fertile
soil for plants, then there are no producers for the food web which would
then destroy the food web. Fertile soil comes from weathered
rock along with living organisms (bacteria and fungi) and the remains of
organisms (mostly plants and animals). It takes thousands of years to produce
just a few centimeters of fertile soil, therefore soil is considered a
nonrenewable resource. Soil normally consists of three layers. The top layer
is the topsoil which is mostly organic material. The middle layer is the
inorganic particles and minerals. The deepest layer is made up of loose rock. Now that you understand the
characteristics of soil, you should understand why it is important for us to
attempt to limit erosion. Erosion
is the process of Earth’s surface (soil) being
carried from one place to another by way of water, ice, wind, or gravity. When
the topsoil is removed it takes too long to replace it, therefore, nothing
will be able to grow in that location. Most farming methods lead to erosion.
There are some ways of conserving the fertile soil such as terracing, cover crop, crop rotation, and contour plowing. |
|
|
Habitat
Destruction |
|
|
As the human population grows, the
resource needs of all humans increase. Some of the resource needs include
food requirements, land/resources for development, and ideal habitats. As
these needs are met, humans begin disturbing ecosystems by destroying or disrupting
habitats. Deforestation begins to occur as more area or land is needed for
development or farming. Deforestation
is the process of removing or clearing forests.
Deforestation eliminates habitats for many organisms and decreases
biodiversity, which entirely disrupts food webs. Deforestation also increases
the likelihood for erosion. |
|
Environment
Solutions
It is very
important for humans to protect the environment and the resources it provides,
for many of the reasons which you have already covered. Protecting the
environment is something that can be and is accomplished as individuals, a
group, a city, a state, a nation, or a world-wide community. There are
activities and technologies that have been created to help with dealing with
current and possible environmental problems. All of the activities and
technologies fall into two basic areas, either conservation or restoration.
Conservation involves protecting the
natural resources we currently have. Restoration
involves attempting to clean and fix damaged natural
resources back to their original state.

One method
we have to help conserve natural resources is “reduce, reuse, recycle”. Reduce refers to reducing the amount of
energy we use and reducing the amount of waste we produce. Reuse refers to using certain materials and products several times,
when possible, instead of using something once then disposing of it. Recycling is the
process of recovering valuable or useful material from scrap or waste. Recycling
provides a way of using the same resource in many different forms without
collecting more of the resource from the environment. The process of recycling
usually costs less for manufacturers, uses less energy than mining more of the
resource from the environment, and prevents pollution.
Click on the
Quizlet icon below to access the
quizlet.com vocabulary flash cards. Review the vocabulary before completing
your assessment.
 Now answer questions 1 through 20.
Now answer questions 1 through 20.